Abstract
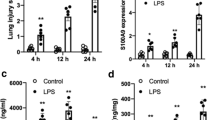
Acute lung injury (ALI) is a syndrome characterized by damage to the alveolar-capillary wall, pulmonary edema and recruitment of inflammatory cells. Previous studies have indicated that aquaporin 4 (AQP4) plays a key role in brain edema formation and resolution. However, the role of AQP4 in the development and progression of ALI is not clear and needs to be resolved. In our current study, mouse ALI was induced by intratracheal instillation of lipopolysaccharide (LPS) at a concentration of 30 mg/kg. For the inhibition of AQP4, 200 mg/kg of TGN-020 (Sigma, USA) was administered intraperitoneally every 6 h starting at 30 min before intratracheal instillation of LPS. The results of the present work indicate, for the first time, that mice treated with the AQP4 inhibitor TGN-020 had attenuated LPS-induced lung injury, reduced proinflammatory cytokine release (including IL-1α, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, IL-23, and IL-17A), and an improved survival rate. Additionally, we found that the attenuated lung injury scores, increased survival rate, and decreased BALF total protein concentration in TGN-020-treated mice were all abrogated by rIL-17A administration. Furthermore, TGN-020 treatment downregulated the phosphorylation of PI3K and Akt, increased the expression of SOCS3, and decreased the expression of p-STAT3 and RORγt. In conclusion, inhibition of AQP4 by TGN-020 has a detectable protective effect against lung tissue injury induced by LPS, and this effect is associated with inhibition of IL-17A through the downregulation of the PI3K/Akt signaling pathway and upregulation of SOCS3 protein.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sheu, C.C., M.N. Gong, R. Zhai, F. Chen, E.K. Bajwa, P.F. Clardy, D.C. Gallagher, B.T. Thompson, and D.C. Christiani. 2010. Clinical characteristics and outcomes of sepsis-related vs non-sepsis-related ARDS. Chest. 138: 559–567.
Cooke, C.R., C.V. Shah, R. Gallop, S. Bellamy, M. Ancukiewicz, M.D. Eisner, P.N. Lanken, A.R. Localio, and J.D. Christie. 2009. A simple clinical predictive index for objective estimates of mortality in acute lung injury. Critical Care Medicine 37: 1913–1920.
Zemans, R.L., and M.A. Matthay. 2004. Bench-to-bedside review: the role of the alveolar epithelium in the resolution of pulmonary edema in acute lung injury. Critical Care 8: 469–477.
Grommes, J., and O. Soehnlein. 2011. Contribution of neutrophils to acute lung injury. Molecular Medicine 17: 293–307.
Verkman, Alan S., Marc O. Anderson, and Marios C. Papadopoulos. 2014. Aquaporins: important but elusive drug targets. Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery 13 (4): 259–277.
Verschuur, C.V., A.J. Kooi, and D. Troost. 2015. Anti-aquaporin 4 related paraneoplastic neuromyelitis optica in the presence of adenocarcinoma of the lung. Clinical Neuropathology 34: 232–236.
Sorani, M.D. 2008. Novel variants in human aquaporin-4 reduce cellular water permeability. Human Molecular Genetics 17 (15): 2379–2389.
Verkman, A.S. 2013. Biology of AQP4 and anti-AQP4 antibody: therapeutic implications. Brain Pathology 23 (6): 684–695.
Bloch, O., and G.T. Manley. 2007. The role of aquaporin-4 in cerebral water transport and edema. Neurosurgical Focus, Neurosurg. Focus. 22: E3.
Papadopoulos, M.C., and A.S. Verkman. 2007. Aquaporin-4 and brain edema. Pediatric Nephrology 22 (6): 778–784.
Xiong, L.L., Y. Tan, H.Y. Ma, P. Dai, Y.X. Qin, R.A. Yang, Y.Y. Xu, Z. Deng, W. Zhao, Q.J. Xia, T.H. Wang, and Y.H. Zhang. 2016. Administration of SB239063, a potent p38 MAPK inhibitor, alleviates acute lung injury induced by intestinal ischemia reperfusion in rats associated with AQP4 downregulation. International Immunopharmacology 38: 54–60.
Li, Y., H. Lu, X. Lv, Q. Tang, W. Li, H. Zhu, and Y. Long. 2018. Blockade of aquaporin 4 inhibits irradiation-induced pulmonary inflammation and modulates macrophage polarization in mice. Inflammation. 41 (6): 2196–2205.
McFarland, H.F., and R. Martin. 2007. Multiple sclerosis: a complicated picture of autoimmunity. Nature Immunology 8: 913–919.
Wu, M.P., Y.S. Zhang, Q.M. Zhou, J. Xiong, Y.R. Dong, and C. Yan. 2016. Higenamine protects ischemia/reperfusion induced cardiac injury and myocyte apoptosis through activation of β2-AR/PI3K/AKT signaling pathway. Pharmacological Research 104: 115–123.
Wang, L., T. Wang, H. Li, Q. Liu, Z. Zhang, W. Xie, Y. Feng, T. Socorburam, G. Wu, Z. Xia, and Q. Wu. 2016. Receptor interacting protein 3- mediated necroptosis promotes lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammation and acute respiratory distress syndrome in mice. PLoS One 11 (5): e0155723.
Ayasoufi, K., N. Kohei, M. Nicosia, et al. 2018. Aquaporin 4 blockade improves survival of murine heart allografts subjected to prolonged cold ischemia. American Journal of Transplantation 00: 1–9.
Yang, B.L., F. Chen, L.J. Xu, J.H. Xing, and X.F. Wang. 2017. HMGB1-TLR4-IL23-IL17A axis promotes paraquat-induced acute lung injury by mediating neutrophil infiltration in mice. Scientific Reports 7: 597.
Liao, Y.H., N. Xia, S.F. Zhou, T.T. Tang, and X.X. Yan. 2012. Interleukin-17A contributes to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury by regulating cardiomyocyte apoptosis and neutrophil infiltration. Journal of the American College of Cardiology 59 (4): 420–429.
Li, Y.H., H.L. Fu, M.L. Tian, Y.Q. Wang, W. Chen, L.L. Cai, X.H. Zhou, and H.B. Yuan. 2016. Neuron-derived FGF10 ameliorates cerebral ischemia injury via inhibiting NF-κB-dependent neuroinflammation and activating PI3K/Akt survival signaling pathway in mice. Scientific Reports 6: 19869.
Chen, W., Z. Zhou, L. Li, C.Q. Zhong, X. Zheng, X. Wu, Y. Zhang, H. Ma, D. Huang, W. Li, Z. Xia, and J. Han. 2013. Diverse sequence determinants control human and mouse receptor interacting protein 3 (RIP3) and mixed lineage kinase domain-like (MLKL) interaction in necroptotic signaling. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 288 (23): 16247–16261.
Chen, W., V. Jadhav, J. Tang, and J.H. Zhang. 2008. HIF-1alpha inhibition ameliorates neonatal brain injury in a rat pup hypoxic-ischemic model. Neurobiology 31: 433–441.
Bhargava, M., and C.H. Wendt. 2012. Biomarkers in acute lung injury. Translational Research 159 (4): 205–217.
Han, J., C.Q. Zhong, and D.W. Zhang. 2011. Programmed necrosis: backup to and competitor with apoptosis in the immune system. Nature Immunology 12 (12): 1143–1149.
Chignard, M., and V. Balloy. 2000. Neutrophil recruitment and increased permeability during acute lung injury induced by lipopolysaccharide. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 279 (6): L1083–L1090.
Kantrow, S.P., Z. Shen, T. Jagneaux, P. Zhang, and S. Nelson. 2009. Neutrophil-mediated lung permeability and host defense proteins. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 297 (4): L738–L745.
Risso, K., et al. 2005. Early infectious acute respiratory distress syndrome is characterized by activation and proliferation of alveolar T-cells. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 34: 1111–1118.
Yan, Z., Z. Xiaoyu, S. Zhixin, Q. di, D. Xinyu, X. Jing, H. Jing, D. Wang, Z. Xi, Z. Chunrong, and W. Daoxin. 2016. Rapamycin attenuates acute lung injury induced by LPS through inhibition of Th17 cell proliferation in mice. Scientific Reports 6: 20156.
Yu, Z.X., M.S. Ji, J. Yan, Y. Cai, J. Liu, H.F. Yang, Y. Li, Z.C. Jin, and J.X. Zheng. 2015. The ratio of Th17/Treg cells as a risk indicator in early acute respiratory distress syndrome. Critical Care 19: 82.
Dai, H., L. Xu, Y. Tang, Z. Liu, and T. Sun. 2015. Treatment with a neutralising anti-rat interleukin-17 antibody after multiple-trauma reduces lung inflammation. Injury. 46 (8): 1465–1470.
Kluger, M.A., A. Nosko, T. Ramcke, B. Goerke, M.C. Meyer, C. Wegscheid, M. Luig, G. Tiegs, R.A.K. Stahl, and O.M. Steinmetz. 2017. RORγt expression in Tregs promotes systemic lupus erythematosus via IL-17 secretion, alteration of Treg phenotype and suppression of Th2 responses. Clinical and Experimental Immunology 188 (1): 63–78.
Marone, R., V. Cmiljanovic, B. Giese, and M.P. Wymann. 2008. Targeting phosphoinositide 3-kinase: moving towards therapy. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta 1784: 159–185.
Osaka, D., Y. Shibata, K. Kanouchi, M. Nishiwaki, T. Kimura, H. Kishi, S. Abe, S. Inoue, Y. Tokairin, A. Igarashi, K. Yamauchi, Y. Aida, T. Nemoto, K. Nunomiya, K. Fukuzaki, and I. Kubota. 2011. Soluble endothelial selectin in acute lung injury complicated by severe pneumonia. International Journal of Medical Sciences 8: 302–308.
Seki, H., K. Fukunaga, M. Arita, H. Arai, H. Nakanishi, R. Taguchi, T. Miyasho, R. Takamiya, K. Asano, A. Ishizaka, J. Takeda, and B.D. Levy. 2010. The anti-inflammatory and proresolving mediator resolvin E1 protects rat from bacterial pneumonia and acute lung injury. Journal of Immunology 184: 836–843.
Nieuwenhuizen, L., P.G. de Groot, J.C. Grutters, and D.H. Biesma. 2009. A review of pulmonary coagulopathy in acute lung injury, acute respiratory distress syndrome and pneumonia. European Journal of Haematology 82: 413–425.
Curtis, M.M., and S.S. Way. 2009. Interleukin-17 in host defence against bacterial, mycobacterial and fungal pathogens. Immunology. 126: 177–185.
Li, J.T., A.C. Melton, G. Su, D.E. Hamm, M. LaFemina, J. Howard, X. Fang, S. Bhat, K.M. Huynh, C.M. O’Kane, R.J. Ingram, R.R. Muir, D.F. McAuley, M.A. Matthay, and D. Sheppard. 2015. Unexpected role for adaptive αβTh17 cells in acute respiratory distress syndrome. Journal of Immunology 195: 87–95.
Risso, K., G. Kumar, M. Ticchioni, C. Sanfiorenzo, J. Dellamonica, F. Guillouet-de Salvador, G. Bernardin, C.H. Marquette, and P.M. Roger. 2015. Early infectious acute respiratory distress syndrome is characterized by activation and proliferation of alveolar T-cells. European Journal of Clinical Microbiology & Infectious Diseases 34: 1111–1118.
Noack, M., and P. Miossec. 2014. Th17 and regulatory T cell balance in autoimmune and inflammatory diseases. Autoimmunity Reviews 13: 668–677.
D’Alessio, F.R., et al. 2009. CD4+ CD25+ Foxp3+ Tregs resolve experimental lung injury in mice and are present in humans with acute lung injury. The Journal of Clinical Investigation 119: 2898–2913.
Guha, M., and N. Mackman. 2002. The phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-Akt pathway limits lipopolysaccharide activation of signaling pathways and expression of inflammatory mediators in human monocytic cells. The Journal of Biological Chemistry 277: 32124–32132.
Lee, J.P., Y.C. Li, H.Y. Chen, R.H. Lin, S.S. Huang, H.L. Chen, P.C. Kuan, M.F. Liao, C.J. Chen, and Y.H. Kuan. 2010. Protective effects of luteolin against lipopolysaccharide-induced acute lung injury involves inhibition of MEK/ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways in neutrophils. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica 31: 831–838.
Lu, Y., J. Zhou, C. Xu, H. Lin, J. Xiao, Z. Wang, and B. Yang. 2008. JAK/STAT and PI3K/AKT pathways form a mutual transactivation loop and afford resistance to oxidative stress-induced apoptosis in cardiomyocytes. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 21: 305–314.
Wu, S., J. Xue, Y. Yang, H. Zhu, F. Chen, J. Wang, G. Lou, Y. Liu, Y. Shi, Y. Yu, C. Xia, Y. Hu, and Z. Chen. 2015. Isoliquiritigenin inhibits interferon-γ-inducible genes expression in hepatocytes through down-regulating activation of JAK1/STAT1, IRF3/MyD88, ERK/MAPK, JNK/MAPK and PI3K/Akt signaling pathways. Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry 37: 501–514.
Ma, C.S., G.Y.J. Chew, N. Simpson, A. Priyadarshi, M. Wong, B. Grimbacher, D.A. Fulcher, S.G. Tangye, and M.C. Cook. 2008. Deficiency of Th17 cells in hyper IgE syndrome due to mutations in STAT3. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 205: 1551–1557.
Renner, E.D., S. Rylaarsdam, S. Aňover-Sombke, A.L. Rack, J. Reichenbach, J.C. Carey, Q. Zhu, A.F. Jansson, J. Barboza, L.F. Schimke, M.F. Leppert, M.M. Getz, R.A. Seger, H.R. Hill, B.H. Belohradsky, T.R. Torgerson, and H.D. Ochs. 2008. Novel signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 (STAT3) mutations, reduced T H 17 cell numbers, and variably defective STAT3 phosphorylation in hyper-IgE syndrome. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 122: 181–187.
Yan, C., P.A. Ward, X. Wang, and H. Gao. 2013. Myeloid depletion of SOCS3 enhances LPS-induced acute lung injury through CCAAT/enhancer binding protein delta pathway. The FASEB Journal 27: 2967–2976.
Zhao, J., H. Yu, Y. Liu, S.A. Gibson, Z. Yan, X. Xu, A. Gaggar, P.K. Li, C. Li, S. Wei, E.N. Benveniste, and H. Qin. 2016. Protective effect of suppressing STAT3 activity in LPS-induced acute lung injury. American Journal of Physiology. Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology 311: L868–L880.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Experiments were approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee at Hubei Province Academy of Traditional Chinese Medicine.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guo, C., Wu, T., Zhu, H. et al. Aquaporin 4 Blockade Attenuates Acute Lung Injury Through Inhibition of Th17 Cell Proliferation in Mice. Inflammation 42, 1401–1412 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01002-4
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-019-01002-4