Abstract
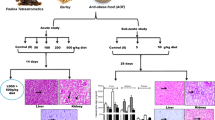
Eucheuma denticulatum is a red edible seaweed found in the east coast of Malaysia. This seaweed has shown to promote potential health benefits. The present work aimed to assess the anti-obesity effect of E. denticulatum freeze-dried powder supplemented with high-fat diet (HFD) on an in vivo model. Male Sprague Dawley rats aged 6–7 weeks (weighing 200-250 g) were divided into six groups (n = 6 per group) according to the following diet: normal diet group (CTR), high-fat diet group (HFD), HFD with orlistat (50 mg kg−1) (HFD + OR), HFD with 10% E. denticulatum (HFD-10), HFD with 15% E. denticulatum (HFD-15), and HFD with 20% E. denticulatum (HFD-20). Each group was fed for 7 weeks ad libitum, and food intake was monitored. At the end of the nutritional period, the rats were sacrificed. Blood was collected for determination of biochemical parameters and obesity biomarkers while tissue samples for histological analysis. Acute oral toxicity was employed to assess E. denticulatum for possible toxicity. Eucheuma denticulatum-fed rats significantly (p < 0.05) reduced weight gain, BMI, Lee index, visceral fat mass, triglyceride, liver enzymes, insulin, and leptin while improving ghrelin level relative to the HFD-fed rat. Food and energy intakes did not differ between the HFD and treatment groups. Histopathological examination showed E. denticulatum supplementation decreased fat size and reduced lipid droplets in the liver. Moreover, E. denticulatum showed no sign of toxicity in rodent acute oral toxicity study. Eucheuma denticulatum effectively attenuates weight gain independent of food intake and improving its related biomarkers, highlighting the potential of E. denticulatum in tackling obesity associated pathologies.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Antunes LC, Elkfury JL, Jornada MN, Foletto KC, Bertoluci MC (2016) Validation of HOMA-IR in a model of insulin-resistance induced by a high-fat diet in Wistar rats. Arch Endocrinol Metab 60:138–142
Arasaki S, Arasaki T (1983) Low calorie, high nutrition vegetables from the sea to help you look and feel better. Japan Publications, Tokyo
Balasubramaniam V, Mustar S, Khalid NM, Rashed AA, Noh MFM, Wilcox MD, Chater PI, Brownlee IA, Pearson JP (2013) Inhibitory activities of three Malaysian edible seaweeds on lipase and alpha-amylase. J Appl Phycol 25:1405–1412
Balasubramaniam V, Lee JC, Noh MFM, Ahmad S, Brownlee IA, Ismail A (2015) Alpha-amylase, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory activities of Eucheuma denticulatum (N.L. Burman) F.S. Collins and Hervey. J Appl Phycol 28:1965–1974
Bernardis L (1970) Prediction of carcass fat, water and lean body mass from Lee’s “nutritive ratio” in rats with hypothalamic obesity. Experientia 26:789–790
Chin YX, Mi Y, Cao WX, Lim PE, Xue CH, Tang QJ (2019) A pilot study on anti-obesity mechanisms of Kappaphycus alvarezii: the role of native κ-carrageenan and the leftover sans-carrageenan fraction. Nutrients 11:E1133
Cohen JC, Horton JD, Hobbs HH (2011) Human fatty liver disease: old questions and new insights. Science 332:1519–1523
David A (2008) Role of lipoprotein lipase in triglyceride metabolism: potential therapeutic target. Futur Lipidol 3:385–397
Dawczynski C, Schubert R, Jahreis G (2007) Amino acids, fatty acids, and dietary fibre in edible seaweed products. Food Chem 103:891–899
Flachs P, Mohamed-Ali V, Horakova O, Rossmeisl M, Hosseinzadeh-Attar MJ, Hensler M, Ruzickova J, Kopecky J (2006) Polyunsaturated fatty acids of marine origin induce adiponectin in mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetologia 49:394–397
Gomez-Zavaglia A, Prieto-Lage MA, Jimenez-Lopez C, Mejuto JC, Simal-Gandara J (2019) The potential of seaweeds as a source of functional ingredients of prebiotic and antioxidant value. Antioxidants (Basel) 8:406
Handjieva-Darlenska T, Boyadjieva N (2009) The effect of high-fat diet on plasma ghrelin and leptin levels in rats. J Physiol Biochem 65:157–164
Hariri N, Thibault L (2010) High-fat diet-induced obesity in animal models. Nutr Res Rev 23:270–299
Harris RBS (2014) Direct and indirect effects of leptin on adipocyte metabolism. Biochim Biophys Acta 1842:414–423
Holdt SL, Kraan S (2011) Bioactive compounds in seaweed: functional food applications and legislation. J Appl Phycol 23:543–597
Institute for Public Health (IPH) (2015) National Health and morbidity survey 2015 (NHMS 2015). Vol. II: Non-communicable diseases, risk factors & other health problems. Ministry of Health Malaysia, Kuala Lumpur
Iso H (2011) Lifestyle and cardiovascular disease in Japan. J Atheroscler Thromb 18:83–88
Jéquier E (2006) Leptin signaling, adiposity and, energy balance. Ann N Y Acad Sci 967:379–388
Kang JG, Park CY (2012) Anti-obesity drugs: a review about their effects and safety. Diabetes Metab J 36:13–25
Kang MC, Kang N, Kim SY, Lima IS, Ko SC, Kim YT, Kim YB, Jeung HD, Choi KS, Jeon YJ (2016) Popular edible seaweed, Gelidium amansii prevents against diet-induced obesity. Food Chem Toxicol 90:181–187
Kearns K, Dee A, Fitzgerald AP, Doherty E, Perry IJ (2014) Chronic disease burden associated with overweight and obesity in Ireland: the effects of a small BMI reduction at population level. BMC Public Health 14:1–10
Lahaye M (1991) Marine algae as sources of fibres: determination of soluble and insoluble dietary fibre contents in some ‘sea vegetables’. J Sci Food Agric 54:587–594
Lange KW, Hauser J, Nakamura Y, Kanaya S (2015) Dietary seaweeds and obesity. Food Sci Human Wellness 4:87–96
Li RY, Li XS, Shao L, Wu ZY, Du WH, Li SX, Zhao SX, Chen KM, Chen MD, Song HD (2009) Influence of visceral adiposity on ghrelin secretion and expression in rats during fasting. J Mol Endocrinol 42:67–74
Lim TO, Ding LM, Zaki M, Suleiman AB, Fatimah S, Siti S, Tahir A, Maimunah AH (2000) Distribution of body weight, height and body mass index in a national sample of Malaysian adults. Med J Malaysia 55:108–128
Matanjun P, Mohamed S, Mustapha NM, Muhammad K (2009) Nutrient content of tropical edible seaweeds Eucheuma cottonii, Caulerpa lentillifera and Sargassum polycystum. J Appl Phycol 21:75–80
Matthews DR, Hosker JP, Rudenski AS, Naylor BA, Treacher DF, Turner RC (1985) Homeostasis model assessment: insulin resistance and beta-cell function from fasting plasma glucose and insulin concentrations in man. Diabetologia 28:412–419
Nagao K, Inoue N, Wang YM, Yanagita T (2003) Conjugated linoleic acid enhances plasma adiponectin level and alleviates hyperinsulinemia and hypertension in Zucker diabetic fatty (fa/fa) rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 310:562–566
Nanri A, Mizoue T, Shimazu T, Ishihara J, Takachi R, Noda M, Iso H, Sasazuki S, Sawada N, Tsugane S, Japan Public Health Center–based Prospective Study Group (2017) Dietary patterns and all-cause, cancer, and cardiovascular disease mortality in Japanese men and women: the Japan public health center-based prospective study. PLoS One 12(4): e0174848
Nascimento AF, Sugizaki MM, Leopoldo AS, Lima-Leopoldo AP, Luvizotto RAM, Nogueira CR, Cicogna AC (2008) A Hypercaloric pellet-diet cycle induces obesity and co-morbidities in Wistar rats. Arq Bras Endocrinol Metabol 52:968–974
Norziah MH, Ching CY (2000) Nutritional composition of edible seaweed Gracilaria changgi. Food Chem 68:69–76
Novelli ELB, Diniz YS, Galhardi CM, Ebaid G, Rodrigues HG, Mani F, Fernandes AA, Cicogna AC, Novelli Filho JL (2007) Anthropometrical parameters and markers of obesity in rats. Lab Anim 41:111–119
Ntzouvani A, Fragopoulou E, Panagiotakos D, Pitsavos C, Antonopoulou S (2016) Reduced circulating adiponectin levels are associated with the metabolic syndrome independently of obesity, lipid indices and serum insulin levels: a cross-sectional study. Lipids Health Dis 15:140
Olivares-García V, Torre-Villalvazo I, Velázquez-Villegas L, Alemán G, Lara N, López-Romero P, Torres N, Tovar AR, Díaz-Villaseñor A (2015) Fasting and postprandial regulation of the intracellular localization of adiponectin and of adipokines secretion by dietary fat in rats. Nutr Diabetes 5:e184
Park HJ, Lee MK, Park YB, Shin YC, Choi MS (2011) Beneficial effects of Undaria pinnatifida ethanol extract on diet-induced-insulin resistance in C57BL/6J mice. Food Chem Toxicol 49:727–733
Rabiu A, Wale H, Garba K, Sabo AM, Hassan Z, Shugaba AI, Egesie UG, Odeh SO (2017) Body mass index of male and female Wistar rats following administration of leptin hormone after a dietary regime. Annals of Bioanthropology 5(1):22
Rubio MA, Gargallo M, Isabel Millán A, Moreno B (2007) Drugs in the treatment of obesity: sibutramine, orlistat and rimonabant. Public Health Nutr 10:1200–1205
Sanjeewa KKA, Lee WW, Jeon YJ (2018) Nutrients and bioactive potentials of edible green and red seaweed in Korea. Fish and Aqua Sci 21:1–11
Shah NR, Braverman ER (2012) Measuring adiposity in patients: the utility of body mass index (BMI), percent body fat, and leptin. PLoS One 7:e33308
Skrzypczyk VM, Hermon KM, Norambuena F, Turchini GM, Keast R, Bellgrove A (2019) Is Australian seaweed worth eating? Nutritional and sensorial properties of wild-harvested Australian versus commercially available seaweeds. J Appl Phycol 31:709–724
Stone TW, McPherson M, Gail Darlington L (2018) Obesity and cancer: existing and new hypotheses for a causal connection. EBioMedicine 30:14–28
Suleiman AI, Muazu GA, Muhammed SA, Muhammad AU, Abdullahi D (2017) Effect of antioxidant rich nutraceuticals on histological changes due to high fat diet induced obesity in rats. Am J Res Med Sci 1:8–13
Travlos GS, Morris R, Elwell MR, Duke A, Rosenblum S, Thompson MB (1996) Frequency and relationships of clinical chemistry and liver and kidney histopathology findings in 13-week toxicity studies in rats. Toxicol 107:17–29
Wanyonyi S, Du Preez R, Brown L, Paul NA, Panchal SK (2017) Kappaphycus alvarezii as a food supplement prevents diet-induced metabolic syndrome in rats. Nutrients 9:17–18
WHO (2018) Obesity and overweight. https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight; searched on 5 November 2019
WHO (2019) Sugary drinks tax important first step, but obesity in Malaysia demands further action. https://www.who.int/malaysia/news/commentaries/detail/sugary-drinks-tax-important-first-step-but-obesity-in-malaysia-demands-further-action?; searched on 5 November 2019
Woods SC, Seeley RJ, Rushing PA, D’Alessio D, Tso P (2018) A controlled high-fat diet induces an obese syndrome in rats. J Nutr 133:1081–1087
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the Director General of Health Malaysia and the Director of Institute for Medical Research (IMR), Malaysia, for giving the permission to publish this article. We also thank the staff of the Nutrition Unit, Institute for Medical Research, for their continuous support.
Funding
This project was funded by Ministry of Health Malaysia Research Grant (NMRR-16-666-30541; 16-015).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balasubramaniam, V., Aznyda, N., Hussin, M. et al. Effect of red edible seaweed Eucheuma denticulatum on diet-induced obesity in vivo. J Appl Phycol 32, 2407–2417 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02061-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-020-02061-z