Abstract
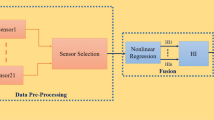
Reliability of prognostics and health management systems relies upon accurate understanding of critical components’ degradation process to predict the remaining useful life (RUL). Traditionally, degradation process is represented in the form of physical or expert models. Such models require extensive experimentation and verification that are not always feasible. Another approach that builds up knowledge about the system degradation over the time from component sensor data is known as data driven. Data driven models, however, require that sufficient historical data have been collected. In this paper, a two phases data driven method for RUL prediction is presented. In the offline phase, the proposed method builds on finding variables that contain information about the degradation behavior using unsupervised variable selection method. Different health indicators (HIs) are constructed from the selected variables, which represent the degradation as a function of time, and saved in the offline database as reference models. In the online phase, the method finds the most similar offline HI, to the online HI, using k-nearest neighbors classifier to use it as a RUL predictor. The method finally estimates the degradation state using discrete Bayesian filter. The method is verified using battery and turbofan engine degradation simulation data acquired from NASA data repository. The results show the effectiveness of the method in predicting the RUL for both applications.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benkedjouh, T., Medjaher, K., Zerhouni, N., Rechak, S. (2013). “Health assessment and life prediction of cutting tools based on support vector regression”. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, article published online 19 April 2013. doi:10.1007/s10845-013-0774-6.
Box, G. E. P., & Jenkins, G. M. (1976). Time series analysis: Forecasting and control. San Francisco: Holden-Day.
Brezak, D., Majetic, D., Udiljak, T., & Kasac, J. (2012). Tool wear estimation using an analytic fuzzy classifier and support vector machines. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23, 797–809.
Chaari, Fakher, Fakhfakh, Tahar, & Haddar, Mohamed. (2009). Analytical modelling of spur gear tooth crack and influence on gearmesh stiffness. European Journal of Mechanics-A/Solids, 28(3), 461–468. doi:10.1016/j.euromechsol.2008.07.007.
Choi, Kihoon, Singh, Satnam, Kodali, Anuradha, Pattipati, Krishna R., Sheppard, John W., Namburu, Setu Madhavi, et al. (2009). Novel classifier fusion approaches for fault diagnosis in automotive systems. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement, 58(3), 602–611. doi:10.1109/TIM.2008.2004340.
Dong, Jianfei, Verhaegen, Michel, & Gustafsson, Fredrik. (2012). Robust fault detection with statistical uncertainty in identified parameters. IEEE Transactions on Signal Processing, 60(10), 5064–5076. doi:10.1109/TSP.2012.2208638.
Gajate, A., Haber, R., Del Toro, R., Vega, P., & Bustillo, A. (2012). Tool wear monitoring using neuro-fuzzy techniques: A comparative study in a turning process. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23, 869–882.
Gebraeel, N., Lawley, M., Liu, R., & Parmeshwaran, V. (2004). Residual life predictions from vibration-based degradation signals: A neural network approach. IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics, 51(3), 694–700.
Gorjian, N., Ma, L., Mittinty, M., Yarlagadda, P., Sun, Y. (2009) Review on degradation models in reliability analysis. In: Proceedings of the 4th world congress on engineering asset management, 28–30 Sept, Athens, Greece.
He, D., Li, R., & Bechhoefer, E. (2012). Stochastic modeling of damage physics for mechanical component prognostics using condition indicators. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23, 221–226.
Heng, Aiwina, Zhang, Sheng, Tan, Andy C. C., & Mathew, Joseph. (2009). Rotating machinery prognostics: State of the art, challenges and opportunities. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 23(3), 724–739. doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2008.06.009.
Huang, N. E., Shen, Z., Long, S. R., Wu, M. C., Shih, H. H., Zheng, Q., et al. (1998). The empirical mode decomposition and the hilbert spectrum for nonlinear and non-stationary time series analysis. In Proceedings of the royal society of London series A mathematical Physical and engineering sciences (pp. 903–995).
Huang, R., Xi, L., Li, X., Qiu, H., & Lee, J. (2007). Residual life predictions for ball bearings based on self-organizing map and back propagation neural network methods. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 21(1), 193–207.
Isermann, R. (2006). Fault-diagnosis systems: An introduction from fault detection to fault tolerance. Heidelberg: Springer.
Iyer, N., Goebel, K., & Bonissone, P. (2006). Framework for post-prognostic decision support. IEEE Aerospace Conference, 9(1), 3962–3971. doi:10.1109/AERO.2006.1656108.
Jardine, Andrew K. S., Lin, Daming, & Banjevic, Dragan. (2006). A review on machinery diagnostics and prognostics implementing condition-based maintenance. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 20(7), 14831510. doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2005.09.012.
Javed, K., Gouriveau, R., & Zerhouni, N. (2013) “ Novel failure prognostics approach with dynamic thresholds for machine degradation”. In 39th annual conference of the IEEE industrial electronics society, (IECON), (pp. 4404–4409), 10–13 November 2013 doi:10.1109/IECON.2013.6699844.
Javed, K., Gouriveau, R., Zerhouni, N., & Nectoux, P. (2013) “A feature extraction procedure based on trigonometric functions and cumulative descriptors to enhance prognostics modeling”. In IEEE prognostics and health management (PHM) conference (Vol. 1(7), pp. 24–27). doi:10.1109/ICPHM.2013.6621413.
Kothamasu, Ranganath, Huang, Samuel H., & VerDuin, William H. (2006). System health monitoring and prognostics a review of current paradigms and practices. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 28(9–10), 1012–1024. doi:10.1007/s00170-004-2131-6.
Lee, J., Ni, J., Djurdjanovic, D., Qiu, H., & Liao, H. (2006). Intelligent prognostics tools and e-maintenance. Computers in Industry, 57(6), 476–489.
Lei, Z., Xingshan, L., Jinsong, Y., ZhanBao, G. (2007). A genetic training algorithm of wavelet neural networks for fault prognostics in condition based maintenance. In Proceedings of the eighth international conference on electronic measurement and instruments (pp. 584–589). IEEE
Lewis, F. (1992). Applied optimal control and estimation: Digital design and implementation. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Li, Lin, & Ni, Jun. (2009). Short-term decision support system for maintenance task prioritization. International Journal of Production Economics, 121(1), 195–202.
Luo, J., Namburu, M., Pattipati, K., Qiao, L., Kawamoto, M., & Chigusa, S. (2003). Model-based prognostic techniques, Anaheim, CA, United States: 2003 (pp. 330–340). Piscataway, NJ, United States: Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.
Medjaher, Kamal, Tobon-Mejia, Diego A., & Zerhouni, Noureddine. (2012). Remaining useful life estimation of critical components with application to bearings. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 61(2), 292–302. doi:10.1109/TR.2012.2194175.
Montgomery, N., Banjevic, D., & Jardine, A. K. S. (2012). Minor maintenance actions and their impact on diagnostic and prognostic CBM models. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(2), 303–311. doi:10.1007/s10845-009-0352-0.
Mosallam, A., Byttner, S., Svensson, M. T. R. (2011). “Nonlinear relation mining for maintenance prediction”. In IEEE Aerospace Conference, (pp. 1–9), March 2011. doi:10.1109/AERO.2011.5747581.
Mosallam, A., Medjaher, K., & Zerhouni, N. (2013). Nonparametric time series modelling for industrial prognostics and health management. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 69(5), 1685–1699. doi:10.1007/s00170-013-5065-z.
Nectoux, P., Gouriveau, R., Medjaher, K., Ramasso, E., Chebel-Morello, B., Zerhouni, N., Varnier, C. (2012) “Pronostia: An experimental platform for bearings accelerated degradation tests”. In IEEE international conference on prognostics and health management, Denver, Colorado, USA.
Pal, S., Heyns, P. S., Freyer, B. H., Theron, N. J., & Pal, S. K. (2011). Tool wear monitoring and selection of optimum cutting conditions with progressive tool wear effect and input uncertainties. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 22, 491–504.
Peng, Ying, Dong, Ming, & Zuo, Ming Jian. (2010). Current status of machine prognostics in condition-based maintenance: A review. The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology, 50(1–4), 297–313. doi:10.1007/s00170-009-2482-0.
Purushothaman, S. (2010). Tool wear monitoring using artificial neural network based on extended Kalman filter weight updation with transformed input patterns. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 21, 717–730.
Ramasso, Emmanuel, Rombaut, Michle, & Zerhouni, Noureddine. (2013). Joint prediction of continuous and discrete states in time-series based on belief functions. IEEE Transactions on Cybernetics, 43(1), 37–50. doi:10.1109/TSMCB.2012.2198882.
Saha, B., Goebel, K. (2007). “Battery Data Set”, NASA Ames Prognostics Data Repository. [http://ti.arc.nasa.gov/project/prognostic-data-repository]. NASA Ames, Moffett Field, CA
Saha, Bhaskar, & Goebel, Kai. (2008). Uncertainty management for diagnostics and prognostics of batteries using Bayesian techniques. IEEE Aerospace Conference, 1(8), 1–8. doi:10.1109/AERO.2008.4526631.
Sarah S. S., Radzi, N. H. M., Haron, H. (2012). “Review on scheduling techniques of preventive maintenance activities of railway”. In Fourth international conference on computational intelligence, modelling and simulation (CIMSiM) (pp. 310–315), 25–27 Sept. 2012, Kuantan, Malaysia. doi:10.1109/CIMSim.2012.56.
Satish, B., & Sarma, N. D. R. (2005). A fuzzy BP approach for diagnosis and prognosis of bearing faults in induction motors. In: IEEE power engineering society general meeting (pp. 2291–2294). IEEE
Saxena, A., Goebel, K. (2008). “C-MAPSS Data Set”, NASA Ames Prognostics Data Repository. [http://ti.arc.nasa.gov/project/prognostic-data-repository]. NASA Ames, Moffett Field, CA
Schwabacher, M. A. (2005). A survey of data-driven prognostic. In Infotech@Aerospace (pp. 26–29). Arlington, Virginia.
Sikorska, J. Z., Hodkiewicz, M., & Ma, L. (2011). Prognostic modelling options for remaining useful life estimation by industry. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 25(5), 1803–1836. doi:10.1016/j.ymssp.2005.09.012.
Tian, Zhigang. (2012). An artificial neural network method for remaining useful life prediction of equipment subject to condition monitoring. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 23(2), 227–237. doi:10.1007/s10845-009-0356-9.
Tobon-Mejia, Diego A., Medjaher, Kamal, Zerhouni, Noureddine, & Tripot, Gerard. (2012). A data-driven failure prognostics method based on mixture of Gaussians hidden Markov models. IEEE Transactions on Reliability, 61(2), 491–503. doi:10.1109/TR.2012.2194177.
Trincavelli, M., Coradeschi, S., & Loutfi, A. (2009). Odour classification system for continuous monitoring applications. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 139(2), 265–273, 4 June 2009, ISSN: 0925–4005. doi:10.1016/j.snb.2009.03.018.
Tsay, R. S. (2000). Time series and forecasting: Brief history and future research. Journal of the American Statistical Association, 95(450), 638–643.
Vachtsevanos, G., Lewis, F., Roemer, M., Hess, A., & Wu, B. (2006). Intelligent fault diagnosis and prognosis for engineering systems. Hoboken, New Jersey: Wiley.
Vassilopoulos, A. P., Georgopoulos, E. F., & Dionysopoulos, V. (2007). Artificial neural networks in spectrum fatigue life prediction of composite materials. International Journal of Fatigue, 29(1), 20–29.
Wang, Tianyi, Jianbo, Yu., Siegel, D., & Lee, J. (2008). A similarity-based prognostics approach for remaining useful life estimation of engineered systems. IEEE International Conference on Prognostics and Health Management, 1(6), 6–9. doi:10.1109/PHM.2008.4711421.
Wu, W., Hu, J., & Zhang, J. (2007). Prognostics of machine health condition using an improved ARIMA-based prediction method (pp. 1062–1067). Harbin, China: IEEE.
Xia, Tangbin, Xi, Lifeng, Zhou, Xiaojun, & Lee, Jay. (2012). Dynamic maintenance decision-making for series-parallel hybrid multi-unit manufacturing system based on MAM-MTW methodology. European Journal of Operational Research, 221, 231–240.
Yan, J., Koc, M., & Lee, J. (2004). A prognostic algorithm for machine performance assessment and its application. Production Planning and Control, 76, 796–801.
Yeo, S. H., Khoo, L. P., & Neo, S. S. (2000). Tool condition monitoring using reflectance of chip surface and neural network. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 11, 507–514.
Zhang, G. P. (2003). Time series forecasting using a hybrid ARIMA and neural network model. Neurocomputing, 50, 159–175.
Zhang, Zhenyou, Wang, Yi, & Wang, Kesheng. (2013). Fault diagnosis and prognosis using wavelet packet decomposition, Fourier transform and artificial neural network. Journal of Intelligent Manufacturing, 24(6), 1213–1227. doi:10.1007/s10845-012-0657-2.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mosallam, A., Medjaher, K. & Zerhouni, N. Data-driven prognostic method based on Bayesian approaches for direct remaining useful life prediction. J Intell Manuf 27, 1037–1048 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0933-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10845-014-0933-4