Abstract
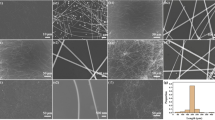
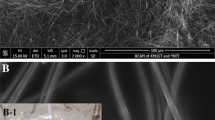
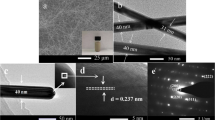
Flexible transparent conductive films (TCFs) based on silver nanowires (AgNWs) networks have been widely researched as an alternative to indium tin oxide (ITO) for optoelectronic devices. However, AgNW-based TCFs still involve issues such as high haze and poor transmittance for practical application. The innovation point of our work is the synthesis of ultra-fine and high aspect ratio AgNWs, and they are developed to prepare high-performance AgNW-based TCFs. In this study, a rapid and rationally designed method to synthesize ultra-fine AgNWs through dual ionic assistants assisted has been explored. As a result, the as-synthesized AgNWs have a uniform ~ 20 nm diameter, and a high aspect ratio of 2000, which are the minimum diameter and maximum aspect ratio among the values reported previously for solvothermal-processed AgNWs. A highly transparent and bendable AgNW-based conductive film shows a 97.71% transmittance and a haze of 1.49% under the condition of disregarding the transmittance and haze of bare PET substrate. The sheet resistance (Rsheet) of the resulting AgNW-based conductive film is ~ 15 Ω sq–1. Most importantly, the AgNW-based conductive film exhibits strong adhesion to the substrate. The advanced and wide-ranging features of the as-prepared AgNW-based conductive film greatly contribute to its use as a transparent conductive film in multifunctional flexible optoelectronic devices.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
T. Mochizuki, Y. Takigami, T. Kondo, H. Okuzaki, Fabrication of flexible transparent electrodes using PEDOT:PSS and application to resistive touch screen panels. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 135, 45972 (2018)
S.W. Shin, Y.U. Jung, K.B. Kim, S.W. Choi, S.J. Kang, ITO-free transparent conductive films based on carbon nanomaterials with metal grid for liquid crystal displays. Liq. Cryst. 42, 1–5 (2015)
L.X. Chen, M.H. Lee, Y.W. Wang, Y.S. Lau, A.A. Syed, F.R. Zhu, Interface dipole for remarkable efficiency enhancement in all-solution-processable transparent inverted quantum dot light-emitting diodes. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 2596–2603 (2018)
J. Liu, F.Z. Luo, A.X. Wei, Z. Liu, Y. Zhao, In-situ growth of Cu2ZnSnS4 nanospheres thin film on transparent conducting glass and its application in dye-sensitized solar cells. Mater. Lett. 141, 228–230 (2015)
R. Kumar, R.M. Kumar, D. Lahiri, I. Lahiri, Thermally reduced graphene oxide film on soda lime glass as transparent conducting electrode. Surf. Coat. Tech. 309, 931–937 (2017)
C. Preston, Z.Q. Fang, J. Murray, H.L. Zhu, J.Q. Dai, J.N. Munday, L.B. Hu, Silver nanowire transparent conducting paper-based electrode with high optical haze. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 1248–1254 (2014)
H.Y. Zhou, Y.L. Wang, J.W. Zhang, Z.K.N. Yu, Y.W. Li, L.C. Tan, Y.W. Chen, A facile approach towards chemical modification of Ag nanowires by PEDOT as a transparent electrode for organic solar cells. J. Mater. Chem. C 6, 312–319 (2018)
J.B. Pyo, B.S. Kim, H. Park, T.A. Kim, C.M. Koo, J. Lee, J.G. Son, S.S. Lee, J.H. Park, Floating compression of Ag nanowire networks for effective strain release of stretchable transparent electrodes. Nanoscale 7, 16434–16441 (2015)
X.L. Chen, X.Z. Wu, S.S. Shao, J.Y. Zhuang, L.M. Xie, S.H. Nie, W.M. Su, Z. Chen, Z. Cui, Hybrid printing metal-mesh transparent conductive films with lower energy photonically sintered copper/tin ink. Sci. Rep. 7, 13239 (2017)
H.G. Im, B.W. An, J. Jin, J. Jang, Y.G. Park, J.U. Park, B.S. Bae, A high-performance, flexible and robust metal nanotrough-embedded transparent conducting film for wearable touch screen panels. Nanoscale 8, 3916–3922 (2016)
J.H. Zhang, Z.F. Chen, X.X. Xu, W. Liao, L.Q. Yang, A simple and efficient approach to fabricate graphene/CNT hybrid transparent conductive films. RSC Adv. 7, 52555–52560 (2017)
P. Chamoli, M.K. Das, K.K. Kar, Urea-assisted low temperature green synthesis of graphene nanosheets for transparent conducting film. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 113, 17–25 (2018)
B.P. Singh, S. Nayak, K.K. Nanda, A. Singh, C. Takai, S. Takashi, M. Fuji, Transparent, flexible, and conducting films based on graphene-polymer composites. Polym. Compos. 39, 297–304 (2016)
S. Devaraju, T. Lee, A.K. Mohanty, Y.K. Hong, K.H. Yoon, Y.S. Lee, J.H. Han, H.J. Paik, Fabrication of durable and flexible single-walled carbon nanotube transparent conductive films. RSC Adv. 7, 19267–19272 (2017)
D. Ito, K. Masuko, B.A. Weintraub, L.C. Mckenzie, J.E. Hutchison, Convenient preparation of ITO nanoparticles inks for transparent conductive thin films. J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 149–158 (2012)
Y.X. Ran, W.W. He, K. Wang, S.L. Ji, C.H. Ye, A one-step route to Ag nanowires with a diameter below 40 nm and an aspect ratio above 1000. Chem. Commun. 50, 14877–14880 (2014)
K. Shahzadi, L. Wu, X.S. Ge, F.H. Zhao, H. Li, S.P. Pang, Y.J. Jiang, J. Guan, X.D. Mu, Preparation and characterization of bio-based hybrid film containing chitosan and silver nanowires. Carbohydr. Polym. 137, 732–738 (2016)
C.Y. Chou, H.S. Liu, G.S. Liou, Highly transparent silver nanowire-polyimide electrode as a snow-cleaning device. RSC Adv. 6, 61386–61392 (2016)
Y. Atwa, N. Maheshwari, I.A. Goldthorpe, Silver nanowire coated threads for electrically conductive textiles. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 3908–3912 (2015)
S.Y. Chen, Y.W. Guan, Y. Li, X.W. Yan, H.T. Ni, L. Li, A water-based silver nanowire ink for large-scale flexible transparent conductive films and touch screens. J. Mater. Chem. C 5, 2404–2414 (2017)
F. Fang, Y.Q. Li, G.W. Huang, H.M. Xiao, Q.P. Feng, N. Hu, S.Y. Fu, Electrical anisotropy and multidimensional pressure sensor of aligned Fe3O4 @ sliver nanowire/polyaniline composite films under an extremely low magnetic field. RSC Adv. 7, 4260–4268 (2017)
S.Q. Liu, B. Weng, Z.R. Tang, Y.J. Xu, Constructing one-dimensional silver nanowire-doped reduced graphene oxide integrated with CdS nanowire network hybrid structures toward artificial photosynthesis. Nanoscale 7, 861–866 (2015)
R. Banica, D. Ursu, T. Nyari, A. Kellenberger, Two step polyol-solvothermal growth of think silver nanowires. Mater. Lett. 194, 181–184 (2017)
Q.T. Tang, H.L. Shen, H.Y. Yao, Y. Jiang, C.F. Zheng, K. Gao, Preparation of silver nanowires/AZO composite film as a transparent conductive material. Ceram. Int. 43, 1106–1113 (2017)
N.D. Zhang, X.S. Yin, H. Gong, Highly conductive and flexible transparent films based on silver nanowire/chitosan composite. RSC Adv. 6, 47552–47561 (2016)
H.W. Du, T. Wan, B. Qu, F.Y. Cao, Q.R. Lin, N. Chen, X. Lin, D.W. Chu, Engineering silver nanowire networks: from transparent electrodes to resistive switching devices. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 9, 20762–20770 (2017)
L. Zeng, T.S. Zhao, L. An, A high-performance supportless silver nanowire catalyst for anion exchange membrane fuel cells. J. Mater. Chem. A 3, 1410–1416 (2015)
R.R. da Silva, M.X. Yang, S.-I. Choi, M.F. Chi, M. Luo, C. Zhang, Z.Y. Li, P.H.C. Camargo, S.J.L. Ribeiro, Y.N. Xia, Facile synthesis of sub-20 nm silver nanowires through a bromide-mediated Polyol method. ACS Nano 10, 7892–7900 (2016)
B. Li, S.G. Ye, I.E. Stewart, S. Alvarez, B.J. Wiley, Synthesis and purification of silver nanowires to make conducting films with a transmittance of 99%. Nano Lett. 15, 6722–6726 (2015)
W.P. Zhou, A.M. Hu, S. Bai, Y. Ma, D. Bridges, Anisotropic optical properties of large-scale aligned silver nanowire films via controlled coffee ring effects. RSC Adv. 5, 39103–39109 (2015)
E.J. Lee, M.H. Chang, Y.S. Kim, J.Y. Kim, High-pressure polyol synthesis of ultrathin silver nanowires: electrical and optical properties. APL Mater. 1, 042118 (2013)
T.T. Jiu, M. Nogi, T. Sugahara, T. Tokuno, T. Araki, N. Komoda, K. Suganuma, H. Uchida, K. Shinozaki, Strongly adhesive and flexible transparent silver nanowire conductive films fabricated with a high-intensity pulsed light technique. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 23561–23567 (2012)
Y.X. Jin, D.Y. Deng, Y.R. Cheng, L.Q. Kong, F. Xiao, Annealing-free and strongly adhesive silver nanowire networks with long-term reliability by introduction of a nonconductive and biocompatible polymer binder. Nanoscale 6, 4812–4818 (2014)
J.P. Li, S.H. Qi, J. Li, M.Y. Zhang, Z.F. Wang, A highly thermostable and transparent lateral heat spreader based on silver nanowire/polyimide composite. RSC Adv. 5, 59398–59402 (2015)
L. Lian, D. Dong, D.X. Feng, G.F. He, Low roughness silver nanowire flexible transparent electrode by low temperature solution-processing for organic light emitting diodes. Org. Electron. 49, 9–18 (2017)
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 21761016), Young and Middle-aged Academic and Technical Leaders Reserve Talents Program of Yunnan Province (Grant No. 2017HB060), Applied Basic Research Foundation of Yunnan Province (Grant Nos. 2016FD126, 2017FB142), Major R&D Project of Yunnan Province (Grant No. 2018ZE001), Research Foundation of Key New Products of Yunnan Province (Grant No. 2016BA007), and Research Foundation of Institute of Yunnan Province (Grant No. 2016DC033).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, Y., Yuan, X., Yang, H. et al. Solvothermal synthesis of ultra-fine silver nanowires with a diameter about 20 nm and an aspect ratio approximately 2000 for highly conductive flexible transparent film. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 8883–8891 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01216-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-01216-0