Abstract
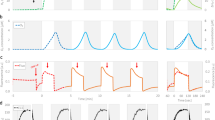
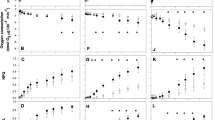
The effect of anaerobiosis on the induction of the xanthophyll cycle was investigated in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. The results showed that, anaerobiosis obtained by either sulfur starvation or by bubbling nitrogen in the culture grown in complete medium induced the xanthophyll cycle even when cultures were exposed to low light conditions. The zeaxanthin content reached 35 mmol mol−1 Chl a, after 110 h in anaerobic sulfur-starved cultures, and 30 mmol mol−1 Chl a within 24 h in sulfur replete cultures bubbled with nitrogen. Both starved and non-starved cultures grown under aerobic conditions, did not exhibit any sizeable increase in the zeaxanthin content. Chlorophyll fluorescence measurements revealed a decrease in the maximum photochemical quantum yield of PSII (Fv/Fm) by more than 50 %. The chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics (OJIP) analysis showed a strong rise at the J-step indicating a strong reduction of QA. Our findings demonstrated that anaerobiosis in low light exposed cultures induced the xanthophyll cycle through a strong increase of the level of plastoquinone pool reduction, which was associated to the formation of a trans-thylakoid membranes proton gradient, while in dark anaerobic cultures, no appreciable induction of xanthophyll cycle could be observed, despite the sizeable increase in non–photochemical quenching.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alric J (2010) Cyclic electron flow around photosystem I in unicellular green algae. Photosynth Res 106:47–56
Alric J, Lavergne J, Rappaport F (2010) Redox and ATP control of photosynthetic cyclic electron flow in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (I) aerobic conditions. Biochim Biophys Acta 1797:44–51
Antal TK, Krendeleva TE, Laurinavichene TV, Makarova W, Ghirardi ML, Rubin AB et al (2003) The dependence of algal H2 production on photosystem II and O2 consumption activities in sulfur-deprived Chlamydomonas reinhardtii cells. Biochim Biophys Acta 1607:153–160
Antal TK, Volgushava AA, Kularskih GP, Bulychev AA, Krendeleva TE, Rubin AB (2006a) Effects of sulfur limitation on photosystem II functioning in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as probed by chlorophyll a fluorescence. Physiol Plant 128:360–367
Antal TK, Volgusheva AA, Kukarskikh GP, Krendeleva TE, Tusov VB, Rubin AB (2006b) Examination of chlorophyll fluorescence in sulfur-deprived cells of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Cell Biophys 51:251–257
Antal TK, Volgusheva AA, Kukarskih GP, Bulychev AA, Krendeleva TE, Rubin AB (2007) Effects of sulfur limitation on photosystem II functioning in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii as probed by chlorophyll a fluorescence. Physiol Plantarum 128:360–367
Antal TK, Krendeleva TE, Rubin AB (2011) Acclimation of green algae to sulfur deficiency: underlying mechanisms and application for hydrogen production. App Microbiol Biotechnol 89:3–15
Appenroth K-J, Stöckel J, Srivastava A, Strasser RJ (2001) Multiple effects of chromate on the photosynthetic apparatus of Spirodela plyrhiza as probed by OJIP chlorophyll a fluorescence measurements. Environ Poll 115:49–64
Bennoun P (1982) Evidence for a respiratory chain in the chloroplast. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:4352–4356
Björkman O (1987) Low temperature chlorophyll fluorescence in leaves and its relationship to photon yield of photosynthesis in photoinhibition. In: Kyle DJ, Osmond CB, Arntzen CJ (eds) Photoinhibition. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 123–144
Bukhov N, Carpentier R (2004) Alternative photosystem I-driven electron transport routes: mechanisms and functions. Photosynth Res 82:17–33
Bulté L, Gans P, Rebeille F, Wollman FA (1990) ATP control on state transitions in vivo in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Biochim Biophys Acta 1020:72–80
Cardol P, Gloire G, Havaux M, Remacle C, Matagne R, Franck F (2003) Photosynthesis and state transitions in mithocondrial mutants of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii affected in respiration. Plant Physiol 133:2010–2020
Cournac L, Latouche G, Cerovic Z, Redding K, Ravenel J, Peltier G (2002) In vivo interactions between photosynthesis, mitorespiration, and chlororespiration in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol 129:1921–1928
Cruz S, Goss R, Wilhelm C, Leegood R, Horton P, Jakob T (2011) Impact of chlororespiration on non-photochemical quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence and the regulation of the diadinoxanthin cycle in the diatom Thalassiosira pseudonana. J Exp Bot 62:509–519
Demmig-Adams B (1990) Carotenoids and photoprotection in plants: a role for the xanthophyll zeaxanthin. Biochim Biophys Acta 1020:1–24
Demmig-Adams B (2003) Linking the xanthophyll cycle with thermal energy dissipation. Photosynth Res 76:73–80
Demmig-Adams B, Winter K, Winkelmann E, Krüger A, Czygan F-C (1989) Photosynthetic characteristics and the ratios of chlorophyll, β-carotene, and the components of the xanthophyll-cycle upon a sudden increase in growth light regime in several plant species. Bot Acta 102:319–325
Depège N, Bellafiore S, Rochaix JD (2003) Role of chloroplast protein Stt7 kinase in LHCII phosphorylation and state transition in Chlamydomonas. Science 299:1572–1575
Diner BA (1977) Dependence of the deactivation reactions of photosystem II on the redox state of plastoquinone pool: a varied under anaerobic conditions. Equilibria on the acceptor side of photosystem II. Biochim Biophys Acta 460:247–258
Doebbe A, Keck M, La Russa M, Mussngug JH, Hankamer B, Tekce E, Niehaus K, Kruse O (2010) The interplay of proton, electron and metabolite supply for photosynthetic H2 production in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. J Biol Chem 285:30247–30260
Endo T, Asada K (1996) Dark induction of the non-photochemical quenching of chlorophyll fluorescence by acetate in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell Physiol 37:551–555
Eriksson M, Moseley JL, Tottey S, Del Campo JA, Quinn J, Kim Y, Merchant S (2004) Genetic dissection of nutritional copper signaling in Chlamydomonas distinguishes regulatory and target genes. Genetics 168:795–807
Faraloni C, Torzillo G (2010) Phenotypic characterization and hydrogen production in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii QB binding D1 protein mutants under sulfur starvation: changes in chlorophyll fluorescence and pigment composition. J Phycol 46:788–799
Ferreira RMB, Teixeira ARN (1992) Sulfur starvation Lemna leads to degradation of ribulose-biphosphate carboxylase without plant death. J Biol Chem 267:7253–7257
Finazzi G, Barbagallo RP, Bergo E, Barbato R, Forti G (2001) Photoinhibition of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii in State 1 and State 2. J Biol Chem 276:22251–22257
Finazzi G, Rappaport F, Furia A, Fleischmann M, Rochaix JD, Zito F, Forti G (2002) Involvement of state transitions in the switch between linear and cyclic electron flow in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. EMBO Rep 3:280–285
Ghirardi ML, Posewitz MC, Maness PC, Dibini A, Yu J, Seibert M (2007) Hydrogenases and hydrogen photoproduction in oxygenic photosynthetic organisms. Ann Rev Plant Biol 58:71–91
Gilmore AM, Yamamoto HY (1993) Linear models relating xanthophylls and lumen acidity to non-photochemical fluorescence quenching; evidence that antheraxanthin explains zeaxanthin-independent quenching. Photosynth Res 35:67–78
Gilmore AM, Hazlett TL, Govindjee (1995) Xanthophyll cycle-dependent quenching of photosystem II chlorophyll a fluorescence: Formation of a quenching complex with a short fluorescence lifetime. PNAS, USA 92:2273–2277
Gilmore AM, Yamamoto HY (2001) Time-resolution of the antheraxanthin- and delta pH-dependent chlorophyll a fluorescence components associated with photosystem II energy dissipation in Mantoniella squamata. Photochem Photobiol 74:291–302
Goss R, Opitz C, Lepetit B, Wilhelm C (2008) The synthesis of NPQ-effective zeaxanthin depends on the presence of a transmembrane proton gradient and a slight basic stromal side of the thylakoid membrane. Planta 228:999–1009
Grossman A (2000) Acclimation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii to its nutrient environment. Protist 151:201–224
Grossman AR, Catalanotti C, Yang W, Dubini A, Magneschi L, Subramanian V, Posewitz MC, Seibert M (2011) Multiple facet of anoxic metabolism and hydrogen production in the unicellular green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. New Phytol 190:279–288
Haldimann P, Strasser RJ (1999) Effects of anaerobiosis as probed by the polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence rise kinetic in pea (Pisum sativum L.). Photosynth Res 62:67–83
Harris E (1989) The Chlamydomonas sourcebook: Vol. 1. Introduction to Chlamydomonas and its laboratory use. Academic Press, Amsterdam, 444 pp
Harris E (2001) Chlamydomonas as a model organism. Ann Rev Plant Mol Biol 52:363–406
Hemschemeier A, Happe T (2011) Alternative photosynthetic electron transport pathways during anaerobiosis in the green alga Chlamydomonas renhardtii. Biochim Biophys Acta 1807:919–926
Jakob T, Goss R, Wilhelm C (1999) Activation of diadinoxanthin de-epoxidase due to a chlororespiration proton gradient in the dark in the diatom Phaeodactylum tricornutum. Plant Biol 1:76–82
Jin E, Yokthongwattana K, Polle JEW, Melis A (2003) Role of the reversible xanthophyll cycle in the photosystem II damage and repair cycle in Dunaliella salina. Plant Physiol 132:352–364
Johnson GN (2005) Cyclic electron transport in C3 plants: fact or artifact? J Exp Bot 56:407–416
Kosourov S, Tsygankov A, Seibert M, Ghirardi ML (2002) Sustained hydrogen photoproduction by Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: effect of culture parameter. Biotechnol Bioeng 78:731–740
Kruse O, Rupprecht J, Bader KP, Thomas Hall S, Schenk PM, Finazzi G, Hankamer B (2005) Improved photobiological H2 production in engineered green algal cells. J Biol Chem 280:34170–34177
Li ZL, Wakao S, Fischer BB, Niyogi KK (2009) Sensing and responding to excess light. Ann Rev Plant Biol 60:239–260
Lichtenthaler HK (1987) Chlorophylls and carotenoids: pigments of photosynthetic membranes. In: Packer L, Douce R (eds) Methods in enzymology, 148th edn. Academic Press, New York, pp 350–382
Melis A (1999) Photosystem-II damage and repair cycle in chloroplasts: what modulates the rate of photodamage in vivo. Trends Plant Sci 4:130–135
Melis A, Zhang L, Forestier M, Ghirardi ML, Siebert M (2000) Sustained photobiological hydrogen gas production upon reversible inactivation of oxygen evolution in the green alga Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol 122:127–136
Morsy FM (2011) Acetate versus sulfur deprivation role in creating anaerobiosis in light for hydrogen production by Chlamydomonas reinhratdii and Spirulina platensis: two different organisms and two different mechanisms. Photochem Photobiol 87:137–142
Mus F, Dubini A, Seibert M, Posewitz MC, Grossman AR (2007) Anaerobic acclimation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii: anoxic gene expression, hydrogenase induction and metabolic pathways. J Biol Chem 282:25475–25486
Naito S, Yokota-Hirai M, Chino M, Komeda Y (1994) Expression of soybean (Glycine max [L.] Merr.) seed storage protein gene in transgenic Arabidopsis thaliana and its response to nutritional stress and to abscisic acid mutations. Plant Physiol 101:497–503
Nixon PJ (2000) Chlororespiration. Phil Trans R Soc London B 355:1541–1547
Peltier G, Cournac L (2002) Chlororespiration. Ann Rev Plant Biol 53:523–550
Posewitz MC, Smolinsky SL, Kanakagiri S, Melis A, Seibert M, Ghirardi ML (2004) Hydrogen photoproduction is attenuated by disruption of an isoamylase gene in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Cell 16:2151–2163
Quinn JM, Eriksson M, Moseley JL, Merchant S (2002) Oxygen deficiency responsive gene expression in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii through a copper-sensing signal transduction pathway. Plant Physiol 12:463–471
Rochaix JD (2007) Role of thylakoid protein kinases in photosynthetic acclimation. FEBS Lett 581:2768–6775
Rumeau D, Peltier G, Cournac L (2007) Chlororespiration and cyclic electron flow around PSI during photosynthesis and plant stress response. Plant Cell 30:1041–1051
Solovchenko AE, Khozin-Goldberg I, Didi-Cohen Z, Merzlyak MN (2008) Effects of light and nitrogen starvation on the content and composition of carotenoids of the green microalga Parietochloris incisa. Russ J Plant Physiol 55:455–462
Stal LJ, Moezelaar R (1997) Fermentation in cyanobacteria. FEMS Microbiol Rev 21:179–211
Strasser R, Srivastava A, Govindge (1995) Polyphasic chlorophyll a fluorescence transient in plants and cyanobacteria. Photochem Photobiol 61:32–42
Strasser RJ, Srivastava A, Tsimilli-Michael M (2004) Analysis of the chlorophyll a fluorescence transient. In: Papageorgiou G and Govindjee (eds) Chlorophyll fluorescence a signature of photosynthesis: advances in photosynthesis and respiration. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht, pp 321–362
Takahashi H, Braby CE, Grossman AR (2001) Sulfur economy and cell wall biosynthesis during sulfur limitation of Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol 127:665–673
Torzillo G, Scoma A, Faraloni C, Ena A, Johanningmeier U (2009) Increased hydrogen photoproduction by means of a sulfur-deprived Chlamydomonas reinhardtii D1 protein mutant. Int J Hydrogen Energy 10:4529–4536
Ulstrup KE, Hill R, Ralph PJ (2005) Photosynthetic impact of hypoxia on in hospite zooxanthellae in the scleractinian coral Pocillopora damicornis. Mar Ecol Progr Ser 286:125–132
Van Heukelem L, Thomas CS (2001) Computer-assisted high performance liquid chromatography method development with applications to the isolation and analysis of phytoplankton pigments. J Chromatogr A 910:31–49
Van Kooten O, Snel JFH (1990) The use of chlorophyll fluorescence nomenclature in plants stress physiology. Photosynth Res 25:145–147
Wykoff DD, Davies JP, Melis A, Grossman AR (1998) The regulation of photosynthetic electron transport during nutrient deprivation in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii. Plant Physiol 117:129–139
Yamane Y, Kashino Y, Koioke H, Satoh K (1997) Increase of the fluorescence F0 level and reversible inhibition of photosystem II reaction center by high-temperature treatments in higher plants. Photosynth Res 52:57–64
Zhang L, Happe T, Melis A (2002) Biochemical and morphological characterization of sulfur-deprived and H2-producing Chlamydomonas reinhardtii (green alga). Planta 214:552–561
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by the MIUR (Italian Ministry of University and Research) through project FISR “Fondo Integrativo Speciale per la Ricerca” contract number 1756 (GP). Partial support was also provided by joint projects under the framework of the Bilateral Scientific Agreement between the National Research Council of Italy and the TUBITAK (Turkey). The information reported in this article was also generated as a part of the International Energy Agency (IEA), Hydrogen Implementing Agreement (HIA) Task 21 Program on Bio-inspired Hydrogen and Biological Hydrogen Production.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Faraloni, C., Torzillo, G. Xanthophyll cycle induction by anaerobic conditions under low light in Chlamydomonas reinhardtii . J Appl Phycol 25, 1457–1471 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-9986-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-013-9986-6