Abstract
Purpose
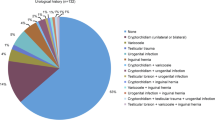
The aim was to assess the correlation of sperm apoptotic transcript levels with cleavage stage embryokinetic and pregnancy outcomes of intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection (IMSI) and ICSI methods in patients with male factor infertility.
Material and methods
Eighty male factor cases were divided into ICSI and IMSI groups. ICSI was done routinely, and for IMSI, sperm was selected at high magnification and injected. On day 3, time-lapse parameters were evaluated, and the best embryos were transferred and followed to delivery. In addition, sperm DNA fragmentation and apoptotic transcript levels were quantified using reverse transcription Q-PCR between the groups.
Results
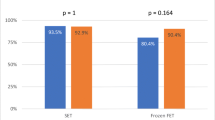
IMSI selected spermatozoa had lower DNA fragmentation and apoptotic transcript levels compared with ICSI (p < 0.0001). Moreover, all cytokinetic variables and cleavage abnormalities were noticeably different between groups (p < 0.0001); the rates of clinical outcomes were higher in the IMSI group. The transcript levels of Caspase 3 showed a moderate negative correlation with s2 and s3 (rs = − 0.57, P = 0.008 and rs = − 0.51, p = 0.021, respectively) in the IMSI group. However, there was no relationship between sperm apoptotic transcript levels and clinical outcomes in two groups.
Conclusions
Sperms selected at high magnification showed lower DNA fragmentation and apoptosis genes transcript. Also, better embryo kinetics and clinical outcomes were confirmed in IMSI than ICSI groups. Some time-lapse parameters may be associated with transcript levels of apoptosis genes. Therefore, these noninvasive techniques may be unique in assisting couples with male factor infertility.
Trial registration
This trial retrospectively registered on 4 July 2020 (IRCT20180130038561N1).





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Teixeira DM, Barbosa MA, Ferriani RA, Navarro PA, Raine-Fenning N, Nastri CO, et al. Regular (ICSI) versus ultra-high magnification (IMSI) sperm selection for assisted reproduction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2013;7:CD010167. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010167.pub2.
Ghazali S, Talebi AR, Khalili MA, Aflatoonian A, Esfandiari N. Large nuclear vacuoles in spermatozoa negatively affect pregnancy rate in IVF cycles. Iran J Reprod Med. 2015;13(7):425–32.
Bartoov B, Berkovitz A, Eltes F, Kogosowski A, Menezo Y, Barak Y. Real-time fine morphology of motile human sperm cells is associated with IVF-ICSI outcome. J Androl. 2002;23(1):1–8. https://doi.org/10.1002/j.1939-4640.2002.tb02595.x.
Cassuto NG, Bouret D, Plouchart JM, Jellad S, Vanderzwalmen P, Balet R, et al. A new real-time morphology classification for human spermatozoa: a link for fertilization and improved embryo quality. Fertil Steril. 2009;92(5):1616–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2008.08.088.
Armstrong S, Arroll N, Cree LM, Jordan V, Farquhar C. Time-lapse systems for embryo incubation and assessment in assisted reproduction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2:CD011320. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD011320.pub2.
Alhelou Y, Mat Adenan NA, Ali J. Embryo culture conditions are significantly improved during uninterrupted incubation: a randomized controlled trial. Reprod Biol. 2017;18:40–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repbio.2017.12.003.
Chamayou S, Patrizio P, Storaci G, Tomaselli V, Alecci C, Ragolia C, et al. The use of morphokinetic parameters to select all embryos with full capacity to implant. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2013;30(5):703–10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-013-9992-2.
Tejera A, Aparicio-Ruiz B, Meseguer M. The use of morphokinetic as a predictor of implantation. Minerva Ginecol. 2017. https://doi.org/10.23736/S0026-4784.17.04098-9.
Dominguez F, Meseguer M, Aparicio-Ruiz B, Piqueras P, Quinonero A, Simon C. New strategy for diagnosing embryo implantation potential by combining proteomics and time-lapse technologies. Fertil Steril. 2015;104:908–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.06.032.
Siristatidis C, Komitopoulou MA, Makris A, Sialakouma A, Botzaki M, Mastorakos G, et al. Morphokinetic parameters of early embryo development via time lapse monitoring and their effect on embryo selection and ICSI outcomes: a prospective cohort study. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2015;32(4):563–70. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-015-0436-z.
Zheng WW, Song G, Wang QL, Liu SW, Zhu XL, Deng SM, et al. Sperm DNA damage has a negative effect on early embryonic development following in vitro fertilization. Asian J Androl. 2017;20:75–9. https://doi.org/10.4103/aja.aja_19_17.
Wdowiak A, Bakalczuk S, Bakalczuk G. The effect of sperm DNA fragmentation on the dynamics of the embryonic development in intracytoplasmatic sperm injection. Reprod Biol. 2015;15(2):94–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repbio.2015.03.003.
Cho CL, Agarwal A. Role of sperm DNA fragmentation in male factor infertility: a systematic review. Arab J Urol. 2018;16(1):21–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aju.2017.11.002.
Fesahat F, Sheikhha MH, Kalantar SM, Tabibnejad N, Firouzabadi RD, Saeedi H, et al. Developmental competence and apoptotic gene expression patterns of mature and immature human oocytes retrieved from controlled ovarian stimulation cycles. Reprod Biol. 2018;18(1):27–32. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.repbio.2017.11.002.
Grunewald S, Paasch U, Wuendrich K, Glander HJ. Sperm caspases become more activated in infertility patients than in healthy donors during cryopreservation. Arch Androl. 2005;51(6):449–60. https://doi.org/10.1080/014850190947813.
Thornberry NA, Lazebnik Y. Caspases: enemies within. Science. 1998;281(5381):1312–6.
Organization WH. WHO laboratory manual for the examination and processing of human semen. 2010.
Mangoli E, Khalili MA, Talebi AR, Ghasemi-Esmailabad S, Hosseini A. Is there any correlation between sperm parameters and chromatin quality with embryo morphokinetics in patients with male infertility? Andrologia. 2018;50(5):e12997. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.12997.
Mangoli E, Khalili MA, Talebi AR, Agha-Rahimi A, Soleimani M, Faramarzi A, et al. IMSI procedure improves clinical outcomes and embryo morphokinetics in patients with different aetiologies of male infertility. Andrologia. 2019;51(8):e13340. https://doi.org/10.1111/and.13340.
Faramarzi A, Khalili MA, Soleimani M. First successful pregnancies following embryo selection using time-lapse technology in Iran: case report. Iran J Reprod Med. 2015;13(4):237–42.
Mangoli E, Khalili MA, Eftekhar M, Macchiarelli G, Palmerini MG. First successful live birth following the use of MSOME and time lapse for sperm and embryo selections in a patient with severe male factor infertility: A case report. J Gynecol Obstet Hum Reprod. 2019;48(10):883–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jogoh.2019.03.004.
Basile N, Vime P, Florensa M, Aparicio Ruiz B, Garcia Velasco JA, Remohi J, et al. The use of morphokinetics as a predictor of implantation: a multicentric study to define and validate an algorithm for embryo selection. Hum Reprod. 2015;30(2):276–83. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/deu331.
Liu Y, Chapple V, Feenan K, Roberts P, Matson P. Clinical significance of intercellular contact at the four-cell stage of human embryos, and the use of abnormal cleavage patterns to identify embryos with low implantation potential: a time-lapse study. Fertil Steril. 2015;103(6):1485–91 e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2015.03.017.
Rubio I, Galan A, Larreategui Z, Ayerdi F, Bellver J, Herrero J, et al. Clinical validation of embryo culture and selection by morphokinetic analysis: a randomized, controlled trial of the EmbryoScope. Fertil Steril. 2014;102(5):1287–94 e5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2014.07.738.
Meseguer M, Herrero J, Tejera A, Hilligsoe KM, Ramsing NB, Remohi J. The use of morphokinetics as a predictor of embryo implantation. Hum Reprod. 2011;26(10):2658–71. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/der256.
Zegers-Hochschild F, Adamson GD, Dyer S, Racowsky C, de Mouzon J, Sokol R, et al. The international glossary on infertility and fertility care, 2017. Hum Reprod. 2017;32(9):1786–801. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/dex234.
Mangoli E, Talebi AR, Anvari M, Taheri F, Vatanparast M, Rahiminia T, et al. Vitamin C attenuates negative effects of vitrification on sperm parameters, chromatin quality, apoptosis and acrosome reaction in neat and prepared normozoospermic samples. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2018;57(2):200–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tjog.2018.02.006.
Talebi AR, Fesahat F, Mangoli E, Ghasemzadeh J, Nayeri M, Sadeghian-Nodoshan F. Relationship between sperm protamine deficiency and apoptosis in couples with unexplained repeated spontaneous abortions. Int J Reprod Biomed (Yazd). 2016;14(3):199–204.
Tabibnejad N, Sheikhha MH, Ghasemi N, Fesahat F, Soleimani M, Aflatoonian A. Association between early embryo morphokinetics plus cumulus cell gene expression and assisted reproduction outcomes in polycystic ovary syndrome women. Reprod BioMed Online. 2019;38(2):139–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2018.10.010.
Cavalcanti MC, Steilmann C, Failing K, Bergmann M, Kliesch S, Weidner W, et al. Apoptotic gene expression in potentially fertile and subfertile men. Mol Hum Reprod. 2011;17(7):415–20. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gar011.
Knez K, Tomazevic T, Vrtacnik-Bokal E, Virant-Klun I. Developmental dynamics of IMSI-derived embryos: a time-lapse prospective study. Reprod BioMed Online. 2013;27(2):161–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2013.04.002.
Herrero J, Tejera A, Albert C, Vidal C, de los Santos MJ, Meseguer M. A time to look back: analysis of morphokinetic characteristics of human embryo development. Fertil Steril. 2013;100(6):1602–9.e1-4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2013.08.033.
Brezinova J, Svobodova M, Oborna I, Fingerova H, Dostal J, Krskova M. Embryo quality evaluation according to the speed of the first cleavage after IntraCytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI). Ceska Gynekol. 2006;71(3):204–8.
Prados FJ, Debrock S, Lemmen JG, Agerholm AI. The cleavage stage embryo. Hum Reprod. 2012;27(S1):i50–71 27(s1):50-71.
Tesarik J. Paternal effects on cell division in the human preimplantation embryo. Reprod BioMed Online. 2005;10(3):370–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1472-6483(10)61798-1.
Desai N, Gill P, Tadros NN, Goldberg JM, Sabanegh E, Falcone T. Azoospermia and embryo morphokinetics: testicular sperm-derived embryos exhibit delays in early cell cycle events and increased arrest prior to compaction. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2018;35(7):1339–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-018-1183-8.
Cassuto NG, Hazout A, Hammoud I, Balet R, Bouret D, Barak Y, et al. Correlation between DNA defect and sperm-head morphology. Reprod BioMed Online. 2012;24(2):211–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2011.10.006.
Boitrelle F, Ferfouri F, Petit JM, Segretain D, Tourain C, Bergere M, et al. Large human sperm vacuoles observed in motile spermatozoa under high magnification: nuclear thumbprints linked to failure of chromatin condensation. Hum Reprod. 2011;26(7):1650–8. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/der129.
Boitrelle F, Guthauser B, Alter L, Bailly M, Wainer R, Vialard F, et al. The nature of human sperm head vacuoles: a systematic literature review. Basic Clin Androl. 2013;23:3. https://doi.org/10.1186/2051-4190-23-3.
Kahraman S, Sahin Y, Yelke H, Kumtepe Y, Tufekci MA, Yapan CC, et al. High rates of aneuploidy, mosaicism and abnormal morphokinetic development in cases with low sperm concentration. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2020;37(3):629–40. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-019-01673-w.
Niederberger C. Re: The Impact of Male Factor Infertility on Early and Late Morphokinetic Parameters: A Retrospective Analysis of 4126 Time-Lapse Monitored Embryos. J Urol. 2020;101097JU000000000000110704. https://doi.org/10.1097/JU.0000000000001107.04.
Souza Setti A, Ferreira RC, Paes de Almeida Ferreira Braga D, de Cassia Savio Figueira R, Iaconelli A Jr, Borges E Jr. Intracytoplasmic sperm injection outcome versus intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection outcome: a meta-analysis. Reprod BioMed Online. 2010;21(4):450–5. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2010.05.017.
Teixeira DM, Hadyme Miyague A, Barbosa MA, Navarro PA, Raine-Fenning N, Nastri CO, et al. Regular (ICSI) versus ultra-high magnification (IMSI) sperm selection for assisted reproduction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020;2:CD010167. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010167.pub3.
Oliveira JB, Cavagna M, Petersen CG, Mauri AL, Massaro FC, Silva LF, et al. Pregnancy outcomes in women with repeated implantation failures after intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection (IMSI). Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2011;9:99. https://doi.org/10.1186/1477-7827-9-99.
Balaban B, Yakin K, Alatas C, Oktem O, Isiklar A, Urman B. Clinical outcome of intracytoplasmic injection of spermatozoa morphologically selected under high magnification: a prospective randomized study. Reprod BioMed Online. 2011;22(5):472–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rbmo.2010.11.003.
Gatimel N, Parinaud J, Leandri RD. Intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection (IMSI) does not improve outcome in patients with two successive IVF-ICSI failures. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2016;33(3):349–55. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-015-0645-5.
La Sala GB, Nicoli A, Fornaciari E, Falbo A, Rondini I, Morini D, et al. Intracytoplasmic morphologically selected sperm injection versus conventional intracytoplasmic sperm injection: a randomized controlled trial. Reprod Biol Endocrinol. 2015;13:97. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12958-015-0096-y.
Goswami G, Sharma M, Jugga D, Gouri DM. Can intracytoplasmic morphologically selected spermatozoa injection be used as first choice of treatment for severe male factor infertility patients? J Hum Reprod Sci. 2018;11(1):40–4. https://doi.org/10.4103/jhrs.JHRS_74_17.
Avendano C, Franchi A, Duran H, Oehninger S. DNA fragmentation of normal spermatozoa negatively impacts embryo quality and intracytoplasmic sperm injection outcome. Fertil Steril. 2010;94(2):549–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fertnstert.2009.02.050.
McDowell S, Kroon B, Ford E, Hook Y, Glujovsky D, Yazdani A. Advanced sperm selection techniques for assisted reproduction. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;10:CD010461. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.CD010461.pub2.
Acharyya S, Kanjilal S, Bhattacharyya AK. Does human sperm nuclear DNA integrity affect embryo quality? Indian J Exp Biol. 2005;43(11):1016–22.
Carrasco B, Arroyo G, Gil Y, Gomez MJ, Rodriguez I, Barri PN, et al. Selecting embryos with the highest implantation potential using data mining and decision tree based on classical embryo morphology and morphokinetics. J Assist Reprod Genet. 2017;34(8):983–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-017-0955-x.
Borini A, Tarozzi N, Bizzaro D, Bonu MA, Fava L, Flamigni C, et al. Sperm DNA fragmentation: paternal effect on early post-implantation embryo development in ART. Hum Reprod. 2006;21(11):2876–81. https://doi.org/10.1093/humrep/del251.
Kohn TP, Kohn JR, Lamb DJ. Role of Sperm Morphology in Deciding Between Various Assisted Reproduction Technologies. Eur Urol Focus. 2018;4(3):311–3. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.euf.2018.07.029.
Sadeghi MR, Lakpour N, Heidari-Vala H, Hodjat M, Amirjannati N, Hossaini Jadda H, et al. Relationship between sperm chromatin status and ICSI outcome in men with obstructive azoospermia and unexplained infertile normozoospermia. Romanian J Morphol Embryol. 2011;52(2):645–51.
Acknowledgments
This study was extracted from the PhD thesis of Esmat Mangoli. The authors thank Dr Hossein Falahzadeh, Professor of Biostatistics, for statistical assistance. We acknowledge the staff of the ART and Molecular Genetics laboratories in Yazd Reproductive Sciences Institute for their great contribution to all the laboratory work and data gathering.
Availability of data and material
The data is available in SPSS format.
Funding
This study was supported by funding from Shahid Sadoughi University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design of study: Esmat Mangoli, Mohammad Ali Khalili, Ali Reza Talebi, Seyed Mehdi Kalantar. Acquisition of data: Esmat Mangoli, Fatemeh Montazeri, Azam Agharahimi. Analysis and interpretation of data: Esmat Mangoli, Mohammad Ali Khalili, Seyed Mehdi Kalantar. Drafting the manuscript: Esmat Mangoli. Revising the manuscript: Mohammad Ali Khalili, Bryan J Woodward. Approval of the version of the manuscript to be published: Esmat Mangoli, Mohammad Ali Khalili, Ali Reza Talebi, Seyed Mehdi Kalantar, Fatemeh Montazeri, Azam Agharahimi, Bryan J Woodward.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of our institute (IR. SSU.MEDICINE.REC.1394.338).
Consent to participate
All patients provide informed consent to participate in study.
Consent for publication
All patients signed informed consent to publish data.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mangoli, E., Khalili, M.A., Talebi, A.R. et al. Association between early embryo morphokinetics plus transcript levels of sperm apoptotic genes and clinical outcomes in IMSI and ICSI cycles of male factor patients. J Assist Reprod Genet 37, 2555–2567 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-020-01910-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10815-020-01910-7