Abstract
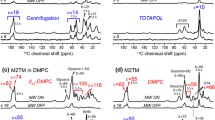
Structural information can be extracted from one-bond residual dipolar couplings (RDC) measured in NMR spectra of systems in field-ordered media. RDC can be on the order of J-couplings if the anisotropy of alignment is ~ 10−2, 10-fold stronger than that typically used for structural studies of water-soluble proteins. In such systems the performance of 1H→ 15N polarization transfer methods of the INEPT type is not satisfactory. In this study we show the effectiveness of adiabatic-passage cross-polarization (APCP) in transferring the 1H→ 15N polarization in the bicelle-associated peptide Leucine Enkephalin (Lenk). APCP is efficient both in static samples and in samples spun at the magic angle (MAS) or any other angle of the spinning axis to the magnetic field (variable-angle spinning, VAS). The anisotropic spectrum of an aligned static sample and the isotropic spectrum of the sample under MAS provide a set of possible values for the 1H–15N RDC of phospholipid-associated Lenk. The unambiguous determination of the 1H–15N RDC was accomplished by means of VAS experiments.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.D. Bertrand W.B. Moniz A.N. Garroway G.C. Chingas (1978) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 100 5227–5229
F.A. Bovey (1988) Nuclear Magnetic Resonance Spectroscopy Academic Press San Diego
R. Bruschweiler R.R. Ernst (1992) J. Chem. Phys. 96 1758–1766
D.P. Burum M. Linder R.R. Ernst (1981) J. Magn. Reson 44 173–188
G.C. Chingas A.N. Garroway W.B. Monitz R.D. Bertrand (1980) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 102 2526–2528
M. Ernst B.H. Meier (2002) NoChapterTitle D.M. Grant R.K. Harris (Eds) Encyclopedia of Nuclear Magnetic Resonance John Wiley & Sons Chichester 23–32
K.J. Glover J.A. Whiles M.J. Wood G. Melacini E.A. Komives R.R. Vold (2001) Biochemistry 40 13137–13142
S.R. Hartmann E.L. Hahn (1962) Phys. Rev. 128 2042–2046
S. Hediger B.H. Meier R.R. Ernst (1995) Chem. Phys. Lett. 240 449–456
S. Hediger B.H. Meier N.D. Kurur G. Bodenhausen R.R. Ernst (1994) Chem. Phys. Lett. 223 283–288
K.P. Howard S.J. Opella (1996) J. Magn. Reson. Ser. B 112 91–94
N. Khaneja B. Luy S.J. Glaser (2003) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 100 13162–13166
M.H. Levitt (1991) J. Chem. Phys. 94 30–38
D.H. Live D.G. Davis W.C. Agosta D. Cowburn (1984) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 106 1939–1943
J.A. Losonczi J.H. Prestegard (1998) Biochemistry 37 706–716
J.A. Losonczi M. Andrec M.W.F. Fischer J.H. Prestegard (1999) J. Magn. Reson. 138 334–342
I. Marcotte F. Separovic M. Auger S.M. Gagne (2004) Biophys. J. 86 1587–1600
M. Mehring (1983) Principles of High Resolution NMR in Solids Springer Berlin
G.A. Morris R. Freeman (1979) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 101 760–762
S.J. Opella F.M. Marassi J.J. Gesell A.P. Valente Y. Kim M. Oblatt-Montal M. Montal (1999) Nat. Struct. Biol. 6 374–379
A. Pines M.G. Gibby J.S. Waugh (1972) J. Chem. Phys. 56 1776–1777
R.S. Prosser H. Bryant R.G. Bryant R.R. Vold (1999) J. Magn. Reson. 141 256–260
R. Riek G. Wider K. Pervushin K. Wüthrich (1999) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96 4918–4923
F. Rinaldi M.F. Lin M.J. Shapiro M. Petersheim (1997) Biophys. J. 73 IssueID6 3337–3348
C.R. Sanders G.C. Landis (1994) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 116 6470–6471
C.R. Sanders G.C. Landis (1995) Biochemistry 34 4030–4040
A. Saupe (1964) Z. Naturforschung 19a 161
A.J. Shaka J. Keeler R. Freeman (1983) J. Magn. Reson 53 313–340
F. Tian J.A. Losonczi M.W.F. Fischer J.H. Prestegard (1999) J. Biomol. NMR 15 145–150
S. Wimperis G. Bodenhausen (1989) Mol. Phys. 66 897–919
C.H. Wu A. Ramamoorthy L.M. Gierasch S.J. Opella (1995) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 117 6148–6149
G. Zandomeneghi M. Tomaselli J.D. van Beek B.H. Meier (2001) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 123 910–913
G. Zandomeneghi M. Tomaselli P.T.F. Williamson B.H. Meier (2003a) J. Biomol. NMR 25 113–123
G. Zandomeneghi P.T.F. Williamson A. Hunkeler B.H. Meier (2003b) J. Biomol. NMR 25 125–132
S. Zhang (1994) J. Magn. Reson. Ser. A 110 73–76
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zandomeneghi, G., Meier, B.H. Adiabatic-passage cross polarization in N-15 NMR spectroscopy of peptides weakly associated to phospholipids: Determination of large RDC. J Biomol NMR 30, 303–309 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-004-3097-2
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10858-004-3097-2