Abstract
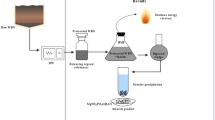
This article focuses on the effects of microwave treatment on sewage sludge with alkali addition. Both the solubilization of organic matters and the settleability of sludge were investigated. It was found that the combined treatment provided a rapid and efficient process to release organics from sludge flocs. Anaerobic digested sludge with low organic content (37%) obtained better results as compared to fresh sludge with high organic content (56%). For digested sludge, 50–70% of VSS was dissolved into a solution at 120–170 °C with a dose 0.2 g NaOH/g-DS within 5 min, and 80% of the total COD was released to supernatants. The liquor soluble COD concentration increased up to 20 g/L. Nearly 60% of nitrogen dissolved at 170 °C. For fresh sludge, solo microwave heating reduced 40% of VSS at 170 °C within 1 min. Adding 0.05 g NaOH/g-DS increased the VSS dissolution ratio to 50% and got 35% of SS reduction. After 1 min microwave treatment with alkali, the treated digested sludge provided a significant settleability improvement. Nevertheless, the high organic content of fresh sludge lessened the improvement of settleability behavior.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
State EPA (2006) China environment yearbook. China environmental science press
Carberry JB (1983) Sludge characteristics and behavior. Martinus Nijhoff Publ
Neyens E, Baeyens J (2003) J Hazard Mater B98:51
Weemaes MPJ, Verstraete WH (1988) J Chem Technol Biotechnol 73:83
Bougrier C, Albasi C (2006) Chem Eng Process 45:711
Brooks RB (1970) Water Pollut Control 69(2):221
Wang ZHJ, Wang W (2006) Environ Sci (in Chinese) 1(26):68
Neyens E, Baeyens J (2003) J Hazard Mater B97:295
Neyens E, Baeyens J (2003) J Hazard Mater B98:275
Li YY, Noike T (1992) Water Sci Technol 26:857
Tanaka S, Kyobayashi T (1997) Water Sci Technol 8:209
Miles NJ (2002) Resour Conserv Recy 34:75
Idris A, Khalid K (2004) Appl Therm Eng 24:905
Komarneni S (1995) Ionics 21:95
Park M, Komarneni S (2000) Mater Lett 43:259
Cigdem E, Kennedy KJ (2006) Water Res 40:3725
Park B, Ahn JH (2004) Water Sci Technol 50(9):17
Wojciechowska E (2005) Water Res 39:4749
Chan W, Wong W (2007) J Environ Sci Health A 42:59
Zhu SHD, Wu YX (2005) Process Biochem 40:3082
Plazl S (1995) Chem Eng J 59:253
Brooks RB (1968) Water Pollut Control 592
Miles A, Ellis TG (2001) Water Sci Technol 43(11):259
Liao PH, Wong WT (2005) J Environ Eng Sci 4:77
Erdincler A, Veslind PA (2000) Water Sci Technol 42(9):119
Nomura T, Araki S (2007) J Mater Cycles Waste Manage 9:34
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by a grant form the National High Technology Research and Development Program of China (863 program) (No. 2006AA06Z384).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Qiao, W., Wang, W., Xun, R. et al. Sewage sludge hydrothermal treatment by microwave irradiation combined with alkali addition. J Mater Sci 43, 2431–2436 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1957-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-007-1957-3