Abstract
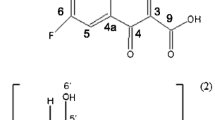
The present research paper is dedicated to the obtaining and physicochemical characterization of a highly potential anti-mycobacterial drug candidate with β-cyclodextrin (βCD). The active substance is a 1,3,4-oxadiazole derivative, 2-phenyl-5-{[(2-phenyl-1,3-dioxolan-2-yl)methyl]sulfanyl}-1,3,4-oxadiazole, further named DIOX. DIOX–βCD binary systems were obtained as a physical mixture and a lyophilized product with molar ratio between the main components equal to 1:1 and 1:2. The obtained systems were submitted to physicochemical characterization applying the following instrumental methods: infrared spectrometry, differential scanning calorimetry, and X-ray crystallographic analysis. Besides, a molecular modeling analysis has been performed. The research data suggested certain intermolecular interaction between DIOX and βCD, suggesting formation of a three-molecular inclusion complex DIOX:βCD, including one DIOX molecule and two molecules of βCD. The main parts of the DIOX molecule included in the hydrophobic cavity of the cyclodextrin molecules most probably are dioxolane cycle and two benzene rings.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
WHO: Anti-tuberculosis drug resistance in the world. http://www.who.int/tb/publications/2008/drs_report4_26feb08.pdf (2008). Accessed 26 March 2011
WHO: Global tuberculosis control report 2010. http://whqlibdoc.who.int/publications/2010/9789241564069_eng.pdf (2010). Accessed 26 March 2011
Kamal, A., Azeeza, S., Malik, M.S., et al.: Efforts towards the development of new antitubercular agents: potential for thiolactomycin based compounds. J. Pharm. Pharm. Sci. 11(2), 56–80 (2008)
Makarov, V., Manina, J., Mikusova, K., et al.: Benzothiazinones kill Mycobacterium tuberculosis by blocking arabinan synthesis. Science 5928, 801–804 (2009)
Sharma, M., Chaturvedi, V., Manju, Y.K., et al.: Substituted quinolinyl chalcones and quinolinyl pyrimidines as a new class of anti-infective agents. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 44(5), 2081–2091 (2009)
De, P., Yoya, G.K., Bedos-Belval, F., Constant, P., et al.: Design, synthesis and biological evaluation of new cinnamic derivatives as antituberculosis agents. J. Med. Chem. 54(5), 1449–1461 (2011)
Macaev, F., Rusu, Gh., Pogrebnoi, S., et al.: Synthesis of novel 5-aryl-2-thio-1,3,4-oxadiazoles and the study of their structure-anti-mycobacterial activities. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 13(16), 4842–4850 (2005)
Lipinski, C.A., Lombardo, F., Dominy, B.W., Feeney, P.J.: Experimental and computational approaches to estimate solubility and permeability in drug discovery and development settings. Adv. Drug. Deliv. Rev. 46(1–3), 3–26 (2001)
Donova, M.N., Nikolayeva, V.M., Dovbnya, D.V., et al.: Methyl-β-cyclodextrin alters growth, activity and cell envelope features of sterol-transforming Mycobacteria. Microbiology 153, 1981–1992 (2007)
Elstner, M., Porezag, D., Jungnickel, G., Elsner, J., Haugk, M., Frauenheim, T., Suhai, S., Seifert, G.: Self-consistent-charge density-functional tight-binding method for simulations of complex materials properties. Phys. Rev. B 58, 7260–7268 (1998)
Elstner, M., Jalkanen, K.J., Knapp-Mohammady, M., Frauenheim, T., Suhai, S.J.: Secondary-structure elements for glycine and alanine based polypeptides: β-sheets, helices, and turn. Chem. Phys. 256, 15–27 (2000)
Elstner, M., Jalkanen, K.J., Knapp-Mohammady, M., Frauenheim, T., Suhai, S.J.: Energetics and structure of glycine and alanine based model peptides: approximated SCC-DFTB, AM1, and PM3 methods in comparison with DFT, HF, and MP2 calculations. Chem. Phys. 263, 203–219 (2001)
Elstner, M., Hobza, P., Frauenheim, T., Suhai, S., Kaxiras, E.J.: Hydrogen bonding and stacking interactions of nucleic acid base pairs: a density-functional-theory based treatment. Chem. Phys. 114, 5149–5155 (2001)
Bende, A., Grosu, I., Turcu, I.: Molecular modeling of phenothiazine derivatives: self-assembling properties. J. Phys. Chem. A 114(47), 12479–12489 (2010)
Niehaus, T.A., Elstner, M., Frauenheim, Th., Suhai, S.: Application of an approximate density-functional method to sulphur containing compounds. J. Mol. Struct. (THEOCHEM) 541, 185 (2001)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boldescu, V., Bratu, I., Borodi, G. et al. Study of binary systems of β-cyclodextrin with a highly potential anti-mycobacterial drug. J Incl Phenom Macrocycl Chem 74, 129–135 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-0091-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10847-011-0091-7