Abstract
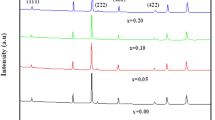
BaFe12−x Al x O19 nanofibers (x = 0–2.0) with average diameter 110 nm have been prepared via the electrospinning and subsequent heat treatment at 1100 °C for 2 h. Individual BaFe12O19 nanofibers were composed of numerous nanocrystallites stacking alternatively along the long axis of fiber and the single crystallites on each nanofibers had random orientations. With increasing Al3+ ions substitution contents from 0 to 2.0, the diameter and morphology of nanofibers were almost no change. However, the lattice parameters decreased due to Fe3+ ions substituted by smaller Al3+ ions and the average grain size calculated by the Scherrer’s equation reduced from 47 to 42 nm. The crystallites possessed a hexagonal plate-like shape at x = 0 while they became rod-like with various Al3+ ions substitution. The X-ray diffraction patterns show that single-phase barium hexaferrite was formed when Al3+ ions substitution contents were less than and equal to 1.0, while other impurity phases were detected when they were more than 1.0. The chemical analysis shows that the element Al was all incorporated into the lattice of BaFe12O19 and evenly distributed throughout the BaFe12−x Al x O19 nanofibers. The magnetic testing shows that the saturation magnetization (M s) decreased obviously from 63.92 to 29.70 A m2/kg, while coercivity (H c) increased significantly from 288.2 to 740.7 kA/m with increasing Al3+ ions substitution.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ghasemi A, Hossienpour A, Morisako A et al (2006) J Magn Magn Mater 302:429. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.10.006
Mallick KK, Shepherd P, Green RJ (2007) J Euro Ceram Soc 27:2045. doi:10.1016/j.jeurceramsoc.2006.05.098
Mu GH, Chen N, Pan XF et al (2008) Mater Lett 63:840. doi:10.1016/j.matlet.2007.06.074
Kojima H (1982) In: Wohlfarth EP (ed) Ferromagnetic materials. North Holland, Amsterdam
Parkin Stuart SP, Hayashi M, Thomas L (2008) Science 320:190. doi:10.1126/science.1145799
Žužek Rožman K, Pečko D, Šturm S et al (2012) Mater Chem Phys 133:218. doi:10.1016/j.matchemphys.2012.01.013
Li YQ, Huang Y, Li Yan (2011) Appl Surf Sci 257:8974. doi:10.1016/j.apsusc.2011.05.075
Pullar RC, Appleton SG, Bhattacharya AK (1998) J Magn Magn Mater 186:326. doi:10.1016/S0304-8853(98)00107-3
Pullar RC, Bhattacharya AK (2006) J Magn Magn Mater 300:490. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2005.06.001
Song FZ, Shen XQ, Liu MQ, Xiang J (2010) Solid State Sci 12:1603. doi:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2010.07.007
Mou FZ, Guan JG, Sun ZG et al (2010) J Solid State Chem 183:736. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2010.01.016
Li CJ, Wang B, Wang JN (2012) J Magn Magn Mater 324:1305. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2011.11.016
Zhang JL, Fu JC, Li FS et al (2012) ACS Nano 6:2273. doi:10.1021/nn204342m
Ounnunkad S (2006) Solid State Commun 138:472. doi:10.1016/j.ssc.2006.03.020
Liu Y, Drew Michael GB, Wang JP et al (2010) J Magn Magn Mater 322:366. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.09.062
Shirtcliffe NJ, Thompson S, O’Keefe ES et al (2007) Mater Res Bull 42:281. doi:10.1016/j.materresbull.2006.06.001
Liu Y, Drew Michael GB, Liu Y et al (2010) J Magn Magn Mater 322:3342. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.06.022
Atkinson R, Gerber R, Papakonstantinou P et al (1992) J Magn Magn Mater 104–107:1005. doi:10.1016/0304-8853(92)90462-W
Luo H, Rai BK, Mishra SR et al (2012) J Magn Magn Mater 324:2602. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2012.02.106
Singhal S, Namgyal T, Singh J et al (2011) Ceram Int 37:1833. doi:10.1016/j.ceramint.2011.02.001
Liu Y, Drew Michael GB, Liu Y (2011) J Magn Magn Mater 323:945. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2010.11.075
Skomski R (2003) J Phys Condens Matter 15:R841. doi:10.1088/0953-8984/15/20/202
Rezlescu L, Rezlescu E, Popa PD et al (1999) J Magn Magn Mater 193:288. doi:10.1016/S0304-8853(98)00442-9
Mali A, Ataie A (2005) Scripta Mater 53:1065. doi:10.1016/j.scriptamat.2005.06.037
Liu Y, Drew Michael GB, Liu Y et al (2010) J Magn Magn Mater 322:814. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2009.11.009
Liu MQ, Shen XQ, Song FZ et al (2011) J Solid State Chem 184:871. doi:10.1016/j.jssc.2011.02.010
Qiu JX, Zhang QG, Gu MY (2005) J Appl Phys 98:5. doi:10.1063/1.2135412
Shanker R (1990) J Mater Sci 25:2465. doi:10.1007/BF00638043
Kazin PE, Trusov LA, Zaitsev DD et al (2008) J Magn Magn Mater 320:1068. doi:10.1016/j.jmmm.2007.10.020
Tsuzuki A, Kani K, Watari K et al (1992) J Mater Sci Lett 11:893. doi:10.1007/bf00730499
Yue ZY, Zhong MJ, Ma HL et al (2008) J Shanghai Univ 12:216. doi:10.1007/s11741-008-0306-1
Dhage Vinod N, Mane ML, Keche AP (2011) Phys B 406:789. doi:10.1016/j.physb.2010.11.094
Acknowledgements
This study was partly supported by the Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Nos. 51073005, 21274006), the Beijing Natural Science Foundation (Grant Nos. 2112013, KZ201010012012), PHR (IHLB), the 973 Project (Grant No. 2010CB933501), Beijing Municipal Science and Technology Development Program (Grant No. Z111103066611004) and Textile Vision Science & Education fund.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, CJ., Huang, BN. & Wang, JN. Effect of aluminum substitution on microstructure and magnetic properties of electrospun BaFe12O19 nanofibers. J Mater Sci 48, 1702–1710 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6928-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-012-6928-7