Abstract
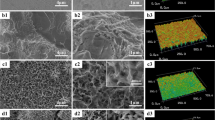
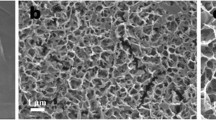
Surface morphology of titanium (Ti) implants plays an important role in regulating cell behaviors at the interface. The purpose of our study was to investigate the effect of surface structures from microscale to nanoscale on the proliferation and differentiation of precursor osteoblasts. Sandblasting and acid etching and anodic oxidation were used to fabricate the micro-structure and nano-structure on Ti surface. Physical properties including surface topography, roughness and wettability were measured by scanning electron microscopy, laser scanning microscopy and contact angle goniometry, respectively. The bioactivity and cytocompatibility of different surface morphology were investigated in vitro. The results showed that the hierarchical micro-/nano-structured surface composed of micro-valleys and self-assembly nanotubes was successfully constructed on the substrate of Ti. The hydrophilicity of the micro-/nano-structured surface was significantly heightened in comparison with the polished surface, micro-structured surface and nano-structured surface. Moreover, a compact layer of hydroxyapatite was observed on the micro-/nano-structured surface after immersing in simulated body fluid for 14 days. Higher proliferation rate and alkaline phosphatases activity as well as enhanced biomineralization were also verified on the hierarchically structured surface. All results indicated that the integration of multiscale structures of micro-valleys and nanotubes can provide a better surrounding microenvironment to improve cell sensitivities and promote the cell proliferation and differentiation.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Zhao D, Witte F, Lu F, Wang J, Li J, Qin L (2017) Current status on clinical applications of magnesium-based orthopaedic implants: a review from clinical translational perspective. Biomaterials 112:287–302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2016.10.017
Geetha M, Singh AK, Asokamani R, Gogia AK (2009) Ti based biomaterials, the ultimate choice for orthopaedic implants—a review. Prog Mater Sci 54(3):397–425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmatsci.2008.06.004
Kaczmarek M, Jurczyk K, Koper JK, Paszel-Jaworska A, Romaniuk A, Lipińska N, Żurawski J, Urbaniak P, Jakubowicz J, Jurczyk MU (2016) In vitro biocompatibility of anodized titanium with deposited silver nanodendrites. J Mater Sci 51(11):5259–5270. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-9829-3
Mishnaevsky L, Levashov E, Valiev RZ, Segurado J, Sabirov I, Enikeev N, Prokoshkin S, Solov’yov AV, Korotitskiy A, Gutmanas E, Gotman I, Rabkin E, Psakh’e S, Dluhoš L, Seefeldt M, Smolin A (2014) Nanostructured titanium-based materials for medical implants: modeling and development. Mater Sci Eng R Rep 81:1–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mser.2014.04.002
Sharmin N, Rudd CD (2017) Structure, thermal properties, dissolution behaviour and biomedical applications of phosphate glasses and fibres: a review. J Mater Sci 52(15):8733–8760. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-017-0784-4
Kokubo T, Yamaguchi S (2016) Novel bioactive materials developed by simulated body fluid evaluation: surface-modified Ti metal and its alloys. Acta Biomater 44:16–30. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2016.08.013
Li G, Cao H, Zhang W, Ding X, Yang G, Qiao Y, Liu X, Jiang X (2016) Enhanced osseointegration of hierarchical micro/nanotopographic titanium fabricated by microarc oxidation and electrochemical treatment. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 8(6):3840–3852. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.5b10633
Wang Y, Lou J, Zeng L, Xiang J, Zhang S, Wang J, Xiong F, Li C, Zhao Y, Zhang R (2017) Osteogenic potential of a novel microarc oxidized coating formed on Ti6Al4 V alloys. Appl Surf Sci 412:29–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.03.191
Le Guehennec L, Soueidan A, Layrolle P, Amouriq Y (2007) Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid osseointegration. Dent Mater off Pub Acad Dent Mater 23(7):844–854. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2006.06.025
Chu S-F, Huang M-T, Ou K-L, Sugiatno E, Cheng H-Y, Huang Y-H, Chiu W-T, Liou T-H (2016) Enhanced biocompatible and hemocompatible nano/micro porous surface as a biological scaffold for functionalizational and biointegrated implants. J Alloy Compd 684:726–732. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.05.134
Rautray TR, Narayanan R, Kwon TY, Kim KH (2010) Surface modification of titanium and titanium alloys by ion implantation. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 93(2):581–591. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.31596
Zhao X, Peng C, You J (2017) Plasma-sprayed ZnO/TiO2 coatings with enhanced biological performance. J Therm Spray Technol 26(6):1301–1307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11666-017-0573-2
Liang J, Song R, Huang Q, Yang Y, Lin L, Zhang Y, Jiang P, Duan H, Dong X, Lin C (2015) Electrochemical construction of a bio-inspired micro/nano-textured structure with cell-sized microhole arrays on biomedical titanium to enhance bioactivity. Electrochim Acta 174:1149–1159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2015.06.100
Peng L, Zhou S, Yang B, Bao M, Chen G, Zhang X (2017) Chemically modified surface having a dual-structured hierarchical topography for controlled cell growth. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 9(28):24339–24347. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.7b06197
Jeon H, Simon CG Jr, Kim G (2014) A mini-review: cell response to microscale, nanoscale, and hierarchical patterning of surface structure. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater 102(7):1580–1594. https://doi.org/10.1002/jbm.b.33158
Schneider GB, Perinpanayagam H, Clegg M, Zaharias R, Seabold D, Keller J, Stanford C (2017) Implant Surface Roughness Affects Osteoblast Gene Expression. J Dent Res 82(5):372–376. https://doi.org/10.1177/154405910308200509
Park JYGCH, Davies JE (2001) Platelet interactions with titanium: modulation of platelet activity by surface topography. Biomaterials 22(19):2671–2682
Stevens M (2005) Exploring and engineering the cell surface interface. Science 310:1135–1138
Leijten J, Khademhosseini A (2016) From nano to macro: multiscale materials for improved stem cell culturing and analysis. Cell Stem Cell 18(1):20–24. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.stem.2015.12.013
Yao X, Peng R, Ding J (2013) Cell-material interactions revealed via material techniques of surface patterning. Adv Mater 25(37):5257–5286. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201301762
Rani VV, Vinoth-Kumar L, Anitha VC, Manzoor K, Deepthy M, Shantikumar VN (2012) Osteointegration of titanium implant is sensitive to specific nanostructure morphology. Acta Biomater 8(5):1976–1989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2012.01.021
Hori N, Iwasa F, Ueno T, Takeuchi K, Tsukimura N, Yamada M, Hattori M, Yamamoto A, Ogawa T (2010) Selective cell affinity of biomimetic micro-nano-hybrid structured TiO2 overcomes the biological dilemma of osteoblasts. Dent Mater off Publ Acad Dent Mater 26(4):275–287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dental.2009.11.077
Wang G, Wan Y, Ren B, Wang T, Liu Z (2017) Surface functionalization of micro/nanostructured titanium with bioactive ions to regulate the behaviors of murine osteoblasts. Adv Eng Mater 19:1700299. https://doi.org/10.1002/adem.201700299
Gittens RA, Olivares-Navarrete R, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD (2014) Implant osseointegration and the role of microroughness and nanostructures: lessons for spine implants. Acta Biomater 10(8):3363–3371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2014.03.037
Huang J, Zhang X, Yan W, Chen Z, Shuai X, Wang A, Wang Y (2017) Nanotubular topography enhances the bioactivity of titanium implants. Nanomed Nanotechnol Biol Med 13(6):1913–1923. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nano.2017.03.017
Moon S-K, Kwon J-S, Uhm S-H, Lee E-J, Gu H-J, Eom T-G, Kim K-N (2014) Biological evaluation of micro–nano patterned implant formed by anodic oxidation. Curr Appl Phys 14:S183–S187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cap.2013.12.030
Alves SA, Ribeiro AR, Gemini-Piperni S, Silva RC, Saraiva AM, Leite PE, Perez G, Oliveira SM, Araujo JR, Archanjo BS, Rodrigues ME, Henriques M, Celis JP, Shokuhfar T, Borojevic R, Granjeiro JM, Rocha LA (2017) TiO2 nanotubes enriched with calcium, phosphorous and zinc: promising bio-selective functional surfaces for osseointegrated titanium implants. RSC Adv 7(78):49720–49738. https://doi.org/10.1039/c7ra08263k
Park JBS, Mark KVD et al (2007) Nanosize and vitality: TiO2 nanotube diameter directs cell fate. Nano Lett 7(6):1686
Bauer S, Park J, von der Mark K, Schmuki P (2008) Improved attachment of mesenchymal stem cells on super-hydrophobic TiO2 nanotubes. Acta Biomater 4(5):1576–1582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2008.04.004
Rosales-Leal JI, Rodríguez-Valverde MA, Mazzaglia G, Ramón-Torregrosa PJ, Díaz-Rodríguez L, García-Martínez O, Vallecillo-Capilla M, Ruiz C, Cabrerizo-Vílchez MA (2010) Effect of roughness, wettability and morphology of engineered titanium surfaces on osteoblast-like cell adhesion. Coll Surf A 365(1–3):222–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2009.12.017
Gittens RA, Scheideler L, Rupp F, Hyzy SL, Geis-Gerstorfer J, Schwartz Z, Boyan BD (2014) A review on the wettability of dental implant surfaces II: biological and clinical aspects. Acta Biomater 10(7):2907–2918. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.actbio.2014.03.032
Faucheux N, Schweiss R, Lutzow K, Werner C, Groth T (2004) Self-assembled monolayers with different terminating groups as model substrates for cell adhesion studies. Biomaterials 25(14):2721–2730. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2003.09.069
Lee JH, Khang G, Lee JW, Lee HB (1998) Interaction of different types of cells on polymer surfaces with wettability gradient. J Colloid Interface Sci 205(2):323–330
Kokubo T, Takadama H (2006) How useful is SBF in predicting in vivo bone bioactivity? Biomaterials 27(15):2907–2915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biomaterials.2006.01.017
Shen X, Ma P, Hu Y, Xu G, Zhou J, Cai K (2015) Mesenchymal stem cell growth behavior on micro/nano hierarchical surfaces of titanium substrates. Coll Surf B 127:221–232. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2015.01.048
Wang T, Wan Y, Liu Z (2016) Fabrication of hierarchical micro/nanotopography on bio-titanium alloy surface for cytocompatibility improvement. J Mater Sci 51(21):9551–9561. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-016-0219-7
Yao S, Jin B, Liu Z, Shao C, Zhao R, Wang X, Tang R (2017) Biomineralization: from Material Tactics to Biological Strategy. Adv Mater 29(14):1605903. https://doi.org/10.1002/adma.201605903
Acknowledgement
This project was funded by National Natural Science Foundation of China [Grant Number 51575320] and Taishan Scholar Foundation [Grant Number TS20130922].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ren, B., Wan, Y., Wang, G. et al. Morphologically modified surface with hierarchical micro-/nano-structures for enhanced bioactivity of titanium implants. J Mater Sci 53, 12679–12691 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2554-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-018-2554-3