Abstract
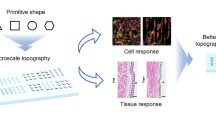
Topographical cues have a significant impact on cell responses and by this means, on the fabrication of innovative implant materials. However, analysis of cell-topography interactions in dependence of the surface feature dimensions is still challenging due to limitations in the fabrication technology. Here, we introduce surface structuring via picosecond laser systems, which enable a fast production of micro-sized topologies. Changes in the processing parameters further control the feature sizes of so-called spikes. Using surfaces with big and small spike-to-spike-distances for comparisons, we focussed on cell adhesion via extracellular matrix adsorption and focal adhesion complexes, morphology, localisation and proliferation of fibroblasts. The observed cell control was dependent on a turnover point related to the structure dimensions: only big spike-to-spike-distances reduced cell behaviour. Therefore, this technology offers a platform to study cell and tissue interactions with a defined microenvironment.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lee J, Cuddihy MJ, Kotov NA. Three-dimensional cell culture matrices: state of art. Tissue Eng Part B. 2008;14(1):61–86.
Giancotti FG, Ruoslathi E. Integrin signalling. Science. 1999;285:1028–32.
Stevens MM, George JH. Exploring and engineering the cell surface interface. Science. 2005;310(18):1135–8.
Flemming RG, Murphy CJ, Abrams GA, Goodman SL, Nealey PF. Effects of synthetic micro- and nano-structured surfaces on cell behavior. Biomaterials. 1999;20:573–88.
Wilkinson CDW, Riehle M, Wood M, Gallagher J, Curtis ASG. The use of materials patterned on a nano- and micro-metric scale in cellular engineering. Mater Sci Eng C. 2002;19:263–9.
Bettinger CJ, Langer R, Borenstein JT. Engineering substrate micro- and nanotopography to control cell funtion. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2009;48(30):5406–14.
Fadeeva E, Schlie S, Koch J, Chichkov BN, Vorobyev AY, Guo C. Femtosecond laser-induced surface structures on platinum and their effects on surface wettability and fibroblast cell proliferation. Cont Angle Wettability Adhes. 2009;6:163–71.
Schlie S, Fadeeva E, Ovsianikov A, Koch J, Ngezahayo A, Chichkov BN. Laser-based nanoengineering for biomedical applications. Photonic Nanostruct Fundam Appl. 2011;9:159–62.
Schlie S, Fadeeva E, Koch J, Ngezahayo A, Chichkov BN. Femtosecond laser fabricated spike structures for selective control of cellular behavior. J Biomater Appl. 2010;25(3):217–33.
Koroleva A, Schlie S, Fadeeva E, Gittard SD, Ovsianikov A, Koch J, Narayan RJ, Chichkov BN. Microreplication of laser-fabricated surfaces and three-dimensional structures. J Opt. 2010. doi:10.1088/2040-8978/12/12/124009.
Anderson JM. Biological responses to biomaterials. Annu Rev Mater Res. 2001;31:81–110.
Berry CC, Dalby MJ, McCloy D, Affrossman S. The fibroblast response to tubes exhibiting internal nanotopography. Biomaterials. 2005;26:4985–92.
Choi C-H, Hagvall SH, Wu BM, Dunn JCY, Beygui RE, Kim C-J. Cell interaction with three-dimensional sharp-tip nanotopography. Biomaterials. 2007;28:1672–9.
Faucheux N, Tzoneva R, Nagel M-D, Groth T. The dependence of fibrillar adhesions in human fibroblasts on substratum chemistry. Biomaterials. 2006;27:234–45.
Baujard-Lamotte L, Noinville S, Goubard F, Marque P, Pauthe E. Kinetics of conformational changes of fibronectin adsorbed onto model surfaces. Colloids Surf B. 2008;63:129–37.
Lo SH. Focal adhesions: what’s new inside. Dev Biol. 2006;294:280–91.
Wozniak MA, Modzelewska K, Kwong L, Keely PJ. Focal adhesion regulation of cell behavior. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1692:103–19.
Selhuber-Unkel C, Erdmann T, López-García M, Kessler H, Schwarz US, Spatz JP. Cell adhesion strength his controlled by intermolecular spacing of adhesion receptors. Biophys J. 2010;98:543–51.
Ingber DE, Tensegrity I. Cell structure and hierarchical systems biology. J Cell Sci. 2003;116:1157–73.
Schlie S, Mazur K, Bintig W, Ngezahayo A. Cell cycle dependent regulation of gap junction coupling and apoptosis in GFSHR-17 granulosa cells. J Biomed Sci Eng. 2010;3:884–91.
Acknowledgments
This work was partly supported by Cluster of Excellence Rebirth “From Regenerative Biology to Reconstructive Therapy” and BMBF-project REMEDIS. The authors thank Prof. Dr. H. Küster, head of the Institute of Biophysics (Leibniz University Hannover, Germany) for granting the use of the microplate reader and fluorescence microscope.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schlie, S., Fadeeva, E., Koroleva, A. et al. Laser-engineered topography: correlation between structure dimensions and cell control. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 23, 2813–2819 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-012-4737-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-012-4737-9