Abstract
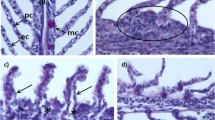
Juveniles of the European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax were exposed to both cell-free medium and whole cell cultures of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima strain PL2V. Fish were also fed a commercial fish diet in tanks containing live P. lima, and Artemia that had ingested the alga. Fish exposed to the cell-free medium and to whole cell cultures were stressed and behaved abnormally when compared to the behaviour of control fish, fish in normal seawater. Stress-related behaviours included hyperactivities (jumps, fast let-right turns, surface swims, etc), poor feeding reflexes and abstinence from feeding. Fish that directly ingested the alga or that ingested Artemia containing the alga died. Histological studies revealed that gills and liver of treated fish were impacted, as opposed to the normal conditions of same tissues in control fish. The diseased organs could have been responsible for the abnormal behaviours and death of treated fish. The aquaculture and ecological implications of the results are discussed.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ajuzie CC (1998) Aspects of behavior in European sea bass juveniles. Aquac Mag 24(2):37–44
Ajuzie CC (2002) Studies on the harmful algal bloom phenomenon: a first perception and monitoring in Nigerian coastal waters, and the effects of the DSP-causing dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima (Ehrenberg) Dodge on other aquatic biota. D.Sc. thesis, Université Libre de Bruxelles, Belgium
Ajuzie CC (2007) Palatability and fatality of the dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima to Artemia salina. J Appl Phycol doi: 10.1007/s10811-007-9164-9
Ajuzie CC, Appelbaum S (1993) Feed attractants for glass eels. Fish Farmer March/April:25–27
Ajuzie CC, Houvenaghel GT (2001) Allelopathic growth inhibition of Prorocentrum micans Ehrenberg by Prorocentrum lima (Ehrenberg) Dodge in laboratory cultures. Can Tech Rep Fish Aquat Sci 2386:54–66
Ajuzie CC, Houvenaghel GT (2003) Prorocentrum lima is toxic to juveniles of the European sea bass Dicentrarchus labrax. Can Tech Rep Fish Aquat Sci 2498:37–45
Andersen RJ, Luu HA, Chen DZX, Holmes CFB, Kent ML, Leblanc L, Taylor FJR, Williams DE (1993) Chemical and biological evidence links microcystins to salmon “netpen liver disease”. Toxicon 31:1315–1323
Arzul G, Bodennec G, Gentien P, Bornens P, Crassous M-P (1998) The effect of dissolved oxygen on the haemolytic property of Gymnodinium ichthyotoxins. In: Reguera B, Blanco J, Fernández ML, Wyatt T (eds) Harmful Algae. Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, pp 611–614
Barbier M, Amzil Z, Mondeguer F, Bhaud Y, Soyer-Gobillard M-O, Lassus P (1999) Okadaic acid and PP2A cellular immunolocalization in Prorocentrum lima (Dinophyceae). Phycologia 38:41–46
Bomber JW, Morton SL, Babinchak JA, Norris DR, Morton JG (1988) Epiphytic dinoflagellates of drift algae-another toxigenic community in the ciguatera food chain. Bull Mar Sci 43:204–214
Bravo I, Fernández ML, Ramilo I, Martínez A (2001) Toxin composition of the toxic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima isolated from different locations along the Galician coast (NW Spain). Toxicon 39:1537–1545
Colin DA, Kirsch R, Leray C (1979) Haemodynamic effects of adenosine on gills of the trout (Salmo gairdneri). J Comp Physiol 130:325–330
Drenner RW, Mummert JR, de Noyelles F Jr, Kettle D (1984) Selective particle ingestion by a filter-feeding fish and its impact on phytoplankton community structure. Limnol Oceanogr 29:941–948
Drenner RW, Hambright KD, Vinyard GL, Gophen M, Pollingher U (1987) Experimental study of size-selective phytoplankton grazing by a filter-feeding cichlid and the cichlid’s effects on plankton community structure. Limnol Oceanogr 32:1138–1144
Edebo L, Hovgaard P, Hu Y, Li XP (1992) On the presence of diarrheic shellfish toxins in fish. Planta Med 58(Suppl. Issue 1):A583–A584
Faust MA (1993a) Alternate asexual reproduction of Prorocentrum lima in culture. In: Smayda TJ, Shimizu Y (eds) Toxic phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 115–120
Faust MA (1993b) Sexuality in a toxic dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum. In: Smayda TJ. Shimizu Y (eds) Toxic phytoplankton blooms in the sea. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 121–126
Grzebyk D, Denardou A, Berland B, Pouchus YF (1997) Evidence of a new toxin in the red-tide dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima. J Plankt Res 19:1111–1124
Haya K, Martin JL, Waiwood BA, Burridge LE, Hungerford JM, Zitko V (1990) Identification of paralytic shellfish toxins in mackerel from southwest Bay of Fundy, Canada. In: Graneli E, Sundstrom B, Edler L, Anderson DM (eds) Toxic marine phytoplankton. Elsevier, New York pp 350–355
Heerbrand TC, Lin J (2006) Larviculture of red front shrimp, Caridina gracilirostris (Atyidae, Decapoda). J World Aquacult Soc 37:186–190
Ho KC, Hodgkiss IJ (1993) The occurrence and environmental significance of red tides caused by Prorocentrum minimum. Book of Abstracts 6th Int. Conf. on Toxic Phytoplankton, Nantes, France, 18–22 Oct. 1993 p 99
Houvenaghel GT, Huet T (1987) Computer-aided production modeling in fish farming, application to the eel. In: Balchen JG (ed) Automation and data processing in aquaculture (IFAC). Pergamon Press, Oxford pp 105–108
Houvenaghel GT, Huet T (1989) A model for eel growth in aquaculture. In: De Pauw N, Jaspers E, Ackefors H, Wilkins N (eds) Aquaculture a biotechnology in Progress, vol. 1. European Aquaculture Society, Bredene pp 179–184
Hughes GM, Perry SF (1976) Morphometric study of trout gills: a light-microscopic method suitable for the evaluation of pollutant action. J Exp Biol 64:447–468
Huynh C, Pinelli E, Puiseux-Dao S, Boulekbache H, Pfohl-Leszkowicz A (1998) Okadiac acid and DNA aduct formation. In: Reguera B, Blanco J, Fernández ML, Wyatt T (eds) Harmful algae. Grafisant, Spain pp 581–583
Jenkinson IR, Arzul G (1998) Effects of the flagellates, Gymnodinium mikimotoi, Heterosigma akashiwo and Pavlova lutheri, on flow through fish gills. In: Reguera B, Blanco J, Fernández ML, Wyatt T (eds) Harmful algae. Grafisant, Spain pp 425–428
Jones KJ, Ayres P, Bullock AM, Roberts RJ, Tett P (1982) A red tide of Gyrodinium aureolum in sea lochs of the Firth of Clyde and associated mortality of pond-reared salmon. J Mar Biol Ass U.K. 62:771–782
Juell J-E (1995) The behaviour of Atlantic salmon in relation to efficient cage-rearing. Rev Fish Biol Fish 5(3):320–335
Keller M, Selvin RC, Claus A, Guillard RRL (1987) Media for the culture of oceanic ultraplankton. J Phycol 23:633–638
Kelly AM, Kohler CC, Tindall DR (1992) Are crustaceans linked to the ciguatera food chain? Environ Biol Fish 33:275–286
Kent ML (1990) Netpen liver disease (NLD) of salmonid fishes reared in seawater; species susceptibility, recovery, and probable cause. Dis Aquat Org 8:21–28
Kent ML, Myers MS, Hinton DE, Eaton WD, Elston RA (1988) Suspected toxicopathic hepatic necrosis and megalocytosis in pen-reared Atlantic salmon Salmo salar in Puget Sound, Washington, USA. Dis Aquat Org 4:91–100
Kim CS, Bae HM, Yun SJ, Cho YC, Kim HG (2000a) Ichthyotoxicity of a harmful dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides: aspect of hematological responses of fish exposed to algal blooms. J Fish Sci Tech 3:111–117
Kim CS, Lee SG, Kim HG (2000b) Biochemical responses of fish exposed to harmful dinoflagellate Cochlodinium polykrikoides. J Exp Mar Biol 254:131–141
Kohler CC, Paleudis GA, Tindall DR (1989) Behavioral abnormalities displayed by ocean surgeon following consumption of ciguatoxigenic dinoflagellates. Proc Assn Is Mar Lab Carib 22:34
Kudela R, Grant P, Probyn T, Figueiras F, Moita T, Trainer V (2005) Harmful algal blooms in coastal upwelling systems. Oceanography 18:184–197
Laurent P (1984) Morphologie et physiology des organes de la respiration aquatique chez les Vertébrés: la branchie. J Physiol Paris 79:98–112
Lawrence JE, Bauder AG, Quilliam MA, Cembella A (1998) Prorocentrum lima: a putative link to diarrhetic shellfish poisoning in Nova Scotia, Canada. In: Reguera B, Blanco J, Fernández ML, Wyatt T (eds) Harmful algae. Grafisant, Spain pp 78–79
Lawrence JE, Grant J, Quilliam MA, Bauder AG, Cembella AD (2000) Colonization and growth of the toxic dinoflagellate Prorocentrum lima and associated fouling macroalgae on mussels in suspended culture. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 201:147–154
Lee J-S, Igarashi T, Fraga S, Dahl E, Hovgaard P, Yasumoto T (1989) Determination of diarrhetic shellfish toxins in various dinoflagellate species. J Appl Phycol 1:147–152
Lewis RJ (1992) Ciguatoxins are potent ichthyotoxins. Toxicon 30:207–211
Linden T, Al Houari D (1993) Hydroacoustic monitoring of fish in Aquaculture—a method for automatic feeding control by detection of fish behaviour. ICES Statutory Meeting 1993. C.M. 1993/F:45/Session/T
Lu S, Hodgkiss IJ (2004) Harmful algal bloom causative collected from Hong Kong waters. Hydrobiologia 512:231–238
Lu J, Takeuchi T, Satoh H (2004) Ingestion and assimilation of three species of freshwater algae by larval tilapia Oreochromis niloticus. Aquaculture 238:437–449
Lush GJ, Hallegraeff GM (1996) High toxicity of the red tide dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum to the brine shrimp Artemia salina. In: Yasumoto T, Oshima Y, Fukuyo Y (eds) Harmful and toxic algal blooms. UNESCO, Paris pp 389–392
Lush GJ, Hallegraeff GM, Munday BL (1998) Histopathological effects in juvenile greenback flounder Rhombosolea taparina exposed to the toxic dinoflagellate Alexandrium minutum. In: Reguera B, Blanco J, Fernández ML, Wyatt T (eds) Harmful algae. Grafisant, Spain pp 609–610
Martínez-Fernández E, Acosta-Salmon H, Rangel-Dávalos C (2004) Ingestion and digestion of 10 species of microalgae by winged pearl oyster Pteria sterna (Gould, 1851) larvae. Aquaculture 230:417–423
Noga EJ (1998) Toxic algae, fish kills and fish disease. Fish Pathol 33:337–342
Okaichi T (1989) Red tide problems in Seto Inland Sea, Japan. In: Okaichi T, Anderson DM, Nemoto T (eds) Red tides: biology, environmental science and toxicology. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 137–142
Pärt P, Tuurala H, Soivio A (1982) Oxygen transfer, gill resistance and structural changes in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri, Richardson) gills perfused with vasoactive agents. Comp Biochem Physiol 71C:7–13
Phillips MJ, Roberts RJ, Stewart JA, Codd GA (1985) The toxicity of the cyanobacterium Microcystis aeruginosa to rainbow trout, Salmo gairdneri Richardson. J Fish Dis 8:339–344
Pillet S, Pereira A, Braekman JC, Houvenaghel G (1995) Patterns in long-term accumulation of okadaic acid and DTX1 in blue mussels, Mytilus edulis, experimentally fed with DSP containing alga Prorocentrum lima. In: Lassus P, Arzul G, Erard-Le Denn E, Gentien P, Marcaillou-Le Baut C (eds) Harmful marine algal blooms. Lavoisier Intercept Ltd, Paris pp 487–492
Prince EK, Lettieri L, McCurdy KJ, Kubanek J (2006) Fitness consequences for copepods feeding on a red tide dinoflagellate: deciphering the effects of nutritional value, toxicity, and feeding behavior. Oecologia 147:479–488
Rabbani MM, Atiq-Ur-Rehman, Harms CE (1990) Mass mortality of fishes caused by dinoflagellate bloom in Gwadar Bay, Southwestern Pakistan. In: Granéli E, Sundström B, Edler L, Anderson DM (eds) Toxic marine phytoplankton. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 209–212
Råbergh CMI, Bylund G, Eriksson JE (1991) Histopathological effects of microcystin-LR, a cyclic peptide toxin from the cyanobacterium (blue-green alga) Microcystis aeruginosa, on common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Aquat Toxicol 20:131–146
Rangel I (2002) Taxonomia fitoplanctónica e mares vermelhas em Angola.10as Jornadas Técnico Cientificas do Instituto de Investigaçao Marinha. Luanda, Angola
Rausch de Traubenberg CR, Morlaix M (1995) Evidence of okadaic acid release into extracellular medium in cultures of Prorocentrum lima (Ehrenberg) Dodge. In: Lassus P, Arzul G, Erard-Le Denn E, Gentien P, Marcaillou-Le Baut C (eds) Harmful marine algal blooms. Lavoisier Intercept Ltd, Paris pp 493–498
Rensel JE (1995) Management of finfish aquaculture resources. In: Hallegraeff GM, Anderson DM, Cembella AD (eds) Manual on harmful marine microalgae. IOC Manuals and Guides No. 33. UNESCO. 463–474
Roberts RJ (1978) The pathophysiology and systematic pathology of theleosts. In: Roberts RJ (ed) Fish pathology. Bailliere Tindall, London pp 55–91
Robineau B, Gagné JA, Fortier L, Cembella AD (1991) Potential impact of a toxic dinoflagellate (Alexandrium excavatum) bloom on survival of fish and crustacean larvae. Mar Biol 108:293–301
Runge J, Bragford B, Cattet M, Haya K, Paranjape M, Pauley K, Robineau B, Roy S, Stasko A, Turriff N (1992) Transfer of phycotoxins in the pelagic foodweb. Can Tech Rep Fish Aqua Sci 1893:73–80
Speare DJ, Ferguson HW (1989) Fixation artifacts in rainbow trout (Salmo gairdneri) gills: a morphometric evaluation. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 46:780–785
Steidinger KA (1993) Some taxonomic and biologic aspects of toxic dinoflagellates. In: Falconer IR (ed) Algal toxins in seafood and drinking water. Academic Press, London pp 1–28
Sueoka E, Fujiki H (1998) Carcinogenesis of okadaic acid class tumor promoters derived from marine natural products. In: Reguera B, Blanco J, Fernández ML, Wyatt T (eds) Harmful algae. Grafisant, Spain pp 573–576
Takayama H, Adachi R (1984) Gymnodinium nagasakiense sp. nov., a red-tide forming dinoflagellate in the adjacent waters of Japan. Bull Plankton Soc Japan 31:7–14
Tang KW, Dam HG (2001) Phytoplankton inhibition of copepod egg hatching: test of an exudates hypothesis. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 209:197–202
Torigoe K, Murata M, Yasumoto T, Iwashita T (1988) Prorocentrolide, a toxic nitrogenous macrocyle from a marine dinoflagellate, Prorocentrum lima. J Am Chem Soc 110:7876–7877
Toyoshima T, Ozaki HS, Shimada M, Okaichi T, Murakami TH (1985) Ultrastructural alterations on chloride cells of the yellowtail Seriola quinqueradiata, following exposure to the red tide species Chattonella antiqua. Mar Biol 88:101–108
White AW (1981a) Sensitivity of marine fishes to toxins from the red-tide dinoflagellate Gonyaulax excavata and implications for fish kills. Mar Biol 65:255–260
White AW (1981b) Marine zooplankton can accumulate and retain dinoflagellate toxins and cause fish kills. Limnol Oceanogr 26:103–109
White AW, Fukuhara O, Anraku M (1989) Mortality of fish larvae from eating toxic dinoflagellates or zooplankton containing dinoflagellate toxins. In: Okaichi T, Anderson DM, Nemoto T (eds) Red tides: biology, environmental science, and toxicology. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 395–398
Yamamori K, Nakamura M, Matsui T, Hara TJ (1988) Gustatory responses to tetrodotoxin and saxitoxin in fish: a possible mechanism for avoiding marine toxins. Can J Fish Aquat Sci 45:2182–2186
Yang CZ, Albright LJ (1992) Effects of the harmful diatom, Chaetoceros concavicornis on respiration of rainbow trout Oncorhynchus mykiss. Dis Aquat Org 14:105–114
Yuki K, Yoshimatsu S (1989) Two fish-killing species of Cochlodinium from Harima Nada, Seto Inland Sea, Japan. In: Okaichi T, Anderson DM, Nemoto T (eds) Red tides: biology, environmental science and toxicology. Elsevier, Amsterdam pp 451–454
Acknowledgements
Support for this study came from “Fondation David & Alice Van Buuren”, ULB, and “Fondation de Meurs-François”, ULB. I thank G. Houvenaghel for his invaluable suggestions and support during the course of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ajuzie, C.C. Toxic Prorocentrum lima induces abnormal behaviour in juvenile sea bass. J Appl Phycol 20, 19–27 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-007-9176-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10811-007-9176-5