Abstract
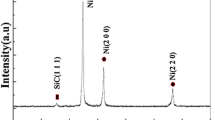
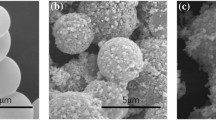
Microporous Co@TiO2 nanoparticles (NPs) have been synthesized by combining chemical de-alloying and sol–gel strategies. The NPs with a mean size of 30 nm display a TiO2 shell of 5 nm in thickness and possess micropores in a range from 0.4 to 0.8 nm. The saturation magnetization (MS) and coercivity (HC) of the NPs are 18.6 emu/g and 337.4 Oe, respectively. The microwave absorption properties of the microporous Co@TiO2 NPs mixed with paraffin were investigated in the range of 2–18 GHz. Due to the relatively high dielectric loss tangent value and low magnetic loss tangent value, the impedance matching of the composite is better than the nonporous counterpart. The composite shows a minimum reflection loss (RL) of − 16.6 dB at a thickness of merely 2.2 mm, and the absorption bandwidth for RL ≤ − 10 dB is as large as 5.0 GHz. At a thickness of 1.9 mm, the maximum absorption bandwidth for RL ≤ − 10 dB of 6.8 GHz can be obtained, which is much larger than that of its nonporous counterpart. Furthermore, the microwave absorption mechanism is discussed on the basis of the synergistic influence of micropores and TiO2 shell. This study provides a good reference for designing novel materials for electromagnetic interference applications.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
D.D.L. Chung, Electromagnetic interference shielding effectiveness of carbon materials. Carbon 39, 279–285 (2001)
S. Ghosh, S. Ganguly, S. Remanan, S. Mondal, S. Jana, P.K. Maji, N. Singha, N.C. Das, Ultra-light weight, water durable and flexible highly electrical conductive polyurethane foam for superior electromagnetic interference shielding materials. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 29, 10177–10189 (2018)
B. Wen, M. Cao, M. Lu, W. Cao, H. Shi, J. Liu, X. Wang, H. Jin, X. Fang, W. Wang, Reduced graphene oxides: light-weight and high-efficiency electromagnetic interference shielding at elevated temperatures. Adv. Mater. 26, 3484–3489 (2014)
Z. Peng, W. Jiang, Y. Wang, S. Zhong, Synthesis and microwave absorption properties of Fe3O4@BaTiO3/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 1304 (2016)
T. Liu, Y. Pang, X. Xie, W. Qi, Y. Wu, S. Kobayashi, J. Zheng, X. Li, Synthesis of microporous Ni/NiO nanoparticles with enhanced microwave absorption properties. J. Alloys Compd. 667, 287–296 (2016)
Y. Qing, W. Zhou, F. Luo, D. Zhu, Epoxy-silicone filled with ulti-walled carbon nanotubes and carbonyl iron particles as a microwave absorber. Carbon 48, 4074–4080 (2010)
X. Tang, B.Y. Zhao, Q. Tian, K.A. Hu, Synthesis, characterization and microwave absorption properties of titania-coated barium ferrite composites. J. Phys. Chem. Solids 67, 2442–2447 (2006)
Z. Ma, Q. Liu, J. Yuan, Z. Wang, C. Cao, J. Wang, Analyses on multiple resonance behaviors and microwave reflection loss in magnetic Co microflowers. Phys. Status Solidi 249, 575–580 (2012)
G. Tong, J. Yuan, W. Wu, Q. Hu, H. Qian, L. Li, J. Shen, Flower-like Co superstructures: morphology and phase evolution mechanism and novel microwave electromagnetic characteristics. Crystengcomm 14, 2071–2079 (2012)
J. Kong, F. Wang, X. Wan, J. Liu, M. Itoh, K.I. Machida, Template-free synthesis of Co nanoporous structures and their electromagnetic wave absorption properties. Mater. Lett. 78, 69–71 (2012)
J. Li, J. Huang, Y. Qin, F. Ma, Magnetic and microwave properties of cobalt nanoplatelets. Mater. Sci. Eng. B 138, 199–204 (2007)
C. He, S. Qiu, X. Wang, J. Liu, L. Luan, W. Liu, M. Itoh, K. Machida, Facile synthesis of hollow porous cobalt spheres and their enhanced electromagnetic properties. J. Mater. Chem. 22, 22160–22166 (2012)
Y. Lü, Y. Wang, H. Li, Y. Lin, Z.Y. Jiang, Z. Xie, Q. Kuang, L.S. Zheng, MOF-derived porous Co/C nanocomposites with excellent electromagnetic wave absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 13604 (2015)
H. Lv, X. Liang, G. Ji, H. Zhang, Y. Du, Porous three-dimensional flower-like Co/CoO and its excellent electromagnetic absorption properties. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 7, 9776 (2015)
A.C. Johnstonpeck, J. Wang, J.B. Tracy, Synthesis and structural and magnetic characterization of Ni(core)/NiO(shell) nanoparticles. ACS Nano 3, 1077–1084 (2009)
T. Liu, Y. Pang, H. Kikuchi, Y. Kamada, S. Takahashi, Superparamagnetic property and high microwave absorption performance of FeAl@(Al, Fe)2O3 nanoparticles induced by surface oxidation. J. Mater. Chem. C 3, 6232–6239 (2015)
F. Ren, G. Zhu, P. Ren, K. Wang, X. Cui, X. Yan, Cyanate ester resin filled with graphene nanosheets and CoFe2O4-reduced graphene oxide nanohybrids as a microwave absorber. Appl. Surf. Sci. 351, 40–47 (2015)
M. Yu, C. Liang, M. Liu, X. Liu, K. Yuan, H. Cao, R. Che, Yolk-shell Fe3O4@ZrO2 prepared by a tunable polymer surfactant assisted sol-gel method for high temperature stable microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 2, 7275–7283 (2014)
B. Yang, Z. Wu, Z. Zou, R. Yu, High-performance Fe/SiO2 soft magnetic composites for low-loss and high-power applications. J. Phys. D Appl. Phys. 43, 365003–365008 (2010)
X.L. Dong, X.F. Zhang, H. Huang, F. Zuo, Enhanced Microwave Absorption in Ni/Polyaniline Nanocomposites by Dual Dielectric Relaxations. Appl. Phys. Lett. 92, 301 (2008)
B. Zhao, G. Shao, B. Fan, W. Zhao, R. Zhang, Investigation of the electromagnetic absorption properties of Ni@TiO2 and Ni@SiO2 composite microspheres with core-shell structure. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 17, 2531 (2015)
Q. Liu, Q. Cao, H. Bi, C. Liang, K. Yuan, W. She, Y. Yang, R. Che, CoNi@SiO2 @TiO2 and CoNi@Air@TiO2 Microspheres with Strong Wideband Microwave Absorption. Adv. Mater. 28, 486 (2016)
A. Kumar, V. Agarwala, D. Singh, Microwave absorbing behavior of metal dispersed TiO2, nanocomposites. Adv. Power Technol. 25, 483–489 (2014)
M.J. Molaei, M.R. Rahimipour, Microwave reflection loss of magnetic/dielectric nanocomposites of BaFe12O19/TiO2. Mater. Chem. Phys. 167, 145–151 (2015)
Z. Yang, F. Luo, Y. Hu, S. Duan, D. Zhu, W. Zhou, Dielectric and microwave absorption properties of TiO2/Al2O3, coatings and improved microwave absorption by FSS incorporation. J. Alloys Compd. 678, 527–532 (2016)
X. Zhang, G. Ji, W. Liu, X. Zhang, Q. Gao, Y. Li, Y. Du, A Novel Co/TiO2 nanocomposite derived from metal-organic framework: synthesis and efficient microwave absorption. J. Mater. Chem. C 4, 1860–1870 (2016)
J. Liu, R. Che, H. Chen, F. Zhang, F. Xia, Q. Wu, M. Wang, Microwave absorption enhancement of multifunctional composite microspheres with Spinel Fe3O4 cores and anatase TiO2 shells. Small 8, 1214–1221 (2012)
Y. Huang, Y. Wang, Z. Li, Z. Yang, C. Shen, C. He, Effect of pore morphology on the dielectric properties of porous carbons for microwave absorption applications. J. Phys. Chem. C 118, 26027–26032 (2014)
D. Sun, Q. Zou, Y. Wang, Y. Wang, W. Jiang, F. Li, Controllable synthesis of porous Fe3O4@ZnO sphere decorated graphene for extraordinary electromagnetic wave absorption. Nanoscale 6, 6557–6562 (2014)
X.B. Xie, M. Chen, M.M. Hu, T. Liu, Recoverable Ni2Al3 nanoparticles and their catalytic effects on Mg-based nanocomposite during hydrogen absorption and desorption cycling. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 43, 21856–21863 (2018)
M. Oezaslan, F. Hasché, P. Strasser, In situ observation of bimetallic alloy nanoparticle formation and growth using high-temperature XRD. Chem. Mater. 23, 2159–2165 (2011)
M. Oezaslan, M. Heggen, P. Strasser, Size-dependent morphology of de-alloyed bimetallic catalysts: linking the nano to the macro scale. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 134, 514–524 (2012)
T. Liu, T. Zhang, M. Zhu, C. Qin, Synthesis and structures of Al–Ti nanoparticles by hydrogen plasma-metal reaction. J. Nanopart. Res. 14, 1–8 (2012)
T. Liu, Y. Pang, M. Zhu, S. Kobayashi, Microporous Co@CoO nanoparticles with superior microwave absorption properties. Nanoscale 6, 2447 (2014)
R. Zha, R. Nadimicherla, X. Guo, Cadmium removal in waste water by nanostructured TiO2 particles. J. Mater. Chem. A 2, 13932–13941 (2014)
C. Chen, Q. Liu, H. Bi, W.B. You, W. She, R. Che, Fabrication of hierarchical TiO2 coating Co20Ni80 particle with tunable core size as high-performance wide-band microwave absorber. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 18, 26712–26718 (2016)
R.P. Buck, E. Lindner, IUPAC recommendations for nomenclature of ion-selective electrodes. Pure Appl. Chem. 66, 2527–2536 (1994)
T. Xia, C. Zhang, N.A. Oyler, X. Chen, Hydrogenated TiO2 nanocrystals: a novel microwave absorbing material. Adv. Mater. 25, 6905–6910 (2013)
R.C. Che, L.M. Peng, X.F. Duan, Q. Chen, X.L. Liang, Microwave absorption enhancement and complex permittivity and permeability of Fe encapsulated within carbon nanotubes. Adv. Mater. 16, 401–405 (2004)
J. Xiang, Y. Chu, X. Zhang, X. Shen, Magnetic and microwave absorption properties of electrospun Co0.5Ni0.5Fe2O4 nanofibers. Appl. Surf. Sci. 263, 3320–3325 (2012)
X.L. Shi, M.S. Cao, J. Yuan, X.Y. Fang, Dual nonlinear dielectric resonance and nesting microwave absorption peaks of hollow cobalt nanochains composites with negative permeability. Appl. Phys. Lett. 95, 477 (2009)
G. Zheng, X. Yin, S. Liu, X. Liu, J. Deng, Q. Li, composite ceramics with multi-shell microstructure. J. Eur. Ceram. Soc. 33, 2173–2180 (2013)
Y.J. Chen, P. Gao, C.L. Zhu, R.X. Wang, Synthesis, magnetic and electromagnetic wave absorption properties of porous Fe3O4/Fe/SiO2, core/shell nanorods. J. Appl. Phys. 106, 054303–054304 (2009)
Y. Du, W. Liu, Q. Rong, W. Ying, X. Han, J. Ma, X. Ping, Shell thickness-dependent microwave absorption of core-shell Fe3O4@C composites. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces 6, 12997 (2014)
S. He, G.S. Wang, C. Lu, J. Liu, B. Wen, H. Liu, L. Guo, M.S. Cao, Enhanced wave absorption of nanocomposites based on the synthesized complex symmetrical CuS nanostructure and poly(vinylidene fluoride). J. Mater. Chem. A 1, 4685–4692 (2013)
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the support of this work by the Joint Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Baosteel Group Corporation (No. U1560106), the Aeronautical Science Foundation of China (No. 2016ZF51050) and the Scientific Research Foundation for the Returned Overseas Chinese Scholars (State Education Ministry).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liao, H., Pang, Y., Li, D. et al. Synergistic influence of micropore architecture and TiO2 coating on the microwave absorption properties of Co nanoparticles. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 5620–5630 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00855-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00855-7