Abstract
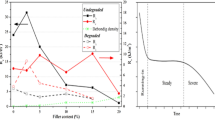
A novel biocomposite of carbon fiber (CF) reinforced hydroxyapatite (HA)/polylactide (PLA) was prepared by hot pressing a prepreg which consisting of PLA, HA and CF. The prepreg was manufactured by solvent impregnation process. Polymer resin PLA dissolved with chloroform was mixed with HA. After reinforcement CF bundle was impregnated in the mixture, the solvent was dried completely and subsequently hot-pressed uniaxially under a pressure of 40 MPa at 170°C for 20 min. A study was carried out to investigate change in mechanical properties of CF/HA/PLA composites before and after degradation in vitro. The composites have excellent mechanical properties. A peak showed in flexural strength, flexural modulus and shear strength aspects, reaching up 430 MPa, 22 GPa, 212 MPa, respectively, as the HA content increased. Degraded in vitro for 3 months, the flexural strength and flexural modulus of the CF/HA/PLA fell 13.2% and 5.4%, respectively, while the shear strength of the CF/HA/PLA composites remains at the 190 MPa level. The SEM photos showed that there were gaps between the PLA matrix and CF after degradation. Water uptake increased to 5%, but the mass loss rate was only 1.6%. The pH values of the PBS dropped less than 0.1. That’s because the alkaline of HA neutralize the acid degrades from PLA, which can prevent the body from the acidity harm.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson LD. Treatment of ununited fractures of the long bones; compression plate fixation and the effect of different types of internal fixation on fracture healing. J Bone Joint Surg Am A. 1965;47:191.
Terjesen T. Bone healing after metal plate fixation and external fixation of the osteotomized rabbit tibia. Acta Orthop Scand. 1984;55:69.
Terjesen T, Apalset K. The influence of different degrees of stiffness of fixation plates on experimental bone healing. J Orthop Res. 1988;6:293. doi:10.1002/jor.1100060218.
Uchikura C, Hirano J, Kudo F, Satomi K, Ohno T. Comparative study of nonbridging and bridging external fixators for unstable distal radius fractures. J Orthop Sci. 2004;9:560. doi:10.1007/s00776-004-0828-x.
Huang TL, Huang CK, Yu JK, Chiu FY, Liu HT, Liu CL, et al. Operative treatment of intra-articular distal radius fractures using the small AO external fixation device. J Chin Med Assoc. 2005;68:474.
Luklinska ZB, Bonfield W. Morphology and ultrastructure of the interface between hydroxyapatite-polyhydroxybutyrate composite implant and bone. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 1997;8:379. doi:10.1023/A:1018589018205.
Rho JY, Kuhn-Spearing L, Zioupos P. Mechanical properties and the hierarchical structure of bone. Med Eng Phys. 1998;20:92. doi:10.1016/S1350-4533(98)00007-1.
Yasunaga T, Matsusue Y, Furukawa T, Shikinami Y, Okuno M, Nakamura T. Bonding behavior of ultrahigh strength unsintered hydroxyapatite particles/poly(l-lactide) composites to surface of tibial cortex in rabbits. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;47:412. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(19991205)47:3<412::AID-JBM17>3.0.CO;2-B.
Kulkarni RK, Moore EG, Hegyeli AF, Leonard F. Biodegradable poly(lactic acid) polymers. J Biomed Mater Res. 1971;5:169. doi:10.1002/jbm.820050305.
Vainionpää S, Rokkanen P, Törmälä P. Surgical applications of biodegradable polymers in human tissues. Prog Polym Sci. 1989;14:679. doi:10.1016/0079-6700(89)90013-0.
Matsusue Y, Yamamuro T, Ikada Y. Tissue reaction of bioabsorbable ultra high strength poly (l-lactide) rod. A long-term study in rabbits. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 1995;317:246.
Devin JE, Attawia MA, Laurencin CT. Three-dimensional degradable porous polymer-ceramic matrices for use in bone repair. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1996;7:661. doi:10.1163/156856296X00435.
Marra KG, Szem JW, Kumta PN, DiMilla PA, Weiss LE. In vitro analysis of biodegradable polymer blend/hydroxyapatite composites for bone tissue engineering. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;47:324. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(19991205)47:3<324::AID-JBM6>3.0.CO;2-Y.
Bleach NC, Tanner KE. Effect of filler type on the mechanical properties of self-reinforced polylactide-calcium phosphate composites. J Mater Sci: Mater Med. 2001;12:911. doi:10.1023/A:1012884310027.
Maquet V, Boccaccini AR, Pravata L, Notingher I, Jérôme R. Porous poly(alpha-hydroxyacid)/Bioglass composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. I: Preparation and in vitro characterisation. Biomaterials. 2004;25:4185. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.10.082.
Zhang R, Ma PX. Poly(alpha-hydroxyl acids)/hydroxyapatite porous composites for bone-tissue engineering. I. Preparation and morphology. J Biomed Mater Res. 1999;44:446. doi:10.1002/(SICI)1097-4636(19990315)44:4<446::AID-JBM11>3.0.CO;2-F.
Shikinami Y, Okuno M. Bioresorbable devices made of forged composites of hydroxyapatite (HA) particles and poly l-lactide (PLLA). Part II: practical properties of miniscrews and miniplates. Biomaterials. 2001;22:3197. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(01)00072-2.
Kasuga T, Maeda TH, Kato K. Preparation of poly(lactic acid) composites containing calcium carbonate (vaterite). Biomaterials. 2003;24:3247. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(03)00190-X.
Hong ZK, Zhang PB, He CL. Nano-composite of poly(l-lactide) and surface grafted hydroxyapatite: mechanical properties and biocompatibility. Biomaterials. 2005;26:6296. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2005.04.018.
Chlopek J, Morawska-Chochol A, Bajor G, Adwent M, Cieslik-Bielecka A, Cieslik M, et al. The influence of carbon fibres on the resorption time and mechanical properties of the lactide-glycolide co-polymer. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 2007;18:1355. doi:10.1163/156856207782246858.
Hojo Y, Kotani Y, Ito M, Abumi K, Kadosawa T, Shikinami Y, et al. A biomechanical and histological evaluation of a bioresorbable lumbar interbody fusion cage. Biomaterials. 2005;26:2643. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2004.07.020.
Al-Shawi AK, Smith SP, Anderson GH. The use of a carbon fiber plate for periprosthetic supracondylar femoral fractures. J Arthroplasty. 2002;17:320. doi:10.1054/arth.2002.30291.
Czajkowska B, Bhiewicz M. Phagocytosis of chemically modified carbon materials. Biomaterials. 1997;18:69. doi:10.1016/S0142-9612(96)00103-2.
BS 2782: Part 3: Methods 340A and 340B. London: British Standards Institution; 1978.
Acknowledgment
This work is financed by the Science & Technology Department of Zhejiang Province of China (Grant no. 2005C21049).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shen, L., Yang, H., Ying, J. et al. Preparation and mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced hydroxyapatite/polylactide biocomposites. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 20, 2259–2265 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3785-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-009-3785-2