Abstract
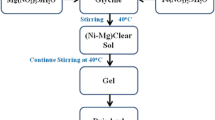
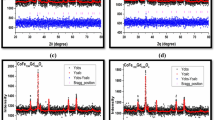
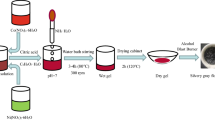
With the development of science and technology, the research on magnetic materials is particularly important. In particular, the application of nanomagnetic materials in computer chips, magnetic recording, and biomedical fields has high research value. In this paper, Ni–Cu–Co ferrite nanomagnetic materials doped with rare earth (RE = Y3+, Sm3+, La3+ and Yb3+) ions were prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion method. The spinel structure of the sample was analyzed by X-ray diffraction (XRD), and the average crystallite size of the doped rare earth ions was calculated by the half width of (311) peak. The samples were further characterized by Fourier-transform infrared spectroscopy (FT-IR). Two characteristic peaks are at the wave number of 603 cm−1 and 391 cm−1, respectively. The morphology of the nanomagnetic grains was observed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), and it was found that the nanomagnetic grains of the samples were all spherical or quasi spherical structure with water chestnut. Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) was used to observe the pure samples and Y3+ ion-doped samples. Through EDS analysis, it is found that the chemical composition of the sample is Ni, Cu, Co, Fe, O, Y, Sm, La, and Yb. Through vibration sample magnetometer (VSM) analysis, the samples of Ni–Cu–Co ferrite doped with different RE3+ ions have the characteristics of ferromagnetism.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.U. Ali, M. Islam, Ishaque et al, Structural and magnetic properties of holmium substituted cobalt ferrites synthesized by chemical co-precipitation method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 324, 3773 (2012)
G.V.M. Williams, T. Prakash, J. Kennedy, S.V. Chong, S. Rubanov, Spin-dependent tunnelling in magnetite nanoparticles. J. Magn Magn Mater. 460, 229–233 (2018)
J. Kennedy, J. Leveneur, G.V.M. Williams et al., Fabrication of surface magnetic nanoclusters using low energy ion implantation and electron beam annealing. Nanotechnology 22, 115602 (2011)
I.A. Auwal, B. Ünal, H. Güngüneş, S.E. Shirsath, A. Baykal, Dielectric properties, cationic distribution calculation and hyperfine interactions of La3+ and Bi3+ doped strontium hexaferrites. Ceram. Int. 42, 9100–9115 (2016)
R.A. Pawar, S.M. Patange, A.R. Shitre, S.K. Gore, S.S. Jadhav, S.E. Shirsath, Crystal chemistry and single-phase synthesis of Gd3+ substituted Co-Zn ferrite nanoparticles for enhanced magnetic properties. Nanoscale Horizons 8, 25258–25267 (2018)
I. Soibam, S. Phanjoubam, H.B. Sharma et al., Effects of cobalt substitution on the dielectric properties of Li–Zn ferrites. Solid State Commun. 148, 399–402 (2008)
Y. Slimani, M.A. Almessiere, A. Demir Korkmaz, S. Guner, H. Güngüneş, M. Sertkol, A. Manikandan, A. Yildiz, S. Akhtar, S.E. Shirsath, A. Baykal, Ni0.4Cu0.2Zn0.4TbxFe2−xO4 nanospinel ferrites: ultrasonic synthesis and physical properties. Ultrason. Sonochem. 59, 104757 (2019)
P.R. Arjunwadkar, R.R. Patil, D.K. Kulkarni, Effect of sintering temperature on the structural, electrical and magnetic properties of Li0.5Al1.0Fe2O4 ferrite prepared by combustion method. J. Alloys Compd. 463, 403–407 (2008)
S. Kumar, Alimuddin, R. Kumar, P. Thakur, K.H. Chae, B. Angadi, W.K. Choi, Electrical transport, magnetic, and electronic structure studies of Mg0.95Mn0.05Fe2−2xTi2xO4 ± δ (0 ≤ x ≤ 0.5) ferrites. J. Phys. Condens. Matter 19, 1–15 (2007)
L. Satyanarayana, K.M. Reddy, S.V. Manorama, Nanosized spinel NiFe2O4: a novel material for the detection of liquefied petroleum gas in air. Mater. Chem. Phys. 82, 21–26 (2003)
F. Kenfack, H. Langbein, Influence of the starting powders on the synthesis of nickel ferrite. Cryst. Res. Technol. 41, 748 (2006)
C.P. Liu, M.W. Li, Z. Cui, J.R. Huang, Y.L. Tian, T. Lin, W.B. Mi, Comparative study of magnesium ferrite nanocrystallites prepared by sol–gel and coprecipitation methods. J. Mater. Sci. 42, 6133 (2007)
P.K. Chakrabarti, B.K. Nath, S. Brahma, S. Das, K. Gosawami, V. Kumar, P.K. Mukhopadhyay, D. das, M. Ammer, F. Mazaleyrat, J. Phys. Condens. Matter 18, 5253 (2006)
S.E. Shirsath, X. Liu, Y. Yasukawa et al., Switching of magnetic easy-axis using crystal orientation for large perpendicular coercivity in CoFe2O4 thin film. Sci. Rep. 30074, 1–11 (2016)
S.E. Shirsath, X. Liu, M.H.N. Assadi et al., Au quantum dots engineered room temperature crystallization and magnetic anisotropy in CoFe2O4 thin films. Nanoscale Horizons 4, 434–444 (2018)
M. Hashim, M. Raghasudha, S.S. Meena et al., Influence of rare earth ion doping (Ce and Dy) on electrical and magnetic properties of cobalt ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 449, 319–327 (2018)
S.E. Shirsath, M.L. Mane, Y. Yasukawa, X. Liu, A. Morisako, Self-ignited high temperature synthesis and enhanced super-exchange interactions of Ho3+-Mn2+-Fe3+-O2- ferromagnetic nanoparticles. Phys. Chem. Phys. 16, 2347–2357 (2014)
S.E. Shirsath, C. Cazorla, T. Lu, L. Zhang, Y.Y. Tay, X. Lou, Y. Liu, S. Li, D. Wang, Interface-charge induced giant electrocaloric effect in lead free ferroelectric thin-film bilayers. Nano Lett. 20, 1262–1271 (2020)
S. Amiri, H. Shokrollahi, Magnetic and structural properties of RE doped Co-ferrite (RE=Nd, Eu, and Gd) nano-particles synthesized by co-precipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 345, 18–23 (2013)
S.E. Shirsath, R.H. Kadam, S.M. Patange, M.L. Mane, A. Ghasemi, A. Morisako, Enhanced magnetic properties of Dy3+ substituted Ni-Cu-Zn ferrite nanoparticles. Appl. Phys. Lett. 100, 042407 (2012)
V. Stevanović, M. d’Avezac, A. Zunger, Simple point-ion electrostatic model explains the cation distribution in spinel oxides. Phys. Rev. Lett. 105, 075501 (2010)
D. Fritsch, C. Ederer, First-principles calculation of magnetoelastic coefficients and magnetostriction in the spinel ferrites CoFe2O4 and NiFe2O4. Phys. Rev. B 86, 014406 (2012)
J. Jing, L. Liangchao, X. Feng, Structural analysis and magnetic properties of Gd3+ ion doped Li-Ni ferrites prepared using rheological phase reaction method. J. Rare Earths 25, 79–83 (2007)
M.P. Reddy, X. Zhou, A. Yann, S. Dua, Q. Huang, A. Mohamed, Low temperature hydrothermal synthesis, structural investigation and functional properties of CoxMn1−xFe2O4 (0 ≤x≤1.0) nanoferrites. Superlattice Microstruct. 81, 233–242 (2015)
E. Ateia, A.A.H. El-Bassuony, Fascinating improvement in physical properties of Cd/Co nanoferrites using different rare earth ions. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron. 28, 11482–11490 (2017)
V. Verma, Structural, electrical and magnetic properties of rare-earth and transition element co-doped bismuth ferrites. J. Alloys Compd. 641, 205–209 (2015)
S.E. Shirsath, D. Wang, S.S. Jadhav, M.L. Mane, S. Li, Ferrites obtained by sol-gel method, in Handbook of Sol-Gel Science and Technology. ed. by L. Klein, M. Aparicio, A. Jitianu (Springer, Cham, 2018), pp. 695–735
R.N. Bhowmik, R. Ranganathan et al., Coexistence of spin glass and superparamagnetism with ferrimagnetic order in polycrystalline spinel Co0.2Zn0.8Fe1.95Ho0.05O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 299, 327–337 (2006)
A.B. Gadkari, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Structural analysis of Y3+-doped Mg–Cd ferrites prepared by oxalate co-precipitation method. Mater. Chem. Phys. 114, 505–510 (2009)
R.D. Shannon, C.T. Prewitt, Acta Crystallogr. B 25, 925 (1969)
K.P. Chae, J.-G. Lee, H.S. Kweon, Y.B. Lee, Synthesis and magnetic properties of AlxCoFe2−xO4 ferrite powders. Phys. Status Solidi 201, 1883–1888 (2004)
S. Singhal, S.K. Barthwal, K. Chandra, XRD, magnetic and Mössbauer spectral studies of nanosize aluminum substituted cobalt ferrites (CoAlxFe2−xO4). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 306, 233–240 (2006)
R.N. Bhowmik, R. Ranganathan, “Super-ferromagnetic” clusters in spinel oxide. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 247, 83–91 (2002)
N. Sharma, P. Aghamkar, S. Kumar, M. Bansal, Anju, R.P. Tondon, Study of structural and magnetic properties of Nd doped zinc ferrites. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 369, 162–167 (2014)
S.K. Sharma, R. Kumar, S. Kumar, M. Knobel et al., J. Phys. Condens. Matter. 20, 235214 (2008)
M. Ben Ali, K. El Maalam, H. El Moussaoui, O. Mounkachi, M. Hamedoun, R. Masrour, E.K. Hlil, A. Benyoussef, Effect of zinc concentration on the structural and magnetic properties of mixed Co-Zn ferrites nanoparticles synthesized by sol/gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 398, 20–25 (2016)
M.I. Abdel-Ati, Study of the jump length effect of Co0.6Zn0.4 ferrites. Phys. Status Solidi (A) 157, 523 (1996)
X. Zhao, W. Wang, Y. Zhang, S. Wu, F. Li, J.P. Liu, Synthesis and characterization of gadolinium doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles with enhanced adsorption capability for Congo Red. Chem. Eng. J. 250, 164–174 (2014)
M.D. Shultz, E.E. Carpenter, S.A. Morrison, S. Calvin, Cation occupancy determination in manganese zinc ferrites using Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy. J. Appl. Phys. 99, 83–86 (2006)
C. Virlan, G. Bulai, O.F. Caltun et al., Rare earth metals influence on the heat generating capability of cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 42, 11958–11965 (2016)
J. Smit, H.P.J. Wijn, Ferrites (Wiley, New York, 1959).
B.D. Cullity, Elements of X-Ray Diffraction, vol. 99 (Addison Wesley, Reading, 1967), p. 96
S.G. Gawas, U.B. Gawas, V.M.S. Verenkar, M.M. Kothawale, R. Pednekar, Structural and magnetic studies of Cu-substituted nanocrystalline Ni–Zn ferrites obtained via hexamine–nitrate combustion route. J. Superconduct. Nov. Magn. 30, 1447–1452 (2017)
H.E. Hassan, T. Sharshar, M.M. Hessien et al., Effect of c-rays irradiation on Mn-Ni ferrites: structure, magnetic properties and positron annihilation studies. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B. 304, 72–79 (2013)
N. Rezlescu, E. Rezlescu, C. Pasnicu, M.L. Craus, Effects of the rare-earth ions on some properties of a nickel-zinc ferrite. I. Phys. Condens. Matter. 6, 5707–5716 (1994)
J.L. Bhosale, S.N. Kulkarni, R.B. Sasmile, B.K. Chougule, Indian J. Pure Appl. Phys. 33, 412 (1999)
Y. Matsuo, K. Ono, M. Ishikura, I. Sasaki, Effects of MoO3 addition on manganese zinc ferrites. IEEE Trans. Magn. 33, 3751–3753 (1997)
K. Siraj, M. Khaleeq-ur-Rahman, S.I. Hussain et al., Effect of deposition temperature on structural, surface, optical and magnetic properties of pulsed laser deposited Al doped CdO thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 6756–6762 (2011)
Y. Slimani, M.A. Almessiereb, E. Hannachi, A. Baykal, A. Manikandan, M. Mumtaz, F. Ben Azzouz, Influence of WO3 nanowires on structural, morphological and flux pinning ability of YBa2Cu3Oy superconductor. Ceram. Int. 45, 2621–2628 (2019)
R.D. Waldron, Phys. Rev. 99, 1727 (1955)
Q.M. Wei, J.B. Li, Y.J. Chen, Cation distribution and infrared properties of NixMn1−xFe2O4 ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. 36, 5115–5118 (2001)
I. Panneer Muthuselvam, R.N. Bhowmik, Connectivity between electrical conduction and thermally activated grain size evolution in Ho-doped CoFe2O4 ferrite. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 43, 3 (2010)
M. Abdullah Dar, V. Verma, S.P. Gairola et al., Low dielectric loss of Mg doped Ni-Cu-Zn nano-ferrites for power applications. Appl. Surf. Sci. 258, 5342–5347 (2012)
S. Maensiri, C. Masingboon, B. Boonchomb, S. Seraphinc, A simple route to synthesize nickel ferrite (NiFe2O4) nanoparticles using egg white. Scr. Mater. 56, 797–800 (2007)
C.K.Y. Yafet, Phys. Rev. 87, 290–294 (1958)
A.A. Ati, Z. Othaman, A. Samavati, F.Y. Doust, Structural and magnetic properties of Co-Al substituted Ni ferrites synthesized by co-precipitation method. J. Mol. Struct. 1058, 136–141 (2014)
V.S. Sawant, A.A. Bagade, S.V. Mohite, K.Y. Rajpure, IR absorption spectroscopic study of mixed cobalt substituted lithium ferrites. Phys. B 451, 39–42 (2014)
S.R. Sawant, S.S. Suryavanshi, Ion-covalent and Yafet Kittle (YK) angle studies of slow cooled and quenched CuZn–system. Curr. Sci. 57, 644–647 (1998)
K.S. Aneesh-Kumar, R.N. Bhowmik, Micro-structural characterization and magnetic study of Ni1.5Fe1.5O4 ferrite synthesized through coprecipitation route at different pH values. Mater. Chem. Phys. 146, 159–169 (2014)
Y. Köseoǧlu, F. Alan, M. Tan, R. Yilgin, M. Öztürk, Low temperature hydrothermal synthesis and characterization of Mn doped cobalt ferrite nanoparticles. Ceram. Int. 38, 3625–3634 (2012)
Y. Feng, M.O. Lai, L. Lu, Enhanced multiferroic properties and valence effect of Ru-doped BiFeO3 thin films. J. Phys. Chem C 114(15), 6994–6998 (2010)
C.N. Chervin, B.J. Clapsaddle, H.W. Chiu et al., Role of cyclic ether and solvent in a non-alkoxide sol-gel synthesis of yttria-stabilized zirconia nanoparticles. Chem. Mater. 18, 4865–4874 (2006)
J. Wang, C. Zeng, Z. Peng, Q. Chen, Synthesis and magnetic properties of Zn1−xMnxFe2O4 nanoparticles. Phys. B 349, 124–128 (2004)
M. Schieber, S. Foner, R. Dodo, E.J. McNiff Jr., J. Appl. Phys. 39, 885 (1968)
E. Bucher, P.H. Schmidt, A. Jayaraman, K. Andres, J.P. Maita, P.D. Dernier, Phys. Rev. 132, 3911 (1970)
I. Dzyaloshinskii, J. Phys. Chem. Solids 4, 241 (1958)
T. Moriya, Phys. Rev. 120, 91 (1960)
J.T. Zhang, X.M. Lu, J. Zhou et al., Origin of magnetic anisotropy and spiral spin order in multiferroic BiFeO3. Appl Phys Lett. 100, 242413 (2012)
M. J. Pourhosseini asl. A. Ghasemi, G.R. Gordani, Structural and magnetic properties of Mn-Ni-Cu substitution of Z-type barium hexaferrite nanoparticles prepared by the coprecipitation method. J. Superlattice Nov. Magn. 28, 109–115 (2015).
T. Ibusuki, S. Kojima, O. Kitakami, Y. Shimada, Magnetic anisotropy and behaviors of Fe nanoparticles. IEEE. Trans. Magn. 37, 2223–2225 (2001)
S.S. Jadhav, S.E. Shirsath, S.M. Patange, K.M. Jadhav, Effect of Zn substitution on magnetic properties of nanocrystalline cobalt ferrites. J. Appl Phys. 108, 2–6 (2010)
E.E. Ateia, F.S. Soliman, Modification of Co/Cu nanoferrites properties via Gd3+/ Er3+ doping. Appl. Phys. A. 123, 312 (2017)
J.M.D. Coey, Rare-Earth Iron Permanent Magnets (Oxford University Press, New York, 1996).
I.P. Muthuselvam, R.N. Bhowmik, Mechanical alloyed Ho3+ doping in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite and understanding of magnetic nanodomains. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 767–776 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Suo, N., Sun, A., Yu, L. et al. Effect of different rare earth (RE = Y3+, Sm3+, La3+, and Yb3+) ions doped on the magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Co ferrite nanomagnetic materials. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 32, 246–264 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04762-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-020-04762-0