Abstract
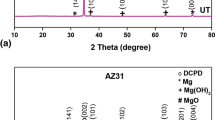
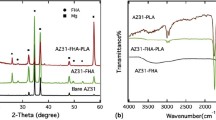
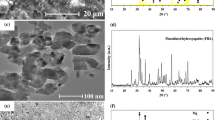
Dicalcium phosphate dihydrate (DCPD) brushite coating with flake like crystal structure for the protection of AZX310 and AM50 magnesium (Mg) alloys was prepared through chemical deposition treatment. Chemical deposition treatment was employed using Ca(NO3)2·4H2O and KH2PO4 along with subsequent heat treatment. The morphological results revealed that the brushite coating with dense and uniform structures was successfully deposited on the surface of AZX310 and AM50 alloys. The X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns and Attenuated total reflectance infrared (ATR-IR) spectrum also revealed the confirmation of DCPD layer formation. Hydrophilic nature of the DCPD coatings was confirmed by Contact angle (CA) measurements. Moreover, electrochemical immersion and in vitro studies were evaluated to measure the corrosion performance and biocompatibility performance. The deposition of DCPD coating for HTI AM50 enables a tenfold increase in the corrosion resistance compared with AZX310. Hence the ability to offer such significant improvement in corrosion resistance for HTI AM50 was coupled with more bioactive nature of the DCPD coating is a viable approach for the development of Mg-based degradable implant materials.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Xin Y, Hu T, Chu PK. In vitro studies of biomedical magnesium alloys in a simulated physiological environment: a review. Acta Biomater. 2011;7:1452–9.
Kannan MB, Raman RK. In vitro degradation and mechanical integrity of calcium-containing magnesium alloys in modified-simulated body fluid. Biomaterials. 2008;29:2306–14.
Li Y, Wen C, Mushahary D, Sravanthi R, Harishankar N, Pande G, Hodgson P. Mg-Zr-Sr alloys as biodegradable implant materials. Acta Biomater. 2012;8:3177–88.
Staiger MP, Pietak AM, Huadmai J, Dias G. Magnesium and its alloys as orthopedic biomaterials: a review. Biomaterials. 2006;27:1728–34.
Saris NEL. Magnesium: an update on physiological, clinical and analytical aspects. Clin Chim Acta. 2000;294:1–26.
Song GL. Control of biodegradation of biocompatable magnesium alloys. Corros Sci. 2007;49:1696–701.
Witte F, Ulrich H, Rudert M, Willbold E. Biodegradable magnesium scaffolds: part I: appropriate inflammatory response. J Biomed Mater Res Part A. 2007;81:748–65.
Gérrard Eddy JP, Sridevi B, Derek F. Biomedical magnesium alloys: a review of material properties, surface modifications and potential as a biodegradable orthopaedic implant. Am J Biomed Eng. 2012;2:218–40.
Regine W, Anneke M, Frank F. Optimization of cell adhesion on Mg based implant materials by pre-Incubation under cell culture conditions. Int J Mol Sci. 2014;15:7639–50.
Pietrzak WS. Principles of development and use of absorbable internal fixation. Tissue Eng. 2000;6:25–433.
Gray-Munro JE, Strong M. The mechanism of deposition of calcium phosphate coatings from solution onto magnesium alloy AZ31. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;90:339–50.
Gray-Munro JE, Seguin C, Strong M. Influence of surface modification on the in vitro corrosion rate of magnesium alloy AZ31. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2009;91:221–30.
Tomozawa M, Hiromoto S. Microstructure of hydroxyapatite and octacalcium phosphate-coatings formed on magnesium by a hydrothermal treatment at various pH values. Acta Mater. 2011;59:355–63.
Chen XB, Birbilis N, Abbott TB. Review of corrosion-resistant conversion coatings for magnesium and its alloys. Corros Sci. 2011;53:2263–8.
Wang HX, Guan SK, Wang X, Ren CX, Wang LG. In vitro degradation and mechanical integrity of Mg-Zn-Ca alloy coated with Ca-deficient hydroxyapatite by the pulse electrodeposition process. Acta Biomater. 2010;6:1743–8.
Song YW, Shan DY, Han EH. Electrodeposition of hydroxyapatite coating on AZ91D magnesium alloy for biomaterial application. Mater Lett. 2008;62:3276–9.
Jamesh M, Kumar S, Sankara Narayanan T. Electrodeposition of hydroxyapatite coating on magnesium for biomedical applications. J Coat Technol Res. 2012;9:495–502.
Wen C, Guan S, Peng L, Ren C, Wang X, Hu Z. Characterization and degradation behavior of AZ31 alloy surface modified by bone-like hydroxyapatite for implant applications. Appl Surf Sci. 2009;255:6433–8.
Dorozhkin SV. Calcium orthophosphate coatings on magnesium and its biodegradable alloys. Acta Biomater. 2014;10:2919–34.
Shadanbaz S, Dias GJ. Calcium phosphate coatings on magnesium alloys for biomedical applications: a review. Acta Biomater. 2012;8:20–30.
Surmenev RA, Surmeneva MA, Ivanova AA. Significance of calcium phosphate coatings for the enhancement of new bone osteogenesis—a review. Acta Biomater. 2014;10:557–79.
Paital SR, Dahotre NB. Calcium phosphate coatings for bio-implant applications: materials, performance factors, and methodologies. Mater Sci Eng R. 2009;66:1–70.
Burg KJL, Porter S, Kellam JF. Biomaterial developments for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2000;21:2347–59.
Müller WD, Nascimento ML, Zeddiese M, Córsico M, Gassa LM, Lorenzo MAF. de Mele, magnesium and its alloys as degradable biomaterials: corrosion studies using potentiodynamic and EIS electrochemical techniques. Mater Res. 2007;10:5–10.
Chen Y, Miao X. Effect of fluorine addition on the corrosion resistance of hydroxyapatite ceramics. Ceram Int. 2004;30:1961–5.
Gopi D, Bhalaji PR, Ramya S, Kavitha L. Evaluation of biodegradability of surface treated AZ91 magnesium alloy in SBF solution. J Ind Eng Chem. 2015;23:218–27.
Hiromoto S, Tomozawa M. Hydroxyapatite coating of AZ31 magnesium alloy by a solution treatment and its corrosion behavior in NaCl solution. Surf Coat Technol. 2011;205:4711–9.
Zucchi F, Grassi V, Furigana A, Monticelli C, Trabanelli G. Electrochemical behaviour of a magnesium alloy containing rare earth elements. J Appl Electrochem. 2006;36:195–204.
Li L, Gao J, Wang Y. Evaluation of cyto-toxicity and corrosion behavior of alkali-heat-treated magnesium in simulated body fluid. Surf Coat Technol. 2004;185:92–98.
Zhu Y, Wu G, Zhang YH, Zhao Q. Growth and characterization of Mg(OH)2 film on magnesium alloy AZ31. Appl Surf Sci. 2011;257:6129–37.
Lorenz C, Brunner JG, Kollmannsberger P, Jaafar L, Fabry B, Virtanen S. Effect of surface pre-treatments on biocompatibility of magnesium. Acta Biomater. 2009;5:2783–9.
Zhao H, Cai S, Niu S, Zhang R, Wu X, Xu G, Ding Z. The influence of alkali pretreatments of AZ31 magnesium alloys on bonding of bioglass–ceramic coatings and corrosion resistance for biomedical applications. Ceram Int. 2015;41:4590–600.
Su Y, Lu Y, Su Y, Hu J, Lian J, Li G. Enhancing the corrosion resistance and surface bioactivity of a calcium-phosphate coating on a biodegradable AZ60 magnesium alloy via a simple fluorine post-treatment method. RSC Adv. 2015;5:56001–10.
Su Y, Li G, Lian JA. Chemical conversion hydroxyapatite coating on AZ60 magnesium alloy and its electrochemical corrosion behaviour. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2012;7:11497–511.
Ou C, Lu W, Zhan Z, Huang P, Yan P, Yan B, Chen M. Effect of Ca and P ion concentrations on the structural and corrosion properties of biomimetic Ca-P coatings on ZK60 magnesium alloy. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2013;8:9518–30.
Kokubo T, Takadama H. How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity. Biomaterials. 2005;27:2907–15.
Wang Y, Wei M, Gao J. Improve corrosion resistance of magnesium in simulated body fluid by dicalcium phosphate dihydrate coating. Mater Sci Eng C. 2009;29:1311–6.
Sridevi B, Gérrard Eddy JP, Derek F. Growth of flower-like brushite structures on magnesium substrates and their subsequent low temperature transformation to hydroxyapatite. Am J Biomed Eng. 2014;4:79–87.
Wen C, Guan S, Peng L, Ren C, Wang X, Hu Z. Characterization and degradation behavior of AZ31 alloy surface modified by bone-like hydroxyapatite for implant applications. Appl Surf Sci. 2009;255:6433–8.
Dorozhkin SV. A review on the dissolution of calcium apatites. Prog Cryst Growth Charact. 2002;44:45–61.
Mukhametkaliyev TM, Surmeneva MA, Vladescu A, Cotruta CM, Braic M, Dinu M, Vranceanu MD, Pana I, Muellere M, Surmenev RA. A biodegradable AZ91 magnesium alloy coated with a thin nanostructured hydroxyapatite for improving the corrosion resistance. Mater Sci Eng C. 2017;75:95–103.
Zhao Y-B, Liu H-P, Li C-Y, Chen Y, Li S-Q, Zeng R-C, Wang Z-L. Corrosion resistance and adhesion strength of a spin-assisted layer-by-layer assembled coating on AZ31 magnesium alloy. Appl Surf Sci. 2018;434:787–95.
Sasikumar Y, Solomon MM, Olasunkanmi LO, Ebenso EE. Effect of surface treatment on the bioactivity and electrochemical behavior of magnesium alloys in simulated body fluid. Mater Corros. 2017;68:776–90.
Zhang YJ, Yan CW, Wang FH, Li WF. Electrochemical behavior of anodized Mg alloy AZ91D in chloride containing aqueous solution. Corros Sci. 2005;47:2816–31.
Chen C, Qiu S, Qin S, Yan G, Zhao H, Wang L. Anticorrosion performance of epoxy coating containing reactive poly (o-phenylenediamine) nanoparticles. Int J Electrochem Sci. 2017;12:3417–31.
Sasikumar Y, Rajendran N. Influence of surface modification on the apatite formation and corrosion behavior of Ti and Ti–15Mo alloy for biomedical applications. Mater Chem Phys. 2013;138:114–23.
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledged for the financial supports received from the funding agencies of Brazil government such as CAPES (BEX 5383/15-3), (PNPD-PhD scholarships) CNPq (304051/2014-4) and FAPERJ (E-26/110.087/2014, 13.577/2015 and /216.730/2015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sasikumar, Y., Kumar, A.M., Babu, R.S. et al. Biocompatible hydrophilic brushite coatings on AZX310 and AM50 alloys for orthopaedic implants. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 29, 123 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-018-6131-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-018-6131-8