Abstract
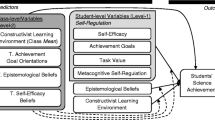
This study aimed to investigate the role of students’ classroom learning environment perceptions and teacher effectiveness in 7th grade students’ self-regulation in science classes. Students’ self-regulation was examined in terms of self-efficacy, achievement goals, and metacognitive strategy use which constitute important components of self-regulation. The relations of students’ perceived classroom learning environment (i.e. student cohesiveness, teacher support, involvement, investigation, task orientation, cooperation, and equity) and teacher effectiveness (i.e. teachers' beliefs, characteristics, and occupational well-being) to students’ self-regulation were tested by conducting separate HLM analyses considering the nested structure of the data. To select a nationally representative sample, two-stage random sampling approach was used. Data were collected from 372 science teachers and their 8198 seventh grade students in Turkey. Results indicated that perceived classroom learning environment variables were good predictors of students’ self-regulation in learning science. Among the learning environment variables, the task orientation appeared to be the most powerful predictor. Additionally, teacher variables were found to have direct relations with students’ self-regulation and moderate the relationships between learning environment and self-regulation variables.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ames, C. (1992). Clasrooms: Goals, structures, and student motivation. Journal of Educational Psychology, 84(3), 261–271.
Arisoy, N. (2007). Examining 8th grade students’ perception of learning environment of science classrooms in relation to motivational beliefs and attitudes (Unpublished master's thesis). Ankara: Middle East Technical University.
Ashton, P. T., & Webb, R. B. (1986). Making a difference: Teachers’ sense of efficacy and student achievement. New York, NY: Longman.
Bandura, A. (1977). Self-efficacy: Toward a unifying theory of behavioral change. Psychological Review, 84(2), 191–215.
Bandura, A. (1986). Social foundations of thought and action: A social cognitive theory. Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice-Hall.
Bandura, A. (1993). Perceived self-efficacy in cognitive development and functioning. Educational Psychologist, 28(2), 117–148.
Bandura, A. (1994). Self-efficacy. In V. S. Ramachaudran (Ed.), Encyclopedia of human behavior (Vol. 4, pp. 71–81). New York, NY: Academic Press.
Bandura, A. (1997). Self-efficacy: The exercise of control. New York, NY: H.Freeman.
Boekaerts, M. (1997). Self-regulated learning: A new concept embraced by researchers, policy makers, educators, teachers, and students. Learning and Instruction, 7, 161–186.
Bolyard, J. J., & Moyer-Packenham, P. S. (2008). A review of the literature on mathematics and science teacher quality. Peabody Journal of Education, 83(4), 509–535.
Bong, M. (2001). Between- and within-domain relations of academic motivation among middle and high school students: Self-efficacy, task value, and achievement goals. Journal of Educational Psychology, 93, 23–34.
Caprara, G. V., Barbaranelli, C., Steca, P., & Malone, P. S. (2006). Teachers’ self-efficacy beliefs as determinants of job satisfaction and students’ academic achievement: A study at the school level. Journal of School Psychology, 44, 473–490.
Church, M. A., Elliot, A. J., & Gable, S. L. (2001). Perceptions of classroom environment, achievement goals, and achievement outcomes. Journal of Educational Psychology, 93(1), 43–54.
Demirtas, Z. (2010). Teachers’ job satisfaction levels. Procedia Social and Behavioral Sciences, 9, 1069–1073.
den Brok, P., Fisher, D., Rickards, T., & Bull, E. (2006). Californian science students’ perceptions of their classroom learning environments. Educational Research and Evaluation: An International Journal on Theory and Practice, 12(1), 3–225.
den Brok, P., Telli, S., Cakiroglu, J., Taconis, R., & Tekkaya, C. (2010). Learning environment profiles of Turkish secondary biology classrooms. Learning Environment Research, 13, 187–204.
Dorman, J. P. (2001). Associations between classroom environment and academic efficacy. Learning Environment Research, 4, 243–257.
Dorman, J. P., Adams, J. E., & Ferguson, J. M. (2003). A cross-national investigation of students’ perceptions of mathematics classroom environment and academic efficacy in secondary schools. International Journal for Mathematics Teaching and Learning, 15. Retrieved February 16, 2018, from http://www.cimt.org.uk/journal/dormanj.pdf
Dweck, C. S. (1996). Implicit theories as organizers of goals and behavior. In P. M. Gollwitzer & J. A. Bargh (Eds.), The psychology of action: Linking cognition and motivation to behavior (pp. 69–90). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Dweck, C. S. (1999). Self-theories: Their role in motivation, personality, and development. Philedelphia, PA: Psychology Press.
Dweck, C. S., & Leggett, E. L. (1988). A social-cognitive approach to motivation and personality. Psychological Review, 95(2), 256–273.
Ee, J., Moore, P. J., & Atputhasamy, L. (2003). High-achieving students: Their motivational goals, self-regulation and achievement and relationship to their teachers' goals and strategy-based instruction. High Ability Studies, 14, 23–39.
Elliot, A. J., & McGregor, H. A. (2001). A 2x2 achievement goal framework. Journal of Personality and Social Psychology, 80(3), 201–519.
Farber, B. A. (1982). Stress and burnout: Implications for teacher motivation. New York, NY: Paper presented at the annual meeting of the American Educational Research Association (AERA).
Farber, B. A., & Miller, J. (1981). Teacher burnout: A psycho-educational perspective. Teachers College Record, 83(2), 235–243.
Flavell, J. (1979). Metacognition and cognitive monitoring. American Psychologist, 34(10), 906–911.
Fraser, B. J. (2002). Learning environments research: Yesterday, today and tomorrow. In S. C. Goh & M. S. Khine (Eds.), Studies in educational environments: An international perspective (pp. 1–25). Singapore: World Scientifiic.
Fraser, B. J. (2012). Classroom learning environments: Retrospect, context and prospect. In J. F. Fraser, K. G. Tobin, & C. J. McRobbie (Eds.), Second international handbook of science education (pp. 1191–1240). New York, NY: Springer.
Fraser, B. J., Fisher, D. L., & McRobbie, C. J. (1996). Development, validation and use of personal and class forms of a new classroom environment instrument. New York, NY: Paper presented at the annual meeting of American Educational Research Association.
Fraser, B. J., McRobbie, C. J., & Fisher, D. L. (1996). Development, validation and use of personal and class forms of a new classroom environment questionnaire. Proceedings Western Australian Institute for Educational Research Forum. Retrieved on February 16, 2018 from http://www.waier.org.au/forums/1996/fraser.html.
Fraser, B. J., & Walberg, H. J. (1991). Educational environments: Evaluation antecedents and consequences. Oxford: Pergamon Press.
Gherasim, L. R., Butnanu, S., & Mairean, C. (2012). Classroom environment, achievement goals and maths performance: Gender differences. Educational Studies, 39(1), 1–12.
Guo, Y., McDonald Connor, C., Yang, Y., Roehring, A. D., & Morrison, F. (2012). The effects of teacher qualification, teacher self-efficacy, and classroom practices on fifth graders’ literacy outcomes. The Elementary School Journal, 113(1), 3–24.
Haertel, G. D., Walberg, H. J., & Haertel, E. D. (1981). Socio-psychological environments and learning: A quantitative synthesis. British Educational Research Journal, 7(1), 27–36.
Hong, Y., Dweck, C. S., Chiu, C., Lin, D. M.-S., & Wan, W. (1999). Implicit theories, attributions, and coping: A meaning system approach. Journal of Personality & Social Psychology, 77(3), 588–690.
Hoy, A. W., & Davis, H. A. (2005). Teachers’ sense of efficacy and its influence on the achievement of adolescents. In F. Pajares & T. Urdan (Eds.), Adolescence and education: Vol. 5. Self-efficacy beliefs during adolescence (pp. 117–137). Greenwich, CT: Information Age.
Kim, H., Fisher, D. L., & Fraser, B. J. (2000). Classroom environment and teacher interpersonal behaviour in secondary science classes in Korea. Evaluation & Research in Education, 14(1), 3–22.
Klassen, R. M., Tze, V. C., Betts, S. M., & Gordon, K. A. (2011). Teacher efficacy research 1998–2009: Signs of progress or unfulfilled promise? Educational Psychology Research, 23, 21–43.
Klusmann, U., Kunter, M., Trautwein, U., Lüdtke, O., & Baumert, J. (2008). Teachers’ occupational well-being and quality of instruction: The important role of self-regulatory patterns. Journal of Educational Psychology, 100(3), 702–715.
Kyriacou, C. (2001). Teacher stress: Directions for future research. Educational Review, 53, 27–35.
Lau, S., Liem, A. D., & Nie, Y. (2008). Task- and self-related pathways to deep learning: The mediating role of achievement goals, classroom attentiveness, and group participation. British Journal of Educational Psychology, 78, 639–662.
Levy, J., den Brok, P., Wubbels, T., & Brekelmans, M. (2003). Students’ perceptions of interpersonal aspects of the learning environment. Learning Environments Research, 6, 5–26.
Lynott, D. J., & Woolfolk, A. E. (1994). Teachers’ implicit theories of intelligence and their educational goals. The Journal of Research and Development in Education, 27(4), 253–264.
Maslach, C., & Jackson, S. E. (1981). The measurement of experienced burnout. Journal of Occupational Behavior, 2, 99–113.
Maslach, C., & Leiter, M. P. (1999). Teacher burnout: A research agenda. In R. Vandenburghe, & M. Huberman (Eds.), Understanding and preventing teacher stress: A sourcebook of international research and practice (pp. 295-314). Cambridge: Cambridge.
Ministry of National Education of Turkey [MONE]. (2005). Science and technology curriculum of elementary schools (6th–8th grades). Ankara: Board of Education.
Ministry of National Education of Turkey [MONE]. (2010). PISA 2009 project national report. Retrieved on February 16, 2018 from http://pisa.meb.gov.tr/wp-content/uploads/2013/07/PISA-2009-Ulusal-On-Rapor.pdf
Ministry of National Education of Turkey [MONE]. (2011). TIMMS national report. Retrieved on February 16, 2018 from http://timss.meb.gov.tr/?page_id=25
Ololube, N. P. (2006). Teachers job satisfaction and motivation for school effectiveness: An assessment. Essays in Education, 18. Retrieved on March 6, 2018 from https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED496539.pdf
Pamuk, S., Sungur, S., & Oztekin, C. (2017). A multilevel analysis of students’ science achievements in relation to their self-regulation, epistemological beliefs, learning environment perceptions, and teachers’ personal characteristics. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 15(8), 1423–1440.
Pandey, S., & Elliot, W. (2010). Suppressor variables in social work research: Ways to identify in multiple regression models. Journal of the Society for Social Work and Research, 1(1), 28–40.
Paris, S. C., & Paris, A. H. (2001). Classroom applications of research on self-regulated learning. Educational Psychology, 36, 89–101.
Patrick, J., & Smart, R. M. (1998). An empirical evaluation of teacher effectiveness: The emergence of three critical factors. Assessment & Evaluation in Higher Education, 23(2), 165–178.
Peters, M. L. (2013). Examining the relationships among classroom climate, self-efficacy, and achievement in undergraduate mathematics: A multi-level analysis. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 11, 459–480.
Pintrich, P. R. (2000). The role of goal orientation in self-regulated learning. In M. Boekarts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 451–495). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Pintrich, P. R., Smith, D. A. F., Garcia, T., & McKeachie, W. J. (1991). A manual for the use of the motivated strategies for learning questionnaire (MSLQ). Ann Arbor, MI: National Center for Research to Improve Postsecondary Teaching and Learning, University of Michigan.
Rakici, N. (2004). Eight grade students’ perceptions of their science learning environment and teachers’ interpersonal behavior (Unpublished master's thesis). Ankara: Middle East Technical University.
Raudenbush, S. W., & Bryk, A. S. (2002). Hierarchical linear model: Applications and data analysis method. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage.
Risemberg, R., & Zimmerman, B. J. (1992). Self-regulated learning in gifted students. Roeper Review, 15(2), 98–101.
Schraw, G., Crippen, K. J., & Hartley, K. (2006). Promoting self-regulation in science education: Metacognition as part of a broader perspective on learning. Research in Science Education, 36, 111–139.
Schraw, G., & Moshman, D. (1995). Metacognitive theories. Educational Psychology Review, 7(4), 351–371.
Shim, S. S., Cho, Y., & Cassady, J. (2013). Goal structures: The role of teachers’ achievement goals and theories of intelligence. The Journal of Experimental Education, 81, 84–104.
Skaalvik, E. M., & Skaalvik, S. (2010). Teacher self-efficacy and teacher burnout: A study of relations. Teaching and Teacher Education, 26, 1059–1069.
Sungur, S., & Gungoren, S. (2009). The role of classroom environment perceptions in self-regulated learning and science achievement. Elementary Education Online, 8(3), 883–900.
Tabachnick, B. G., & Fidell, L. S. (2007). Using multivariate statistics (5th ed.). Boston, MA: Allyn & Bacon.
Tas, Y. (2008). The interplay of students’ perceptions of classroom goal structures, personal goal orientations and learning related variables (Unpublished master's thesis). Ankara: Middle East Technical University.
Tas, Y., Sungur, S., & Oztekin, C. (2016). Development and validation of science homework scale for middle-school students. International Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 14(3), 417–444.
Tekbıyık, A., & Akdeniz, A. R. (2008). Teachers’ views about adoption and application of primary science and technology curriculum. Necatibey Faculty of Education Electronic Journal of Science and Mathematics Education, 2(2), 23–37.
Topcu, M. S., & Yılmaz-Tuzun, O. (2009). Elementary students’ metacognition and epistemological beliefs considering science achievement, gender and socioeconomic status. Elementary Education Online, 8(3), 676–693.
Tschannen-Moran, M., & Hoy, A. W. (2001). Teacher efficacy: Capturing an elusive construct. Teaching and Teacher Education, 17(7), 783–805.
Tschannen-Moran, M., & Hoy, A. W. (2007). The differential antecedents of self-efficacy beliefs of novice and experienced teachers. Teaching and Teacher Education, 23, 944–956.
Tschannen-Moran, M., Hoy, A. W., & Hoy, W. K. (1998). Teacher efficacy: Its meaning and measure. Review of Educational Research, 68(2), 202–248.
Wan, C. P. (2005). Teaching efficacy beliefs of pre service teachers. Jurnal IPBA, 2(2), 122–129.
Wolf, S. J., & Fraser, B. J. (2008). Learning environment, attitudes and achievement among middle-school science students using inquiry-based laboratory activities. Research in Science Education, 38, 321–341.
Wolters, C. A., & Pintrich, P. R. (1998). Contextual differences in student motivation and self-regulated learning in mathematics, English, and social studies classroom. Instructional Science, 26, 27–47.
Xin, T., Xu, Z., & Tatsuoka, K. (2004). Linkage between teacher quality, student achievement, and cognitive skills: A rule-space model. Studies in Educational Evaluation, 30(3), 205–223.
Yildirim, S. (2012). Teacher support, motivation, learning, strategy use, and achievement: A multilevel mediation model. The Journal of Experimental Education, 80(2), 150–172.
Yilmaz-Tuzun, O., & Topcu, M. S. (2010). Investigating the relationships among elementary school students’ epistemological beliefs, metacognition, and constructivist science learning environment. Journal of Science Teacher Education, 21, 255–273.
Zimmerman, B. J. (2000). Attaining self-regulation: A social cognitive perspective. In M. Boekaerts, P. R. Pintrich, & M. Zeidner (Eds.), Handbook of self-regulation (pp. 13–39). San Diego, CA: Academic Press.
Acknowledgements
This study is a part of the first author’s dissertation. Thanks to Turkish Ministry of Education, Education Research and Development Department for their supports to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yerdelen, S., Sungur, S. Multilevel Investigation of Students’ Self-regulation Processes in Learning Science: Classroom Learning Environment and Teacher Effectiveness. Int J of Sci and Math Educ 17, 89–110 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-018-9921-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10763-018-9921-z