Abstract
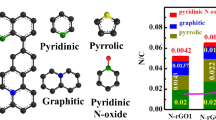
The electronic and chemical properties of reduced graphene oxide (RGO) can be modulated by chemical doping foreign atoms and functional moieties. Nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide (N-RGO) is a promising candidate for oxygen reduction reaction (ORR) in fuel cells. However, there are still some challenges in further preparation and modification of N-RGO. In this work, a low-cost industrial material, urea, was chosen to modify RGO by a facile, catalyst-free thermal annealing approach in large scale. The obtained N-RGO, as a metal-free catalyst for oxygen reduction was characterized by XRD, XPS, Raman, SEM, TEM, and electrochemical measurements. It was found that the optimum synthesis conditions were a mass ratio of graphene oxide and urea equal to 1:10 and an annealing temperature of 800 °C. Detailed X-ray photoelectron spectrum analysis of the optimum product shows that the atomic percentage of N-RGO samples can be adjusted up to 2.6 %, and the resultant product can act as an efficient metal-free catalyst, exhibiting enhanced electrocatalytic properties for ORR in alkaline electrolytes. This simple, cost-effective, and scalable approach opens up the possibility for the synthesis of other nitrogen doping materials in gram-scale. It can be applied to various carbon materials for the development of other metal-free efficient ORR catalysts for fuel cell applications, and even new catalytic materials for applications beyond fuel cells.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nagaiah TC, Kundu S, Bron M (2010) Electrochem Commun 12:338
Ma Y, Sun L, Huang W (2011) J Phys Chem C 115:24592
Yang S, Feng X, Wang X (2011) Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 50:5339
Li H, Liu H, Jong Z (2011) Int J Hydrogen Energ 36:2258
Wang S, Yu D, Dai L (2011) J Am Chem Soc 133:5182
Wang H, Bo X, Luhana C (2011) Electrochem Commun 21:5
Xiao W, Wang D, Lou XW (2010) J Phys Chem C 114:1694
Lefe M, Dodelet JP, Bertrand P (2002) J Phys Chem B 106:8705
Ma G, Jia R, Zhao J (2011) J Phys Chem C 115:25148
Zheng B, Wang J, Wang FB (2013) Electrochem Commun 28:24
Yang Z, Yao Z, Li GF (2011) ACS Nano 6:205
Sheng ZH, Gao HL, Bao WJ (2012) J Mater Chem 22:390
Kwon OS, Park SJ, Hong JY (2012) ACS Nano 6:1486
Tsai CW, Tu MH, Chen CJ (2011) RSC Adv 1:1349
Yang SY, Chang KH, Huang YL (2012) Electrochem Commun 14:39
Sheng Z, Shao L, Chen J (2011) ACS Nano 5:4350
Lin Z, Waller G, Liu Y (2012) Adv Energy Mater 2:884
Sun Y, Wu Q, Shi G (2011) Energ Environ Sci 4:1113
Wang S, Yu D, Dai L (2011) ACS Nano 5:6202
Lee SU, Belosludov RV, Mizuseki H (2009) Small 5:1769
Qu L, Liu Y, Baek JB (2010) ACS Nano 4:1321
Liu RL, Wu DQ, Feng XL, Müllen K (2010) Angew Chem Int Ed 49:2565
Hummers WS, Offeman RB (1958) J Am Chem Soc 80:1339
Zhao B, Liu P, Jiang Y, Pan D (2012) J Power Sources 198:423
Lee KR, Lee KU, Lee JW (2010) Electrochem Commun 12:1052
Geng DS, Yang SL, Zhang Y (2011) Appl Surf Sci 257:9193
Srinivas G, Zhu YW, Piner R, Skipper N, Ellerby M, Ruoff R (2010) Carbon 48:630
Chen P, Xiao TY, Li HH (2012) ACS Nano 6:712
Mao Y, Duan H, Xu B, Zhang L (2012) Energ Environ Sci 5:7950
Zhang CZ, Hao R, Liao HB (2013) Nano Energ 2:88
Sun L, Wang L, Tian C (2012) RSC Adv 2:4498
Lin Z, Song MK, Ding Y (2012) Phys Chem Chem Phys 14:3381
Zhu S, Chen Z, Li B (2011) Electrochim Acta 56:5080
Geng DS, Liu H, Chen YG (2011) J Power Sources 196:1795
Yang W, Fellinger TP, Antonietti M (2011) J Am Chem Soc 133:206
Zhou X, Yang Z, Nie H (2011) J Power Sources 196:9970
Luo Z, Lim S, Tian Z (2011) J Mater Chem 21:8038
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the financial support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (21063014 and 21163021).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, ZJ., Xu, MW., Bao, SJ. et al. Facile preparation of nitrogen-doped reduced graphene oxide as a metal-free catalyst for oxygen reduction reaction. J Mater Sci 48, 8101–8107 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7622-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-013-7622-0