Abstract
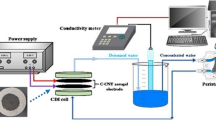
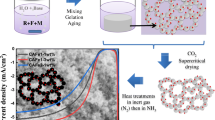
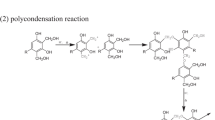
Three-activated carbon aerogels were synthesized by CO2 activation of the materials prepared by the polycondensation of resorcinol and formaldehyde mixtures followed by supercritical drying. The obtained carbon aerogels were characterized and used as electrode materials for the electrosorption of sodium phosphate and nitrate. X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy showed the dependence of the structural ordering of the aerogels with the resorcinol/catalyst ratio and the extent of activation. The electrosorption capacitance evaluated by cyclic voltammetry revealed large values for the activated samples containing a large contribution of mesopores, regardless the electrolyte salt. Due to an adequate combination of chemical and porous features, the desalting capacity of the activated carbon aerogel electrodes exceeded that of the as-prepared materials. The evaluation of the kinetic properties by chronocoulometric relaxation and impedance spectroscopy showed a decrease of time constant and resistances for highly mesoporous activated samples. A high deionization capacity and fast electrode discharge was detected for the deionization of sodium nitrate on the highly mesoporous activated aerogel. Data also showed the efficient electrosorption of ionic species on consecutive charge/discharge cycles, confirming the stability of the aerogel electrodes at the high applied potentials.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Porada S, Zhao R, van der Wal A, Presser V, Biesheuvel PM (2013) Review on the science and technology of water desalination by capacitive deionization. Prog Mater Sci 58:1388–1442
Candelaria SL, Shao Y, Zhou W, Li X, Xiao J, Zhang JG, Wang Y, Liu J, Li J, Cao G (2012) Nanostructured carbon for energy storage and conversion. Nano Energy 1:195–220
Oren Y (2008) Review on the science and technology of water desalination by capacitive deionization. Desalination 228:10–29
Marsh H, Rodríguez-Reinoso F (2006) Activated carbon. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Anderson MA, Cudero AL, Palma J (2010) Capacitive deionization as an electrochemical means of saving energy and delivering clean water. Comparison to present desalination practices: will it compete? Electrochim Acta 55:3845–3856
Dehkhoda AM, Ellis N, Gyenge E (2014) Electrosorption on activated biochar: effect of thermo-chemical activation treatment on the electric double layer capacitance. J Appl Electrochem 44:141–157
Peng Z, Zhang D, Shi L, Yan T, Yuan S, Li H, Gao R, Fang J (2011) Comparative electroadsorption study of mesoporous carbon electrodes with various pore structures. J Phys Chem C 115:17068–17076
Ania CO, Pernak J, Stefaniak F, Raymundo-Pinero E, Beguin F (2009) Polarization-induced distortion of ions in the pores of carbon electrodes for electrochemical capacitors. Carbon 47:3158–3166
Chmiola J, Largeot C, Taberna PL, Simon P, Gogotsi Y (2008) Desolvation of ions in subnanometer pores and its effect on capacitance and double layer theory. Angew Chem 47:1–5
Zhang D, Yan T, Shi L, Peng Z, Wen X, Zhang J (2012) Enhanced capacitive deionization performance of graphene/carbon nanotube composites. J Mater Chem 22:14696–14704
Liang P, Yuan L, Yang X, Zhou S, Huang X (2013) Coupling ion-exchangers with inexpensive activated carbon fiber electrodes to enhance the performance of capacitive deionization cells for domestic wastewater desalination. Water Res 47:2523–2530
Seo SJ, Jeon H, Lee JK, Kim GY, Park D, Nojima H, Lee J, Moon SH (2010) Investigation on removal of hardness ions by capacitive deionization (CDI) for water softening applications. Water Res 44:2267–2275
Porada S, Weinstein L, Dash R, van der Wal A, Bryjak M, Gogotsi Y, Biesheuvel PM (2012) Water desalination using capacitive deionization with microporous carbon electrodes. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 4:1194–1199
Punckt C, Pope MA, Liu J, Lin Y, Aksay IA (2010) Electrochemical performance of graphene as effected by electrode porosity and graphene functionalization electroanalysis. Electroanalysis 22:2834–2841
Ban A, Schafer A, Wendt H (1998) Fundamentals of electrosorption on activated carbon for wastewater treatment of industrial effluents. J Appl Electrochem 157:602–615
Tsouris C, Mayes R, Kiggans J, Sharma K, Yiacoumi S, DePaoli D, Dai S (2011) Mesoporous carbon for capacitive deionization of saline water. Environ Sci Technol 45:10243–10249
Xu LY, Shi ZG, Feng YQ (2008) Preparation of a carbon monolith with bimodal perfusion pores. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 115:618–623
Wen X, Zhang D, Yan T, Wang H, Zhang J, Shi L (2013) Three-dimensional graphene-based hierarchically porous carbon composites prepared by a dual-template strategy for capacitive deionization. J Mater Chem A 1:12334–12344
Wang H, Shi L, Yan T, Zhang J, Zhong Q, Zhang D (2014) Design of graphene-coated hollow mesoporous carbon spheres as high performance electrodes for capacitive deionization. J Mater Chem A 2:4739–4750
Pekala RW, Farmer JC, Alviso CT, Tran TD, Mayer ST, Miller JM, Dunn B (1998) Carbon aerogels for electrochemical applications. J Non Cryst Solids 225:74–80
Gross J, Scherer GW, Alviso CT, Pekala RW (1997) Elastic properties of crosslinked resorcinol–formaldehyde gels and aerogels. J Non Cryst Solids 211:132–142
Hadas A, Sagiv B, Haruvy N (1999) Agricultural practices, soil fertility management modes and resultant nitrogen leaching rates under semi-arid conditions. Agric Water Manag 42:81–95
Broséus R, Cigana J, Barbeau B, Daines-Martinez C, Suty H (2009) Removal of total dissolved solids, nitrates and ammonium ions from drinking water using charge-barrier capacitive deionisation. Desalination 249:217–223
Pekala RW (1989) Organic aerogels from the polycondensation of resorcinol with formaldehyde. J Mater Sci 24:3221–3227
Haro M, Rasines G, Macías C, Ania CO (2011) Stability of a carbon gel electrode when used for the electro-assisted removal of ions from brackish water. Carbon 49:3723–3730
Rouquerol F, Rouquerol J, Sing K (1999) Adsorption by powders and porous solids. Academic Press, London
Tuinstra F, Koenig JL (1970) Raman spectrum of graphite. J Chem Phys 53:1126–1130
Cuesta A, Dhamelincourt P, Laureyns J, Martinez-Alonso A, Tascon JMD (1994) Raman microprobe studies on carbon materials. Carbon 32:1523–1532
Jawhari T, Roid A, Casado J (1995) Raman spectroscopic characterization of some commercially available carbon black materials. Carbon 33:1561–1565
Sze SK, Siddique N, Sloan JJ, Escribano R (2001) Raman spectroscopic characterisation of carbonaceous aerosol. Atmos Environ 35:561–568
Dresselhaus MS, Dresselhaus G (1982) Light-scattering in graphite-intercalation compounds. Springer, Berlin
Rouzaud JN, Oberlin A, Beny-Bassez C (1983) Carbon-films-structure and microtexture (optical and electron-microscopy, raman-spectroscopy). Thin Solid Films 105:75–96
Dippel B, Jander H, Heintzenberg J (1999) NIR FT Raman spectroscopic study of flame soot. Phys Chem Chem Phys 1:4707–4712
Biniak S, Szymanski G, Siedlewski J, Swiatkowski A (1997) The characterization of activated carbons with oxygen and nitrogen surface groups. Carbon 35:1799–1810
Oh HJ, Lee JH, Ahn H-J, Jeong Y, Kim YJ, Chi CS (2006) Nanoporous activated carbon cloth for capacitive deionization of aqueous solution. Thin Solid Films 515:220–225
Tamon H, Ishizaka H, Araki T, Okazaki M (1998) Control of mesoporous structure of organic and carbon aerogels. Carbon 36:1257–1262
Job N, Thery A, Pirard R, Marien J, Kocon L, Rouzaud JN, Beguin F, Pirard JP (2005) Carbon aerogels, cryogels and xerogels: influence of the drying method on the textural properties of porous carbon materials. Carbon 43:2481–2494
Tamon H, Ishizaka H, Mikami M, Okazaki M (1997) Porous structure of organic and carbon aerogels synthesized by sol–gel polycondensation of resorcinol with formaldehyde. Carbon 35:791–796
Peng Z, Zhang D, Yana T, Zhang J, Shi L (2013) Three-dimensional micro/mesoporous carbon composites with carbon nanotube networks for capacitive deionization. Appl Surf Sci 282:965–973
Hsieh CT, Teng H (2002) Influence of oxygen treatment on electric double-layer capacitance of activated carbon fabrics. Carbon 40:667–674
Pröbstle H, Wiener M, Fricke J (2003) Carbon aerogels for electrochemical double layer capacitors. J Porous Mater 10:213–222
Huang W, Zhang Y, Bao S, Cruz R, Song S (2014) Desalination by capacitive deionization process using nitric acid-modified activated carbon as the electrodes. Desalination 340:67–72
Wen X, Zhang D, Shi L, Yan T, Wang H, Zhang J (2012) Three-dimensional hierarchical porous carbon with a bimodal pore arrangement for capacitive deionization. J Mater Chem 22:23835–23844
Peng Z, Zhang D, Shi L, Yan T (2012) High performance ordered mesoporous carbon/carbon nanotube composite electrodes for capacitive deionization. J Mater Chem 22:6603–6612
Noked M, Avraham E, Soffer A, Aurbach D (2009) The rate-determining step of electroadsorption processes into nanoporous carbon electrodes related to water desalination. J Phys Chem C 113:21319–21327
Miller JM, Dunn B (1999) Morphology and electrochemistry of ruthenium/carbon aerogel nanostructures. Langmuir 15:799–806
Zafra MC, Lavela P, Macías C, Rasines G, Tirado JL (2013) Electrosorption of environmental concerning anions on a highly porous carbon aerogel. J Electroanal Chem 708:80–86
Yang J, Zou L (2014) Using recyclable calcium citrate templates to prepare mesoporous carbons as electrodes for capacitive deionization. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 183:91–98
Afkhami A (2003) Adsorption and electrosorption of nitrate and nitrite on high-area carbon cloth: an approach to purification of water and waste-water samples. Carbon 41:1309–1328
Acknowledgments
The authors are indebted to the MICINN (Contract IPT-2011-1450-310000 (ADECAR), and CTM2011/23378) for the financial support. We also thank the fruitful collaboration of Isolux Ingeniería, S.A., Fundación Imdea Energia and Proingesa.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Macías, C., Lavela, P., Rasines, G. et al. Improved electro-assisted removal of phosphates and nitrates using mesoporous carbon aerogels with controlled porosity. J Appl Electrochem 44, 963–976 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-014-0705-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10800-014-0705-z