Abstract
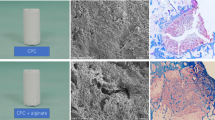
Calcium phosphate cement (CPC) sets in situ to form resorbable hydroxyapatite and is promising for orthopaedic applications. However, it requires on-site powder-liquid mixing during surgery, which prolongs surgical time and raises concerns of inhomogeneous mixing. The objective of this study was to develop a premixed CPC scaffold with macropores suitable for tissue ingrowth. To avoid the on-site powder-liquid mixing, the CPC paste was mixed in advance and did not set in storage; it set only after placement in a physiological solution. Using 30% and 40% mass fractions of mannitol porogen, the premixed CPC scaffold with fibers had flexural strength (mean ± sd; n = 5) of (3.9 ± 1.4) MPa and (1.8 ± 0.8) MPa, respectively. The scaffold porosity reached (68.6 ± 0.7)% and (74.7 ± 1.2)%, respectively. Osteoblast cells colonized in the surface macropores of the scaffold and attached to the hydroxyapatite crystals. Cell viability values for the premixed CPC scaffold was not significantly different from that of a conventional non-premixed CPC known to be biocompatible (P > 0.1). In conclusion, using fast-dissolving porogen and slow-dissolving fibers, a premixed macroporous CPC scaffold was developed with strength approaching the reported strengths of sintered porous hydroxyapatite implants and cancellous bone, and non-cytotoxicity similar to a biocompatible non-premixed CPC.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. L. HENCH, J. WILSON, in “Introduction to Bioceramics” (World Scientific, Singapore, 1993)
R. Z. LEGEROS, Clinical. Mater. 14 (1993) 65
K. A. HING, S. M. BEST and W. BONFIELD, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. in Med. 10 (1999) 135
W. SUCHANEK and M. YOSHIMURA, J. Mater. Res. 13 (1998) 94
C. T. LAURENCIN, A. M. AMBROSIO, M. D. BORDEN and J. A. COOPER, Annu. Rev. Biomed. Eng. 1 (1999) 19
W. E. Brown, L. C. Chow, In Cements research progress, edited by P. W. Brown (American Ceramic Society, Westerville, OH, 1986) p. 352
M. P. GINEBRA, E. FERNANDEZ, E. A. De MAEYER, R. M. VERBEECK, M. G. BOLTONG, J. GINEBRA, F. C. DRIESSENS and J. A. PLANELL, J. Dent. Res. 76 (1997) 905
Y. MIYAMOTO, K. ISHIKAWA, M. TAKECHI, T. TOH, T. YUASA, M. NAGAYAMA and K. SUZUKI, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. (Appl. Biomater.) 48 (1999) 36
L. C. CHOW, Mat. Res. Symp. Proc. 599 (2000) 27
P. D. COSTANTINO, C. D. FRIEDMAN, K. JONES, L. C. CHOW and G. A. SISSON, Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 90 (1992) 174
C. D. FRIEDMAN, P. D. COSTANTINO, S. TAKAGI and L. C. CHOW, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. (Appl. Biomater.) 43 (1998) 428
H. H. K. XU, J. B. QUINN, S. TAKAGI and L. C. CHOW, J. Dent. Res. 81 (2002) 219
H. H. K. XU, S. TAKAGI, J. B. QUINN and L. C. CHOW, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 68A (2004) 725
H. H. K. XU and C. G. SIMON Jr, J. Orthop. Res. 22 (2004) 535
S. TAKAGI, L. C. CHOW, S. HIRAYAMA and A. SUGAWARA, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. (Appl. Biomater.) 67B (2003) 689
L. E. CAREY, H. H. K. XU, C. G. SIMON Jr, S. TAKAGI and L. C. CHOW, Biomaterials 26 (2005) 5002
S. TAKAGI and L. C. CHOW, J. Mater. Sci.: Mater. Med. 12 (2001) 135
H. H. K. XU, J. B. QUINN, S. TAKAGI, L. C. CHOW and F. C. EICHMILLER, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 57 (2001) 457
ISO 10993–5. Biological evaluation of medical devices - Part 5: Tests for in vitro cytotoxicity (International Standards Organization, Geneva, Switzerland, 1999)
C. J. DAMIEN and J. R. PARSONS, J. Appl. Biomater. 2 (1991) 187
M. ISHIYAMA, M. SHIGA, K. SASAMOTO, M. MIZOGUCHI and P. G. HE, Chem. Pharm. Bull. 41 (1993) 1118
R. M. PILLIAR, M. J. FILIAGGI, J. D. WELLS, M. D. GRYNPAS and R. A. KANDEL, Biomaterials 22 (2001) 963
K. A. HING, S. M. BEST, K. E. TANNER, W. BONFIELD and P. A. REVELL, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 68A (2004) 187
T. LIVINGSTON, P. DUCHEYNE and J. GARINO, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 62 (2002) 1
H. H. K. XU, F. C. EICHMILLER and A. A. GIUSEPPETTI, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 52 (2000) 107
N. TAMAI, A. MYOUI, T. TOMITA, T. NAKASE, J. TANAKA, T. OCHI and H. YOSHIKAWA, J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 59 (2002) 110
R. WINTER, in “A consumer’s dictionary of food additives” (Crown Publishers, New York, 1978)
J. Darnell, H. LODISH, D. BALTIMORE, in “Molecular cell biology, 2nd edn” (Freeman and Company, New York, 1990) p. 890
B. ANNAZ, K. A. HING, M. KAYSER, T. BUCKLAND and L. DI SILVIOF, J. Microscopy. 215 (2004) 100
Acknowledgments
We gratefully thank Dr. S. Takagi for discussions and experimental help, and Drs. L. C. Chow, F. C. Eichmiller, and S. H. Dickens for discussions. This study was supported by USPHS grant DE14190 (Xu), Y1-DE-1021 (Simon), NIST, and the ADAF.
Disclaimer
Certain commercial materials and equipment are identified to specify experimental procedures. In no instance does such identification imply recommendation by NIST or the ADA Foundation or that the material identified is necessarily the best available for the purpose.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Official contribution of the National Institute of Standards and Technology; not subject to copyright in the United States.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, H.H.K., Carey, L.E. & Simon, C.G. Premixed macroporous calcium phosphate cement scaffold. J Mater Sci: Mater Med 18, 1345–1353 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-0146-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10856-007-0146-x