Abstract
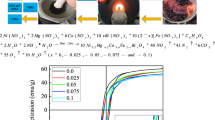
Bismuth doped Ni–Cu–Co nano ferrites with the chemical composition Ni0.2Cu0.2Co0.6Fe2−xBixO4 (x = 0.0, 0.025, 0.05, 0.075, 0.1) were prepared by sol–gel auto-combustion technology. The analysis of the X-ray diffraction (XRD) patterns confirms that all the samples have a cubic spinel structure. The particle sizes of the prepared samples (between 51 and 55 nm) are determined by the Scherrer equation. The obtained Fourier transform infrared measurement also confirms the formation of the spinel structure. It was observed that with the increase of Bi3+ ion concentration, the protruding absorption band was slightly shifted to the high frequency side. Transmission electron microscopy images show the presence of particles which are spherically cubic shaped crystallites. It has been proved that the synthesized ferrite has pure phase and structure by Energy dispersive X-ray, and Bi3+-doping was successfully achieved. Cation redistribution in spinel ferrite nanoparticles are confirmed by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS). The magnetic parameters of the samples are measured by Vibration sample magnetometer (VSM) at room temperature with a maximum magnetic field of 1 T. It can be clearly observed that the magnetic properties such as saturation magnetization (Ms), remanent magnetization (Mr) and coercivity (Hc) decrease significantly with the bismuth ion concentration increases. This is because Bi3+ ions replace Fe3+ ions, and Bi3+–Fe3+ ion interactions are more predominates than Fe2+–Fe3+ ion interactions. This also indicates that the bismuth doped nickel copper cobalt ferrite has low magnetic properties.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. Pallai, D.O. Shah, Synthesis of high coercivity cobalt ferrite particles using water-in-oil microemulsions. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 163, 243–248 (1996)
S. Kumar, T.J. Shinde, P.N. Vasambekar, Microwave synthesis and characterization of nano crystalline Mn-Zn Ferrites. Adv. Mater. Lett. 4, 373–377 (2013)
G. Dixit, J.P. Singh, R.C. Srivastava, H.M. Agrawal, R.J. Chaudhary, Structural, magnetic and optical studies of nickel ferrite thin films. Adv. Mater. Lett. 3, 21–28 (2012)
T. Giannakopoulou, L. Kompotiatis, A. Kontogeorgakos, G. Kordas, Microwave behavior of ferrites prepared via sol-gel method. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 246, 360–365 (2002)
G.A. Sawatzky, F.V.D. Woude, A.H. Morrish, Cation distributions in octahedral and tetrahedral sites of the ferrimagnetic spinel CoFe2O4.. J. Appl. Phys. 39, 1204–1205 (1968)
S.M. Asgarian, S. Pourmasoud, Z. Kargar, A. Sobhani-Nasab, M. Eghbali-Arani, Investigation of positron annihilation lifetime and magnetic properties of Co1 – xCuxFe2O4 nanoparticles. Mater. Res. Express. 6, 15023 (2019)
L.D. Tung, V.L. Kolesnichenko, D. Caruntu, N.H. Chou, C.J. O’Connor, C.J.L. Spinu, Magnetic properties of ultrafine cobalt ferrite particles. J. Appl. Phys. 93, 7486–7488 (2003)
A. Sobhani-Nasab, A. Ziarati, M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.R. Ganjali, A. Badiei, Five-component domino synthesis of tetrahydropyridines using hexagonal PbCrxFe12–xO19 as efficient magnetic nanocatalyst. Res. Chem. Intermediat. 43, 6155–6165 (2017)
A. Ziarati, A. Sobhani-Nasab, M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M.R. Ganjali, A. Badiei, Sonication method synergism with rare earth based nanocatalyst: preparation of NiFe2 – xEuxO4 nanostructures and its catalytic applications for the synthesis of benzimidazoles, benzoxazoles, and benzothiazoles under ultrasonic irradiation. J. Rare Earths 35, 374–381 (2017)
J. Amighian, M. Mozaffari, B. Nasr, Preparation of nano-sized manganese ferrite (MnFe2O4) via co-precipitation method. Phys. Status Solidi C 3, 3188–3192 (2011)
S. Uday Bhasker et al., Preparation and characterization of cobalt magnesium nano ferrites using auto-combustion method. Adv. Mater. Res. 584, 280–284 (2012)
N. Ranvah, Y. Melikhov, I.C. Nlebedim, D.C. Jiles, J.E. Snyder, A.J. Moses, P.I. Williams, Temperature dependence of magnetic anisotropy of germanium/cobalt cosubstituted cobalt ferrite. J. Appl. Phys. 105, 5181–5183 (2009)
J.A. Paulsen, C.C.H. Lo, J.E. Snyder, A.P. Ring, L.L. Jones, D.C. Jiles, Study of the curie temperature of cobalt ferrite based composites for stress sensor applications. IEEE. Trans. Magn. 39, 3316–3318 (2003)
M. Srivastava, A.K. Ojha, S. Chaubey, P.K. Sharma, A.C. Pandey, Influence of pH on structural morphology and magnetic properties of ordered phase cobalt doped lithium ferrites nanoparticles synthesized by sol–gel method. Sci. Eng. B. 175, 14–21 (2010)
A.T. Raghavendar, D. Pajic, K. Zadro, T. Milekovic, P.V. Rao, K.M. Jadhav, D. Ravinder, Synthesis and magnetic properties of NiFe2–xAlxO4 nanoparticles. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 316, 1–7 (2007)
J. Jing, L. Liangchao, X. Feng, Structural analysis and magnetic properties of Gd-doped Li–Ni ferrites prepared using rheological phase reaction. J. Rare Earths 25, 79–83 (2007)
G. Chandrasekaran, S. Selvandan, K. Manivannane, Electrical and FTIR studies on Al substituted Mn–Zn mixed ferrites. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 15, 15–18 (2004)
S. Anjum, A. Rashid, F. Bashir, S. Riaz, M. Pervaiz, R. Zia, Effect of Cu-doped nickel ferrites on structural, magnetic, and dielectric properties. Mater. Today Proc. 2, 5559–5567 (2015)
M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Behpour, A. Sobhani-Nasab, S.M. Hosseinpour-Mashkani, ZnFe2–xLaxO4 nanostructure: synthesis, characterization, and its magnetic properties. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 26, 9776–9781 (2015)
K. Siraj, M. Khaleeq-ur-Rahman, S.I. Hussain, M.S. Rafique, S. Anjum, Effect of deposition temperature on structural, surface, optical and magnetic properties of pulsed laser deposited Al-doped CdO thin films. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 6756–6762 (2011)
R. Arulmurugan, B. Jeyadevan, G. Vaidyanathan, S. Sendhilnathan, Effect of zinc substitution on Co–Zn and Mn–Zn ferrite nanoparticles prepared by coprecipitation. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 288, 470–477 (2005)
K. Praveena, B. Radhika, S. Srinath, Dielectric and magnetic properties of NiFe2–xBixO4 nanoparticles at microwave frequencies prepared via co-precipitation method. Procedia Eng. 76, 1–7 (2014)
I.P. Muthuselvam, R.N. Bhowmik, Mechanical alloyed Ho3+ doping in CoFe2O4 spinel ferrite and understanding of magnetic nanodomains. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 767–776 (2010)
H.M. Zaki, H.A. Dawoud, Far-Infrared spectra for copper–zinc mixed ferrites. Physica B. 405, 4476–4479 (2010)
R.C. Kambale, K.M. Song, Y.S. Koo, N. Hur, Low temperature synthesis of nano crystalline Dy3+ doped cobalt ferrite: structural and magnetic properties. J. Appl. Phys. 110, 535 (2011)
M. Srivastava, S. Chaubey, A.K. Ojha, Investigation on size dependent structural and magnetic behavior of nickel ferrite nanoparticles prepared by sol-gel and hydrothermal methods. Mater. Chem. Phys. 118, 174–180 (2009)
Z. Yang, Z. Ye, Z. Xu, B. Zhao, Effect of the morphology on the optical properties of ZnO nanostructures. Physica E. 42, 116–119 (2010)
A. Gholizadeh, E. Jafari, Effects of sintering atmosphere and temperature on structural and magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Zn ferrite nano-particles: magnetic enhancement by a reducing atmosphere. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 422, 328–336 (2017)
M.M. Eltabey, K.M. El-Shokrofy, S.A. Gharbia, Enhancement of the magnetic properties of Ni–Cu–Zn ferrites by the non-magnetic Al3+-ions substitution. J. Alloys Compd. 509, 2473–2477 (2011)
M. Rahimi-Nasrabadi, M. Behpour, A. Sobhani-Nasab, M.R. Jeddy, Nanocrystalline Ce-doped copper ferrite: synthesis, characterization, and its photocatalyst application. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 27, 11691–11697 (2016)
K. Nakamoto, Infrared and raman spectra of inorganic and coordination compounds, part A and part B, Two Volume Set, 6th edn. Sex. Transm. Infect. 85, 182–186 (2008)
U.B. Gawas, V.M.S. Verenkar, S.R. Barman, S.S. Meena, P. Bhatt, Synthesis of nanosize and sintered Mn0.3Ni0.3Zn0.4Fe2O4 ferrite and their structural and dielectric studies. J. Alloys Compd. 555, 225–231 (2013)
R.S. Yadav, I. Kuřitka, J. Vilcakova, J. Havlica, J. Masilko, L. Kalina et al., Structural, dielectric, electrical and magnetic properties of CuFe2O4 nanoparticles synthesized by honey mediated sol–gel combustion method and annealing effect. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 6245–6261 (2017)
R.S. Yadav, I. Kuřitka, J. Vilcakova, J. Havlica, L. Kalina et al., Influence of La3+ on structural, magnetic, dielectric, electrical and modulus spectroscopic characteristics of single phase CoFe2–xLaxO4 nanoparticles. J. Mater. Sci. Mater. Electron. 28, 9139–9154 (2017)
Y. Kang, L. Wang, Y. Wang, H. Zhang, Y. Wang, D. Hong, Y. Qv, S. Wang, Construction and enhanced gas sensing performances of CuO-modified α-Fe2O3 hybrid hollow spheres. Sensors Actuators B. 177, 570–576 (2013)
L. Zhang, J. Zhao, H. Lu, L. Gong, L. Li, J. Zheng, H. Li, Z. Zhu, High sensitive and selective formaldehyde sensors based on nanoparticle-assembled ZnO micro-octa-hedrons synthesized by homogeneous precipitation method. Sensors Actuators B. 160, 364–370 (2011)
S. Singhal, S. Jauhar, N. Lakshmi, S. Bansal, Mn3+ substituted Co-Cd ferrites, CoCd0.4MnxFe1.6–xO4 (0.1 ≤ x ≤ 0.6): cation distribution, structural, magnetic and electrical properties. J. Mol. Struct. 1038, 45–51 (2013)
A. Miller, Distribution of cations in spinels. J. Appl. Phys. 30, S24–S25 (1959)
S. Singhal, S. Jauhar, Investigation of structural, magnetic, electrical and optical properties of chromium substituted cobalt ferrites (CoCrxFe2–xO4, 0 ≤ x ≤ 1) synthesized using sol gel auto combustion method. J. Mol. Struct. 1012, 182–188 (2012)
S. Singhal, S.K. Barthwal, K. Chandra, XRD, magnetic and mössbauer spectral studies of nano size aluminum substituted cobalt ferrites (CoAlxFe2–xO4). J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 306, 233–240 (2006)
A.V. Raut, R.S. Barkule, D.R. Shengule, K.M. Jadhav, Synthesis, structural investigation and magnetic properties of Zn2+ substituted cobalt ferrite nanoparticles prepared by the sol-gel auto-combustion technique. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 358, 87–92 (2014)
T. Ibusuki, S. Kojima, O. Kitakami, Y. Shimada, Magnetic anisotropy and behaviors of Fe nanoparticles. IEEE. Trans. Magn. 37, 2223–2225 (2001)
L. Néel, Magnetic properties of ferrites: ferrimagnetism and antiferromagnetism. Ann. Phys. 3, 137–198 (1948)
N.K. Dung, N.H. Tuan, The effect of cobalt substitution on structure and magnetic properties of nickel ferrite. J. Sci. Math. Phys. 25, 153–159 (2009)
S. Bhukal, T. Namgyal, S. Mor, S. Bansal, S. Singhal, Structural, electrical, optical and magnetic properties of chromium substituted Co-Zn nanoferrites Co0.6Zn0.4CrxFe2–xO4 (0 ≤ x ≤ 1.0) prepared via sol–gel Au-to-combustion method. J. Mol. Struct. 1012, 162–167 (2012)
J.S. Smart, The Néel theory of ferrimagnetism. Am. J. Phys. 23, 356–370 (2005)
P.A. Shaikh, R.C. Kambale, A.V. Rao, Y.D. Kolekar, Effect of Ni doping on structural and magnetic properties of Co1–xNixFe1.9Mn0.1O4. J. Magn. Magn. Mater. 322, 718–726 (2010)
J.M.D. Coey, Rare earth-iron permanent magnets. ChemInform. 23 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1002/chin.199211311
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pan, X., Sun, A., Han, Y. et al. Structural and magnetic properties of Bi3+ ion doped Ni–Cu–Co nano ferrites prepared by sol–gel auto combustion method. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron 30, 4644–4657 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00757-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-019-00757-8