Abstract
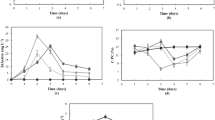
Diammonium phosphate (DAP) and urea are commonly used fertilizers throughout the world. The effects of these fertilizers on the freshwater flagellate Euglena gracilis was studied after 7 days of growth using morphological, physiological and biochemical parameters as end points. NOEC and EC50 values for various parameters like cell density, motility, velocity, cell shape, gravitaxis, chlorophyll a, b and total carotenoids were calculated. NOEC and EC50 values of DAP varied from 0.5 to 2.5 g L−1 and 3.14 to 5.96 g L−1, respectively, for different parameters. NOEC and EC50 values for urea ranged from 5 to 25 g L−1 and 28 to 44.05 g L−1, respectively, for various parameters. Photosynthetic pigments were found to be more sensitive to both fertilizers as compared to other measured end points. The NOEC and EC50 values obtained for DAP were much lower than those for urea; i.e., DAP showed a stronger inhibitory effect as compared to urea. Application of DAP resulted in an increased concentration of ammonia in Euglena cultures but urea did not. The stronger inhibitory effect of DAP is attributed to release of free ammonia in the culture due to DAP decompostion. No release of ammonia by urea occurred due to the absence of the enzyme urease in E. gracilis.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abeliovich A (1969) Waterblooms of blue green algae and oxygen regime in fish ponds. Verh Internat Verein Limnol 17:594–601
Abeliovich A, Azov Y (1976) Toxicity of ammonia to algae in sewage oxidation ponds. Appl Environ Microbiol 31:801–806
Ahmed H, Häder D-P (2010) A fast algal bioassay for assessment of copper toxicity in water using Euglena gracilis. J Appl Phycol 22:785–792
Ali AA, Mannan MA, Parween S (2007) Effect of urea and malathion on the freshwater prawn, Macrobrachium lamarrei (H.M. Edwards). Univ J Zool Rajshahi Univ 26:107–108
Anderson JM, Aro E-M (1994) Grana stacking and protection of photosystem II in thylakoid membranes of higher plant leaves under sustained high irradiance: a hypothesis. Photosynth Res 41:315–326
Anderson JM, Osmond CB (1987) Shade-sun responses: compromises between acclimation and photoinhibition. In: Kyle DJ, Osmond CB, Arntzen CJ (eds) Photoinhibition. 1–38. 1987. Elsevier
Anonymous (2009) Material safety data sheet (diammonium phosphate). Parchem, New Rochelle
Azov Y, Goldman JC (1982) Free ammonia inhibition of algal photosynthesis in intensive cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:735–739
Bringmann G, Kühn R (1982) Results of toxic action of water pollutants on Daphnia magna Straus tested by an improved standarized procedure. Z Wasser- Abwasserforsch 15:1–6
Brinley FJ (1929) The effect of ammonium salts on protoplasm of amoeba. Biol Bull Woods Hole 56:371–378
Bulich AA, Greene MW, Isenberg DL (1981) The reliability of the bacterial luminescence assay for the determination of toxicity of pure compounds and complex effluents. In: Branson DR, Dickson KL (eds) Aquatic toxicology and hazard assessment STP 737. American Society for Testing and Materials, USA, pp 338–347
Burhenne M, (2000) Biotestsystem mit Bodenalgen zur ökotoxikologischen Bewertung von Schwermetallen und Pflanzenschutzmitteln am Beispiel von Cadmium und Isoproturon. Humboldt-Universität zu Berlin
Carter DR, Cheeseman JM (1993) The effects of external NaCl on thylakoid stacking in lettuce plants. Plant Cell Environ 16:215–222
Casper-Lindley C, Björkman O (1998) Fluorescence quenching in four unicellular algae with different light-harvesting and xanthophyll-cycle pigments. Photosynth Res 56:277–289
Checcucci A, Colombetti G, Ferrara R, Lenci F (1976) Action spectra for photoaccumulation of green and colorless Euglena: evidence for identification of receptor pigments. Photochem Photobiol 23:51–54
Chouhan MS, Pandey AK (1987) On the tolerance limits and toxicity symptoms of guppy (Lenbistes reticulates) to urea and ammonium sulfate. Comp Physiol Ecol 12:77–80
Coleman LW, Rosen BH, Schwartzbach SD (1988) Environmental control of carbohydrate and lipid synthesis in Euglena. Plant Cell Physiol 29:423–432
Conforti V (1998) Morphological changes of Euglenophyta in response to organic enrichment. Hydrobiologia 369:277–285
Drath M, Kloft N, Batschauer A, Marin K, Novak J, Forchhammer K (2008) Ammonia triggers photodamage of photosystem II in the cyanobacterium Synechocystis sp. strain PCC 6803. Plant Physiol 147:206–215
Emerson K, Russo RC, Lund RE, Thurston RV (1975) Aqueous ammonia equilibrium calculations: effect of pH and temperature. J Fish Res Board Can 32:2379–2383
Emmens CWW (1940) The dose/response relation for certain principles of the pituitary gland, and of the serum and urine of pregnancy. J Endocrinol 2:194–225
Fent K (1998) Ökotoxikologie. Thieme, Stuttgart
Fodorpataki L, Marton AL, Csorba TL (2001) Stress-physiological investigation of algal cell cultures in polluted media. Contrib Bot 36:101–108
Glibert PM, Harrison J, Heil C, Seitzinger S (2006) Escalating worldwide use of urea—a global change contributing to coastal eutrophication. Biogeochem 77:441–463
Gonzáles-Moreno S, Gómez-Barrera J, Perales H, Moreno-Sánchez R (1997) Multiple effects of salinity on photosynthesis of the protist Euglena gracilis. Physiol Plant 101:777–786
Häder D-P (1987) Polarotaxis, gravitaxis and vertical phototaxis in the green flagellate, Euglena gracilis. Arch Microbiol 147:179–183
Häder D-P, Vogel K (1990) Graviorientation in photosynthetic flagellates. In: Proceedings of the Fourth European Symposium on Life Science Research in Space (ESA SP-307), pp 521–526
Häder D-P, Lebert M, Richter P (1998) Gravitaxis and graviperception in Euglena gracilis. Adv Space Res 21:1277–1284
Häder D-P, Lebert M, Richter P (1999) Gravitaxis and graviperception in flagellates and ciliates. Proceedings 14th ESA Symposium on European Rocket and Balloon Programmes and Related Research (ESA SP-437), Potsdam, Germany, pp. 479–486
Huovinen P, Matos J, Sousa Pinto I, Figueroa FL (2006) The role of ammonium in photoprotection against high irradiance in the red alga Grateloupia lanceola. Aquat Bot 84:308–316
Keeley JE (1990) Photosynthetic pathways in freshwater aquatic plants. Trends Ecol Evol 5:330–333
Kolber Z, Falkowski PG (1993) Use of active fluorescence to estimate phytoplankton photosynthesis in situ. Limnol Oceanogr 38:1646–1665
Küpper H, Setlik I, Spiller M, Küpper FC, Prasil O (2002) Heavy metal-induced inhibition of photosynthesis: targets of in vivo heavy metal chlorophyll formation. J Phycol 38:429–441
Lebert M, Häder D-P (1999) Aquarack: long-term growth facility for ‘professional’ gravisensing cells. In: Proceedings of the 2nd European Symposium on the Utilisation of the International Space Station, ESTEC, Noordwijk, The Netherlands. 16-18 November 1998 (ESA-SP 433), pp 533–537
Lichtenthaler HK, Wellburn AR (1983) Determinations of total carotenoids and chlorophylls a and b of leaf extracts in different solvents. Biochem Soc Trans 11:591–592
Murray JM (1981) Control of cell shape by calcium in the Euglenophyceae. J Cell Sci 49:99–117
Nass MM, Ben Shaul Y (1973) Effects of ethidium bromide on growth, chlorophyll synthesis, ultrastructure and mitochondrial DNA in green and bleached mutant, Euglena gracilis. J Cell Sci 13:567–590
Natarajan KV (1970) Toxicity of ammonia to marine diatoms. J Water Pollut Control Fed 42:184–190
Oda Y, Miyatake K, Kitaoka S (1979) Inability of Euglena gracilis Z to utilize nitrate, nitrite and urea as the nitrogen sources. Bull Univ Osaka Pref Ser B 31:43–48
Olaveson MM, Nalewajko C (2000) Effects of acidity on the growth of two Euglena species. Hydrobiologia 433:39–56
Osafune T, Sumida S (2006) Physiological events occurring during the conversion from heterotrophy to autotrophy in Euglena gracilis. Bull Nippon Sport Sci Univ 36:137–147
Palanichamy S, Arunachalam S, Balasubramanian MP (1985) Food Consumption of Sarotherodon mossambicus (Trewaves) exposed to sublethal concentration of diammonium phosphate. Hydrobiologia 128:233–237
Palanivelu V, Vijayavel K, Ezhilarasibalasubramanian S, Balasubramanian MP (2005) Impact of fertilizer (urea) on oxygen consumption and feeding energetics in the fresh water fish Oreochromis mossambicus. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 19:351–355
Pettersson M, Ekelund NGA (2006) Effects of the herbicides Roundup and Avans on Euglena gracilis. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 50:175–181
Rai LC, Gaur JP, Soeder CJ (1994) Algae and water pollution, E. Schweizerbart'sche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart
Richter PR, (2000) Untersuchungen zur Gravitaxis (in German). Friedrich-Alexander-University Erlangen-Nuremberg
Richter P, Börnig A, Streb C, Ntefidou M, Lebert M, Häder D-P (2003) Effects of increased salinity on gravitaxis in Euglena gracilis. J Plant Physiol 160:651–656
Richter P, Helbling W, Streb C, Häder D-P (2007) PAR and UV effects on vertical migration and photosynthesis in Euglena gracilis. Photochem Photobiol 83:818–823
Rottenberg H, Grunwald T, Avron M (1971) Direct determination of ∆pH in chloroplasts, and its relation to the mechanisms of photoinduced reactions. FEBS Lett 13:41–44
Sakamoto T, Delgaizo VB, Bryant DA (1998) Growth on urea can trigger death and peroxidation of the Cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. strain PCC 7002. Appl Environ Microbiol 64:2361–2366
Schlösser UG (1994) SAG—Sammlung von Algenkulturen at the University of Göttingen. Bot Acta 107:113–186
Shilo M (1971) Toxins of chrysophyceae. In: Kadis S, Ciegler A, Ajl SJ (eds) Microbial toxins, VII. Academic Press, New York, pp 67–103
Stallwitz E, Häder D-P (1994) Effects of heavy metals on motility and gravitactic orientation of the flagellate, Euglena gracilis. Eur J Protistol 30:18–24
Starr RC (1964) The culture collection of algae at Indiana University. Am J Bot 51:1013–1044
Sumida S, Lyman H, Kiyohara N, Osafune T (2007) Mechanism of conversion from heterotrophy to autotrophy in Euglena gracilis. Cytologia 72:447–457
Tahedl H, Häder D-P (1999) Fast examination of water quality using the automatic biotest ECOTOX based on the movement behavior of a freshwater flagellate. Water Res 33:426–432
Tahedl H, Häder D-P (2001) Automated biomonitoring using real time movement analysis of Euglena gracilis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 48:161–169
Takenaka S, Kondo T, Nazeri S, Tamura Y, Tokunaga M, Tsuyama S, Miyatake K, Nakano Y (1997) Accumulation of trehalose as a compatible solute under osmotic stress in Euglena gracilis Z. J Eukaryot Microbiol 44:609–613
Tchounwou PB, Englande AJ, Malek EA (1991) Toxicity evaluation of ammonium sulphate and urea to three developmental stages of freshwater snails. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 21:359–364
Trivedi SP, Singh P, Singh RK (1990) Evaluation of hematotoxic effects of two commonly used fertilizers, diammonium phosphate and urea, on fish Clarias batrachus. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 19:135–142
Velthuys BR (1980) Mechanisms of electron flow in photosystem II and toward photosystem I. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 31:545–567
Warren KS (1962) Ammonia toxicity and pH. Nature 195:47–49
Yancey PH, Clark ME, Hand SC, Bowlus RD, Somero GN (1982) Living with water stress: evolution of osmolyte systems. Science 217:1214–1222
Zhang Z, Dmitrieva NI, Park JH, Levine RL, Burg MB (2004) High urea and NaCl carbonylate proteins in renal cells in culture and in vivo, and high urea causes 8-oxoguanine lesions in their DNA. Proc Nat Acad Sci USA 101:9491–9496
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Kohat University of Science and Technology (KUST), Kohat, Pakistan for granting a scholarship to Azizullah. The skilful and technical support of Ulrike Trenz and Adeel Nasir is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Azizullah, A., Richter, P. & Häder, DP. Responses of morphological, physiological, and biochemical parameters in Euglena gracilis to 7-days exposure to two commonly used fertilizers DAP and urea. J Appl Phycol 24, 21–33 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9641-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-010-9641-4