Abstract
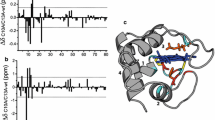
Cytochrome c (Cc) is a soluble electron carrier protein, transferring reducing equivalents between Cc reductase and Cc oxidase in eukaryotes. In this work, we assessed the structural differences between reduced and oxidized Cc in solution by paramagnetic NMR spectroscopy. First, we have obtained nearly-complete backbone NMR resonance assignments for iso-1-yeast Cc and horse Cc in both oxidation states. These were further used to derive pseudocontact shifts (PCSs) arising from the paramagnetic haem group. Then, an extensive dataset comprising over 450 measured PCSs and high-resolution X-ray and solution NMR structures of both proteins were used to define the anisotropic magnetic susceptibility tensor, Δχ. For most nuclei, the PCSs back-calculated from the Δχ tensor are in excellent agreement with the experimental PCS values. However, several contiguous stretches—clustered around G41, N52, and A81—exhibit large deviations both in yeast and horse Cc. This behaviour is indicative of redox-dependent structural changes, the extent of which is likely conserved in the protein family. We propose that the observed discrepancies arise from the changes in protein dynamics and discuss possible functional implications.







Similar content being viewed by others
Notes
The amino-acid numbering for yCc used in this work is based on the sequence alignment with horse heart Cc (hCc), which generates a negative numbering for the first five residues.
References
Baistrocchi P, Banci L, Bertini I, Turano P, Bren KL, Gray HB (1996) Three-dimensional solution structure of Saccharomyces cerevisiae reduced iso-1-cytochrome c. Biochemistry 35:13788–13796
Banci L, Assfalg M (2001) Mitochondrial cytochrome c. In: Messerschmidt A, Huber R, Poulos TL, Wieghardt K (eds) Handbook of metalloproteins. Wiley, Chichester, pp 33–43
Banci L, Bertini I, Bren KL, Gray HB, Sompornpisut P, Turano P (1997a) Solution structure of oxidized Saccharomyces cerevisiae iso-1-cytochrome c. Biochemistry 36:8992–9001
Banci L, Bertini I, Gray HB, Luchinat C, Reddig T, Rosato A, Turano P (1997b) Solution structure of oxidized horse heart cytochrome c. Biochemistry 36:9867–9877
Banci L, Bertini I, Huber JG, Spyroulias GA, Turano P (1999a) Solution structure of reduced horse heart cytochrome c. J Biol Inorg Chem 4:21–31
Banci L, Bertini I, Rosato A, Varani G (1999b) Mitochondrial cytochromes c: a comparative analysis. J Biol Inorg Chem 4:824–837
Banci L, Bertini I, Luchinat C, Turano P (2000) Solution structures of hemoproteins. In: Kadish KM, Smith KM, Guilard R (eds) The porphyrin handbook. Academic Press, San Diego, CA, pp 323–350
Baxter SM, Fetrow JS (1999) Hydrogen exchange behavior of [U-15N]-labeled oxidised and reduced iso-1-cytochrome c. Biochemistry 38:4493–4503
Berghuis AM, Brayer GD (1992) Oxidation state-dependent conformational changes in cytochrome c. J Mol Biol 223:959–976
Bertini I, Luchinat C, Parigi G (2002) Magnetic susceptibility in paramagnetic NMR. Progress in Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy 40:249–273
Boyd J, Dobson CM, Morar AS, Williams RJP, Pielak GJ (1999) 1H and 15N hyperfine shifts of cytochrome c. J Am Chem Soc 121:9247–9248
Bushnell GW, Louie GV, Brayer GD (1990) High-resolution three-dimensional structure of horse heart cytochrome c. J Mol Biol 214:585–595
Delaglio F, Grzesiek S, Vuister GW, Zhu G, Pfeifer J, Bax A (1995) NMRPipe: a multidimensional spectral processing system based on UNIX pipes. J Biomol NMR 6:277–293
DeLano WL (2002) The PyMOL molecular graphics system. DeLano Scientific, Palo Alto
Feng YQ, Roder H, Englander SW (1990) Redox-dependent structure change and hyperfine nuclear magnetic resonance shifts in cytochrome c. Biochemistry 29:3494–3504
Fetrow JS, Baxter SM (1999) Assignment of 15N chemical shifts and 15N relaxation measurements for oxidized and reduced iso-1-cytochrome c. Biochemistry 38:4480–4492
Gao Y, Boyd J, Williams RJP, Pielak GJ (1990) Assignment of proton resonances, identification of secondary structural elements, and analysis of backbone chemical shifts for the C102T variant of yeast iso-1-cytochrome c and horse cytochrome c. Biochemistry 29:6994–7003
Gao Y, Boyd J, Pielak GJ, Williams RJP (1991) Comparison of reduced and oxidized yeast iso-1-cytochrome c using proton paramagnetic shifts. Biochemistry 30:1928–1934
Han B, Liu Y, Ginzinger S, Wishart D (2011) SHIFTX2: significantly improved protein chemical shift prediction. J Biomol NMR 50:43–57
Iwahara J, Schwieters CD, Clore GM (2004) Ensemble approach for NMR structure refinement against 1H paramagnetic relaxation enhancement data arising from a flexible paramagnetic group attached to a macromolecule. J Am Chem Soc 126:5879–5896
John M, Park AY, Pintacuda G, Dixon NE, Otting G (2005) Weak alignment of paramagnetic proteins warrants correction for residual CSA effects in measurements of pseudocontact shifts. J Am Chem Soc 127:17190–17191
Levitt M, Perutz MF (1988) Aromatic rings act as hydrogen bond acceptors. J Mol Biol 201:751–754
Liu W, Rumbley J, Englander SW, Wand AJ (2003) Backbone and side-chain heteronuclear resonance assignments and hyperfine NMR shifts in horse cytochrome c. Prot Sci 12:2104–2108
Louie GV, Brayer GD (1990) High-resolution refinement of yeast iso-1-cytochrome c and comparisons with other eukaryotic cytochromes c. J Mol Biol 214:527–555
Moench SJ, Shi TM, Satterlee JD (1991) Proton-NMR studies of the effects of ionic strength and pH on the hyperfine-shifted resonances and phenylalanine-82 environment of three species of mitochondrial ferricytochrome c. Eur J Biochem 197:631–641
Morar AS, Kakouras D, Young GB, Boyd J, Pielak GJ (1999) Expression of 15N-labeled eukaryotic cytochrome c in Escherichia coli. J Biol Inorg Chem 4:220–222
Pollock WBR, Rosell FI, Twitchett MB, Dumont ME, Mauk AG (1998) Bacterial expression of a mitochondrial cytochrome c. Trimethylation of Lys 72 in yeast iso-1-cytochrome c and the alkaline conformational transition. Biochemistry 37:6124–6131
Qi PX, Beckman RA, Wand AJ (1996) Solution structure of horse heart ferricytochrome c and detection of redox-related structural changes by high-resolution 1H NMR. Biochemistry 35:12275–12286
Rule GS, Hitchens TK (2006) Fundamentals of protein NMR spectroscopy. Springer, Dordrecht
Rumbley JN, Hoang L, Englander SW (2002) Recombinant equine cytochrome c in Escherichia coli: high-level expression, characterization, and folding and assembly mutants. Biochemistry 41:13894–13901
Schmitz C, Stanton-Cook MJ, Su X-C, Otting G, Huber T (2008) Numbat: an interactive software tool for fitting Δχ-tensors to molecular coordinates using pseudocontact shifts. J Biomol NMR 41:179–189
Schwieters CD, Kuszewski JJ, Tjandra N, Clore GM (2003) The Xplor-NIH NMR molecular structure determination package. J Magn Reson 160:66–74
Sukits SF, Erman JE, Satterlee JD (1997) Proton NMR assignments and magnetic axes orientations for wild-type yeast iso-1-ferricytochrome c free in solution and bound to cytochrome c peroxidase. Biochemistry 36:5251–5259
Timkovich R, Cai M (1993) Investigation of the structure of oxidized Pseudomonas aeruginosa cytochrome c-551 by NMR: comparison of observed paramagnetic shifts and calculated pseudocontact shifts. Biochemistry 32:11516–11523
Turner DL, Williams RJP (1993) 1H and 13C NMR investigation of redox-state-dependent and temperature-dependent conformational changes in horse cytochrome c. Eur J Biochem 211:555–562
Ubbink M, Worrall JAR, Canters GW, Groenen EJJ, Huber M (2002) Paramagnetic resonance of biological metal centers. Ann Rev Biophys Biomol Struc 31:393–422
Vranken WF, Boucher W, Stevens TJ, Fogh RH, Pajon A, Llinas M, Ulrich EL, Markley JL, Ionides J, Laue ED (2005) The CCPN data model for NMR spectroscopy: development of a software pipeline. Proteins 59:687–696
Weiner MP, Costa GL, Schoettlin W, Cline J, Mathur E, Bauer JC (1994) Site-directed mutagenesis of double-stranded DNA by the polymerase chain reaction. Gene 151:119–123
Williams G, Clayden NJ, Moore GR, Williams RJP (1985) Comparison of the solution and crystal structures of mitochondrial cytochrome c—analysis of paramagnetic shifts in the nuclear magnetic resonance spectrum of ferricytochrome c. J Mol Biol 183:447–460
Worrall JAR, Kolczak U, Canters GW, Ubbink M (2001) Interaction of yeast iso-1-cytochrome c with cytochrome c peroxidase investigated by [15N, 1H] heteronuclear NMR spectroscopy. Biochemistry 40:7069–7076
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Jonathan Worrall and Prof. Marcellus Ubbink for the kind gifts of the Cc expression vectors, Dr. Christophe Schmitz for useful tips on the installation and use of Numbat software, and Dr. Lieven Buts for the help with the data analysis. ANV is an FWO Post-Doctoral Researcher.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Volkov, A.N., Vanwetswinkel, S., Van de Water, K. et al. Redox-dependent conformational changes in eukaryotic cytochromes revealed by paramagnetic NMR spectroscopy. J Biomol NMR 52, 245–256 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-012-9607-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-012-9607-8