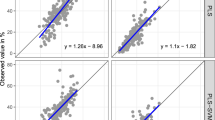
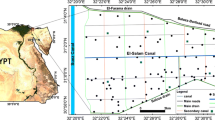
A fast and convenient soil analytical technique is needed for soil quality assessment and precision soil management. The main objective of this study was to evaluate the ability of visible (Vis) and near-infrared (NIR) refl ectance spectroscopy to predict paddy soil properties in a typical Malaysian paddy fi eld. To assess the utility of spectroscopy for soil physical characteristics (bulk density, moisture content, clay, silt and sand) prediction, 118 soil samples were used for laboratory analysis and optical measurement in the Vis-NIR region using an analytical spectral device (ASD) FieldSpec spectroradiometer (350–2500 nm). The Savitzky–Golay algorithm and stepwise multiple linear regression (SMLR) were then applied to preprocess, model, and predict the properties on the basis of their spectral refl ectance within the Vis-NIR range. One-third of the samples (40 samples) were withheld for validation purposes. The study revealed that Vis and NIR spectroscopy calibration models for all the measured soil physical characteristics provided a good fi t (R2 > 0.78); hence Vis and NIR (specifi cally NIR refl ectance) can be considered to be a reliable tool to assess soil physical properties of Malaysian paddy fi elds. The results of this study could contribute signifi cantly to developing site-specifi c management.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
R. A. Viscarra Rossel and A. B. McBratney, Aust. J. Exp. Agr., 38, 765–775 (1998).
L. J. Janik, R. H. Merry, and J. O. Skjemstad, Aust. J. Exp. Agr., 38, No. 7, 681–696 (1998).
G. D. Batten, Aust. J. Exp. Agr., 38, 697–706 (1998).
K. Islam, B. Singh, and A. McBratney, Aust. J. Soil Res., 41, 1101–1114 (2003).
E. Velasquez, P. Lavelle, E. Barrios, R. Joffre, and F. Reversat, Soil Biol. Biochem., 37, 889–898 (2005).
D. J. Brown, M. G. Walsh, M. D. Mays, and T. G. Reinsch, Geoderma, 129, No. 3–4, 215–267 (2005).
D. Cozzolino and A. Morón, Soil Till. Res., 85, No. 1–2, 78–85 (2006).
S. Shibusawa, S. W. Imade Anom, S. Sato, A. Sasao, and S. Hirako, Proc. 3rd Europ. Conf. Prec. Agriculture, Agro Montpellier, France, 497–508 (2001).
A. M. Mouazen, M. R. Maleki, J. De Baerdemaeker, and H. Ramon, Soil Till. Res., 93, 13–27 (2007).
H. Aichi, Y. Fouad, C. Walter, R. A. Viscarra Rossel, C. Zohra Lili, and S. Mustafa, Biosyst. Eng., 104, 442–446 (2009).
S. G. Bajwa, A. R. Mishra, and R. J. Norman, Precision Agric., 11, No. 5, 488–506 (2010).
G. R. Blake and K. H. Hartge. In: Methods of Soil Analysis. Ed. A. Klute, Part 1, Agronomy No. 9, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, 363–375 (1986).
W. H. Gardner. In: Methods of Soil Analysis. Ed. A. Klute, Part 1. Agronomy No. 9, American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, 493–544 (1986).
P. R. Day. In: Methods of Soil Analysis. Ed. C. A. Black, Agronomy No. 9, Part 1. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, WI, 545–567 (1965).
A. J. Green. In: Manual on Soil Sampling and Methods of Analysis. Ed. McKeague, Canadian Society of Soil Science, Ottawa, 4–29 (1981).
Analytical Spectral Devices. FieldSpecTM User’s guide. Analytical spectral devices Inc., Boulder, CO (2005).
H. R. Xu, H. J. Wang, K. Huang, Y. B. Ying, C. Yang, H. Qian, and J. Hu, Spectrosc. Spect. Anal., 28, No. 11, 2523–2526 (2008).
C. H. Spiegelman, M. J. McShane, M. J. Goetz, M. Motamedi, Q. L. Yue, and G. L. Cote, Anal. Chem., 70, 35–44 (1998).
A. Savitzky and M. J. E. Golay, Anal. Chem., 36, 1627 (1964).
M. R. Ehsani, S. K. Upadhyaya, W. R. Fawcett, L. V. Protsailo, and D. Slaughter, Am. J. Agric. Eng., 44, No. 6, 1931–1940 (2001).
P. Williams, Near-infrared Technology – Getting the Best out of Light. PDK Projects, Nanaimo, Canada (2003).
C. W. Chang, D. A. Laird, M. J. Mausbach, R. Charles, and Jr. Hurburgh, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 65, 480–490 (2001).
S. Haiyan, H. Yong, and G. Annia, Proc. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. 27 th Ann. Conf. Shanghai, China, 3149–3152 (2005).
L. K. Sørensen and S. Dalsgaard, Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J., 69, 159–167 (2005).
R. A. Viscarra Rossel, D. J. J. Walvoort, A. B. McBratney, L. J. Janik, and J. O. Skjemstad, Geoderma, 131, 59–75 (2006).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Abstract of article is published in Zhurnal Prikladnoi Spektroskopii, Vol. 81, No. 3, p. 487, May–June, 2014.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gholizadeh, A., Amin, M.S.M., Borůvka, L. et al. Models for Estimating the Physical Properties of Paddy Soil Using Visible and Near Infrared Reflectance Spectroscopy. J Appl Spectrosc 81, 534–540 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-014-9966-x
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10812-014-9966-x