Abstract
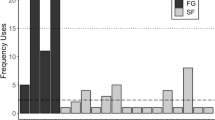
Studying sleeping behavior can provide key information for understanding the ecology of a species. Antipredation is an important factor that affects primate sleeping behavior. We studied antipredation sleeping behavior in skywalker hoolock gibbons (Hoolock tianxing). We studied one group (NA) and a solitary female (NB) at Nankang from July 2010 to September 2011, and another group (BB) at Banchang from May 2013 to December 2014 in Mt. Gaoligong, Yunnan, China. Over the study period, we recorded 67 sleeping trees for members of group NA over 92 days, 17 trees for the solitary female NB over 22 days, and 159 trees for members of group BB over 186 days. Skywalker hoolock gibbons at both sites rarely used the same tree on consecutive days (N = 3 at both sites). They traveled fast to enter sleeping tree a mean of 160 ± SD 43 min before sunset at Nankang, and a mean of 192 ± SD 40 min before sunset at Banchang. They seldom (Nankang: 14%, N = 183 observations; Banchang: 25%, N = 548 observations) defecated in sleeping trees. They slept at sites with more tall and large trees and preferred to sleep on tall trees in the site. They slept on branches of small diameter and closer to tree tops. Our study suggests that antipredation plays an important role in skywalker hoolock gibbons’ sleeping tree selection and sleeping behavior. In addition, our data suggest potential effects of habitat degradation on gibbons’ sleeping behavior. Tall trees are especially important for gibbons in degraded forest and should be protected.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson, J. R. (1998). Sleep, sleeping sites, and sleep-related activities: awakening to their significance. American Journal of Primatology, 46, 63–75.
Anderson, J. R. (2000). Sleep-related behavioural adaptations in freeranging anthropoid primates. Sleep Medicine Reviews, 4, 355–373.
Barnett, A. A., Shaw, P., Spironello, W. R., Maclarnon, A., & Ross, C. (2012). Sleeping site selection by golden-backed uacaris, Cacajao melanocephalus ouakary (Pitheciidae), in Amazonian flooded forests. Primates, 53, 273–285.
Caine, N. G. (1987). Vigilance, vocalizations, and cryptic behavior at retirement in captive groups of red-bellied tamarins (Saguinus labiatus). American Journal of Primatology, 12, 241–250.
Caine, N. G., Potter, M. P., & Mayer, K. E. (1992). Sleeping site selection by captive tamarines (Saguinus labiatus). Ethology, 90, 63–71.
Carvalho, J. S., Meyer, C. F. J., Vicente, L., & Marques, T. A. (2015). Where to nest? Determinants of chimpanzee nest abundance and distribution at the habitat and tree species scale. American Journal of Primatology, 77(2), 186–199.
Chapman, C. A. (1989). Spider monkey sleeping sites: use and availability. American Journal of Primatology, 18, 53–60.
Chapman, C. A., Chapman, L. K., & McLaughlin, R. L. (1989). Multiple central place foraging by spider monkeys: travel consequences of using many sleeping sites. Oecologia, 79, 506–511.
Cheyne, S. M., Höing, A., Rinear, J., & Sheeran, L. K. (2013). Sleeping site selection by agile gibbons: the influence of tree stability, fruit availability and predation risk. Folia Primatologica, 83, 299–311.
Di Bitetti, M. S., Vidal, E. M. L., Baldovino, M. C., & Benesovsky, V. (2000). Sleeping site preferences in tufted capuchin monkeys (Cebus paella nigritus). American Journal of Primatology, 50, 257–274.
Duarte, M. H. L., & Young, R. J. (2011). Sleeping site selection by urban marmosets (Callithric penicillata) under conditions of exceptionally high predator density. International Journal of Primatology, 32(2), 329–334.
Ducourtieux, O., Visonnavong, P., & Rossard, J. (2006). Introducing cash crops in shifting cultivation regions: the experience with cardamom in Laos. Agroforestry Systems, 66(1), 65–76.
Estrada, A., Raboy, B. E., & Oliveira, L. C. (2012). Agroecosystems and primate conservation in the tropics: a review. American Journal of Primatology, 74(8), 696–711.
Fan, P. F., & Jiang, X. L. (2008). Sleeping sites, sleeping trees, and sleep-related behaviors of black crested gibbons (Nomascus concolor jingdong) at Mt. Wuliang, central Yunnan, China. American Journal of Primatology, 70(2), 153–160.
Fan, P. F., Xiao, W., Huo, S., Ai, H. S., Wang, T. C., & Lin, R. T. (2011). Distribution and conservation status of the vulnerable eastern hoolock gibbon Hoolock leuconedys in China. Oryx, 45(1), 129–134.
Fan, P. F., Ai, H. S., Fei, H. L., Zhang, D., & Yuan, S. D. (2013). Seasonal variation of diet and time budget of eastern hoolock gibbons (Hoolock leuconedys) living in a northern montane forest. Primates, 54(2), 137–146.
Fan, P. F., He, K., Chen, X., Ortiz, A., Zhang, B., et al (2017). Description of a new species of Hoolock gibbon (Primates: Hylobatidae) based on integrative taxonomy. American Journal of Primatology. doi:10.1002/ajp.22631.
Fei, H. L., Scott, M. B., Zhang, W., Ma, C. Y., & Fan, P. F. (2012). Sleeping tree selection of Cao Vit gibbon (Nomascus nasutus) living in degraded karst forest in Bangliang, Jingxi, China. American Journal of Primatology, 74(11), 998–1005.
Feilen, K. L., & Marshall, A. J. (2014). Sleeping site selection by proboscis monkeys (Nasalis larvatus) in west Kalimantan, Indonesia. American Journal of Primatology, 76, 1127–1139.
Heymann, E. W. (1995). Sleeping habits of tamarins, Saguinus mystax and Saguinus fuscicollis (Mammalia; Primates; Callitrichidae), in north-eastern Peru. Journal of Zoology, 237(2), 211–226.
Lan, D. Y., Ma, S. L., & Han, L. X. (1995). Distribution, population size and conservation of hoolock gibbons in west Yunnan. Study on the Mammal Biology in China, 1, 11–19.
Liu, Z. H., & Zhao, Q. K. (2004). Sleeping sites of Rhinopithecus bieti at Mt. Fuhe, Yunnan. Primates, 45(4), 241–248.
McCarthy, M. S., Lester, J. D., & Stanford, C. B. (2016). Chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) flexibly use introduced species for nesting and bark feeding in a human-dominated habitat. International Journal of Primatology. doi:10.1007/s10764-016-9916-y.
Phoonjampa, R., Koenig, A., Borries, G., Gale, G. A., & Savini, T. (2010). Selection of sleeping trees in pileated gibbons (Hylobates pileatus). American Journal of Primatology, 72, 617–625.
Reichard, U. (1998). Sleeping sites, sleeping places, and pre-sleep behavior of gibbons (Hylobates lar). American Journal of Primatology, 46, 35–62.
Seiler, M., Holderied, M., & Schwitzer, C. (2013). Effects of habitat degradation on sleeping site choice and use in sahamalaza sportive lemurs (Lepilemur sahamazensis). International Journal of Primatology, 34, 260–280.
Smith, A. C., Knogge, C., Huck, M., Lottker, P., Buchanan-Smith, H. M., & Heymann, E. W. (2007). Long-term patterns of sleeping site use in wild saddleback (Saguinus fuscicollis) and mustached tamarins (S. mystax): effects of foraging, thermoregulation, predation, and resource defense constraints. American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 134, 340–353.
Teichroeb, J. A., Holmes, T. D., & Sicotte, P. (2012). Use of sleeping trees by ursine colobus monkeys (Colobus vellerosus) demonstrates the importance of nearby food. Primates, 53, 287–296.
Tenaza, R., & Tilson, R. L. (1985). Human predation and Kloss’s gibbon (Hylobates klossii) sleeping trees in Siberut Island, Indonesia. American Journal of Primatology, 8, 299–308.
Von Hippel, F. A. (1998). Use of sleeping trees by black and white colobus monkeys (Colobus guereza) in the Kakamega forest, Kenya. American Journal of Primatology, 45, 281–290.
Wang, S. L., Luo, Y., & Cui, G. F. (2011). Sleeping site selection of Francois’s langur (Trachypithecus francoisi) in two habitats in Mayanghe National Nature Reserve, Guizhou, China. Primates, 52(1), 51–60.
Xiang, Z. F., Nie, S. G., Chang, Z. F., Wei, F. W., & Li, M. (2010). Sleeping sites of Rhinopithecus brelichi at Yangaoping, Guizhou. International Journal of Primatology, 31, 59–71.
Yin, L. Y., Fei, H. L., Chen, G. S., Li, J. H., Cui, L. W., & Fan, P. F. (2016). Effects of group density, hunting and temperature on the singing patterns of eastern hoolock gibbon (Hoolock leuconedys) in Gaoligongshan, southwest China. American Journal of Primatology, 78(8), 861–871.
Yuan, S. D., Fei, H. L., Zhu, S. H., Cui, L. W., Ai, H. S., & Fan, P. F. (2014). Effects of tsaolo (Fructus tsaoko) cultivating on tree diversity and canopy structure in the habitats of eastern hoolock gibbon (Hoolock leuconedys). Zoological Research, 35(3), 231–239.
Zhang, D., Yuan, S. D., Cui, L. W., & Fan, P. F. (2011). Singing behavior of eastern white-browed gibbon (Hoolock leuconedys) at Datang, Gaoligongshan nature reserve. Sichuan Journal of Zoology, 30, 856–860.
Zhou, Q. H., Huang, C. M., Li, M., & Wei, F. W. (2009). Sleeping site use by Trachypithecus francoisi at Nonggang nature reserve, China. International Journal of Primatology, 30, 353–365.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (#31160424), the National Program for Support of Top-notch Young Professionals in China, Small Nature Fund of Gaoligong National Nature Reserve (#201306, #201409, #201215), and Collaborative Innovation Center for Biodiversity and Conservation in the Three Parallel Rivers Region of China. We would like to thank the staff from the Gaoligongshan National Nature Reserve for their needed support. We also thank Mr. Yong Chai from Yunnan Forestry Academy of Sciences and Mr. Xiaochun Shi from Gaoligongshan National Nature Reserve for their kind help in identifying the plant herbariums. The manuscript was remarkably improved with the valuable comments from two anonymous reviewers and two editors, Prof. Joanna M. Setchell and Dr. Onja Harinala Razafindratsima.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
All authors claimed no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Handling Editor: Joanna M. Setchell
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fei, HL., Zhang, D., Yuan, SD. et al. Antipredation Sleeping Behavior of Skywalker Hoolock Gibbons (Hoolock tianxing) in Mt. Gaoligong, Yunnan, China. Int J Primatol 38, 629–641 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-017-9970-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10764-017-9970-0