Abstract
Background
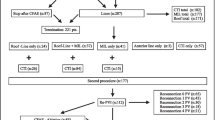
Atrial fibrillation (AF) drivers outside pulmonary veins (PV) may account for failure after PV isolation. The aim of this study was to characterize pre-existent areas of complex fractionated atrial electrograms (CFAEs) recorded in right atrium (RA) and in coronary sinus (CS) during catheter-based PV isolation and to assess their relation to outcome.
Methods and results
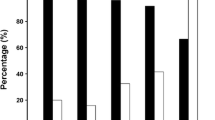
With a tricuspid annulus and CS mapping, CFAEs were retrospectively identified in consecutive patients who underwent PV isolation. Of 224 patients, 161 were found to have CFAEs (81%). No clinical variable was found to be predictive of CFAEs presence. By Kaplan–Meier analysis, following a median follow-up of 23.7 months after a single ablation procedure, 62.8% of patients in the CFAEs(+) group and 85.4% of those in the CFAEs(−) group were free from recurrent atrial tachyarrhythmias (p = 0.013). Multivariable Cox regression analysis showed that CFAEs evidence was an independent predictor of recurrence (p = 0.007).
Conclusions
Pre-existent CFAEs, that can be easily identified in RA and CS during PV isolation, are a powerful independent predictor for AF recurrence. This finding may be helpful for refining AF ablation strategies.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haissaguerre, M., Jais, P., Shah, D. C., Takahashi, A., Hocini, M., Quiniou, G., et al. (1998). Spontaneous initiation of atrial fibrillation by ectopic beats originating in the pulmonary veins. New England Journal of Medicine, 339, 659–666.
Chen, Y. J., & Chen, S. A. (2006). Electrophysiology of pulmonary veins. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 17, 220–224.
Kottkamp, H., Tanner, H., Kobza, R., Schirdewahn, P., Dorszewski, A., Gerds-Li, J. H., et al. (2004). Time courses and quantitative analysis of atrial fibrillation episode number and duration after circular plus linear left atrial lesions. Trigger elimination or substrate modification: Early or delayed cure? Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 44, 869–877.
Pappone, C., Oreto, G., Rosanio, S., Vicedomini, G., Tocchi, M., Gugliotta, F., et al. (2001). Atrial electroanatomic remodeling after circumferential radiofrequency pulmonary vein ablation. Efficacy of an anatomic approach in a large cohort of patients with atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 104, 2539–2544.
Allessie, M. A., Konings, K., Kirchhof, C. J., & Wijffels, M. (1996). Electrophysiologic mechanisms of perpetuation of atrial fibrillation. American Journal of Cardiology, 77, 10A–23A.
Ouyang, F., Bansch, D., Ernst, S., Schaumann, A., Hachiya, H., Chen, M., et al. (2004). Complete isolation of left atrium surrounding the pulmonary veins: New insights from the double-Lasso technique in paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 110, 2090–2096.
Wazni, O. M., Marrouche, N. F., Martin, D. O., Verma, A., Bhargava, M., Saliba, W., et al. (2005). Radiofrequency ablation vs antiarrhythmic drugs as first-line treatment of symptomatic atrial fibrillation: A randomized trial. JAMA, 293, 2634–2640.
Tondo, C., Mantica, M., Russo, G., Avella, A., De Luca, L., Pappalardo, A., et al. (2006). Pulmonary vein vestibule ablation for the control of atrial fibrillation in patients with impaired left ventricular function. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 29, 962–970.
Cappato, R., Calkins, H., Chen, S. A., Davies, W., Iesaka, Y., Kalman, J., et al. (2005). Worldwide survey on the methods, efficacy, and safety of catheter ablation for human atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 111, 1100–1105.
Verma, A., & Natale, A. (2005). Why atrial fibrillation ablation should be considered first-line therapy for some patients. Circulation, 112, 1214–1222.
Fuster, V., Rydén, L. E., Asinger, R. W., Cannom, D. S., Crijns, H. J., Frye, R. L., et al. (2001). ACC/AHA/ESC guidelines for the management of patients with atrial fibrillation: Executive summary a report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Practice Guidelines and the European Society of Cardiology Committee for Practice Guidelines and Policy Conferences (Committee to Develop Guidelines for the Management of Patients With Atrial Fibrillation) developed in collaboration with the North American Society of Pacing and Electrophysiology. Circulation, 104(17), 2118–2150.
Tondo, C., Mantica, M., Russo, G., Karapatsoudi, E., Lucchina, A., Nigro, F., et al. (2005). A new non fluoroscopic navigation system to guide pulmonary vein isolation. Pacing and Clinical Electrophysiology, 28, S102–S105.
Natale, A., Raviele, A., Arentz, T., Calkins, H., Chen, S. A., Haïssaguerre, M., et al. (2007). Venice chart international consensus document on atrial fibrillation ablation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 18(5), 560–580.
Nademanee, K., Schwab, M., Porath, J., & Abbo, A. (2006). How to perform electrogram-guided atrial fibrillation ablation. Heart Rhythm, 3, 981–984.
Oral, H., Knight, B. P., Ozaydin, M., Tada, H., Chugh, A., Hassan, S., et al. (2002). Clinical significance of early recurrences of atrial fibrillation after pulmonary vein isolation. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 40, 100–104.
Wazni, O., Marrouche, N. F., Martin, D. O., Gillinov, A. M., Saliba, W., Saad, E., et al. (2003). Randomized study comparing combined pulmonary vein-left atrial junction disconnection and cavotricuspid isthmus ablation versus pulmonary vein-left atrial junction disconnection alone in patients presenting with typical atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. Circulation, 108, 2479–83.
Nademanee, K., McKenzie, J., Kosar, E., Schwab, M., Sunsaneewitayakul, B., Vasavakul, T., et al. (2004). A new approach for catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Mapping of electrophysiologic substrate. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 43, 2044–2053.
Oral, H., Chugh, A., Good, E., Wimmer, A., Dey, S., Gadeela, N., et al. (2007). Radiofrequency catheter ablation of chronic atrial fibrillation guided by complex electrograms. Circulation, 115, 2606–2612.
Verma, A., Patel, D., Famy, T., Martin, D. O., Burkhardt, J. D., Elayi, S. C., et al. (2007). Efficacy of adjuvant anterior left atrial ablation during intracardiac echocardiography-guided pulmonary vein antrum isolation for atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 18, 151–156.
Wijffels, M. C., Kirchhof, C. J., Dorland, R., & Allessie, M. A. (1995). Atrial fibrillation begets atrial fibrillation: A study in awake chronically instrumented goats. Circulation, 92, 1954–1968.
Sanders, P., Morton, J. B., Davidson, N. C., Spence, S. J., Vohra, J. K., Sparks, P. B., et al. (2003). Electrical remodeling of the atria in congestive heart failure: Electrophysiological and electroanatomic mapping in humans. Circulation, 108, 1461–1468.
Scherr, D., Dalal, D., Cheema, A., Cheng, A., Henrikson, C. A., Spragg, D., et al. (2007). Automated detection and characterization of complex fractionated atrial electrograms in human left atrium during atrial fibrillation. Heart Rhythm, 4, 1013–1020.
Haissaguerre, M., Sanders, P., Hocini, M., Hsu, L. F., Shah, D. C., Scavée, C., et al. (2004). Changes in atrial fibrillation cycle length and inducibility during catheter ablation and their relation to outcome. Circulation, 109, 3007–3013.
Lin, W. S., Tai, C. T., Hsieh, M. H., Tsai, C. F., Lin, Y. K., Tsao, H. M., et al. (2003). Catheter ablation of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation initiated by non-pulmonary vein ectopy. Circulation, 107, 3176–3183.
Sanders, P., Jais, P., Hocini, M., & Haissaguerre, M. (2004). Electrical disconnection of the coronary sinus by radiofrequency catheter ablation to isolate a trigger of atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 15, 364–368.
Haissaguerre, M., Sanders, P., Hocini, M., Takahashi, Y., Rotter, M., Sacher, F., et al. (2005). Catheter ablation of long lasting atrial fibrillation. Critical structures for termination. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 15, 1125–1137.
Haissaguerre, M., Hocini, M., Takahashi, Y., O’Neill, M. D., Pernat, A., Sanders, P., et al. (2007). Impact of catheter ablation of the coronary sinus on paroxysmal or persistent atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 18, 378–386.
Zarse, M., Deharo, J. C., Mast, F., & Allessie, M. A. (2002). Importance of right and left atrial dilation and linear ablation for perpetuation of sustained atrial fibrillation. Journal of Cardiovascular Electrophysiology, 13, 164–171.
Calò, L., Lamberti, F., Loricchio, M. L., De Ruvo, E., Colivicchi, F., Bianconi, L., et al. (2006). Left atrial ablation versus biatrial ablation for persistent and permanent atrial fibrillation a prospective and randomized study. Journal of the American College of Cardiology, 47, 2504–2512.
Natale, A., Pisano, E., Beheiry, S., Richey, M., Leonelli, F., Fanelli, R., et al. (2000). Ablation of right and left atrial premature beats following cardioversion in patients with chronic atrial fibrillation refractory to antiarrhythmic drugs. American Journal of Cardiology, 85, 1372–1375.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Forleo, G.B., Mantica, M., De Luca, L. et al. Impact of pre-existent areas of complex fractionated atrial electrograms on outcome after pulmonary vein isolation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 21, 227–234 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-008-9240-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10840-008-9240-3