Abstract
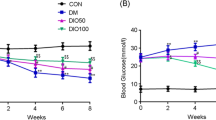
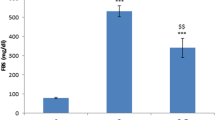
The peripheral nervous system is one of many organ systems that can be profoundly impacted in diabetes mellitus. Diabetic peripheral neuropathy has a significant negative effect on patients’ quality of life as it begins with loss of limbs’ sensation and may result in lower limb amputation. This investigation aimed at exploring the effect of sulforaphane on peripheral neuropathy in diabetic rats. Experimental diabetes was induced through single intraperitoneal injections of nicotinamide (50 mg/kg) and streptozotocin (52.5 mg/kg). Rats were divided into five groups. Two groups were treated with saline or sulforaphane (1 mg/kg, p.o.). Three diabetic groups were either untreated or given sulforaphane (1 mg/kg, p.o.) or pregabalin (10 mg/kg, i.p.). Two weeks after drugs’ administration, biochemical, behavioral, histopathological, and immunohistochemical investigations were carried out. Treatment with sulforaphane restored animals’ body weight, reduced blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin, and increased insulin levels. In parallel, it normalized motor coordination and the latency withdrawal time of tail flick test, increased the latency withdrawal time of cold allodynia test, and ameliorated histopathological changes. Treatment of sulforaphane, likewise, decreased sciatic nerve malondialdehyde, nitric oxide, interleukin-6, and matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 contents. Similarly, it reduced sciatic nerve DNA fragmentation and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and nuclear factor kappa-B p65. Meanwhile, it increased sciatic nerve superoxide dismutase and interleukin-10 contents. These results reveal the neuroprotective effect of sulforaphane against peripheral neuropathy in diabetic rats possibly through modulating oxidative stress, inflammation, and extracellular matrix remodeling.

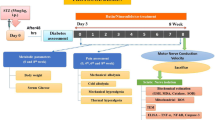
Diagram that illustrates the effects of sulforaphane in treating experimental diabetic peripheral neuropathy. In NA-STZ model of diabetes mellitus, sulforaphane, restored animals’ body weight, reduced blood glucose, glycated hemoglobin and increased insulin levels. In parallel, it normalized motor coordination and the latency withdrawal time of tail flick test, increased the latency withdrawal time of cold allodynia test and ameliorated histopathological changes. Treatment of sulforaphane, likewise, decreased sciatic nerve malondialdehyde, nitric oxide, interleukin-6, matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 contents. Similarly, it reduced sciatic nerve DNA fragmentation and expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and nuclear factor kappa-B p65. Meanwhile, it increased sciatic nerve superoxide dismutase and interleukin-10 contents.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer’s disease
- AGEs:
-
Advanced glycation end products
- ANOVA:
-
Analysis of variance
- COX-2:
-
Cyclooxygenase-2
- DM:
-
Diabetes mellitus
- DPN:
-
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy
- ECM:
-
Extracellular matrix
- ERK1/2:
-
Extracellular signal-regulated protein kinases 1 and 2
- GHBA1c:
-
Glycated hemoglobin
- H&E:
-
Hematoxylin and eosin
- HPWL:
-
Hind paw withdrawal latency
- IL-10:
-
Interleukin-10
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- iNOS:
-
Nitric oxide synthase
- Keap1:
-
Kelch-like ECH associated protein 1
- MDA:
-
Malondialdehyde
- MMP-2:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-2
- MMP-9:
-
Matrix metalloproteinase-9
- NA:
-
Nicotinamide
- NADPH:
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor kappa B
- NO:
-
Nitric oxide
- PD:
-
Parkinson’s disease
- PGB:
-
Pregabalin
- PKC:
-
Protein kinase C
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SFN:
-
Sulforaphane
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- STZ:
-
Streptozotocin
- TWL:
-
Tail withdrawal latency
References
Grote, Caleb W., and Douglas E. Wright. 2016. A role for insulin in diabetic neuropathy. Frontiers in Neuroscience 10: 1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2016.00581 Frontiers Media SA.
Solmaz, Volkan, Bilge Piri Çınar, Gürkan Yiğittürk, Hatice Köse Özlece, Hüseyin Avni Eroglu, Aslan Tekatas, Oytun Erbaş, and Dilek Taşkıran. 2017. Neuroprotective effects of octreotide on diabetic neuropathy in rats. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy 89: 468–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.02.027.
Maria, Galuppo, Giacoppo Sabrina, Bramanti Placido, and Emanuela Mazzon. 2014. Use of natural compounds in the management of diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Molecules 19: 2877–2895. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules19032877.
Vileikyte, Loretta, Richard R. Rubin, and Howard Leventhal. 2004. Psychological aspects of diabetic neuropathic foot complications: An overview. Diabetes/Metabolism Research and Reviews 20: S13–S18. https://doi.org/10.1002/dmrr.437.
Katulanda, Prasad, Priyanga Ranasinghe, Ranil Jayawardena, R. Godwin, M.H. Rezvi Sheriff Constantine, and David R. Matthews. 2012. The prevalence, patterns and predictors of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in a developing country. Diabetology & Metabolic Syndrome 4: 2–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1758-5996-4-21 BioMed Central.
Sobhani, Sahar, Hamid Asayesh, Farshad Sharifi, Shirin Djalalinia, Hamid Reza Baradaran, Seyed Masoud Arzaghi, Morteza Mansourian, Aziz Rezapoor, Hossein Ansari, Mohammad Parvaresh Masoud, and Mostafa Qorbani. 2014. Prevalence of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in Iran: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Journal of Diabetes & Metabolic Disorders 13: 2–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40200-014-0097-y.
Bruschi, Lídia Karla Martinho, Dayvson Araújo da Rocha, Eusínio Lavigne Gesteira Filho, Nathália de Moura Pancoti Barboza, P.A.B. Frisanco, Raquel Milanesi Callegaro, Larissa Bianca Paiva Cunha de Sá, and Alberto Krayyem Arbex. 2017. Diabetes mellitus and diabetic peripheral neuropathy. Open Journal of Endocrine and Metabolic Diseases 7: 12–21. https://doi.org/10.4236/ojemd.2017.71002.
Chen, Long, Bing Li, Biqin Chen, Yiye Shao, Qiong Luo, Xiaohong Shi, and Yinghui Chen. 2016. Thymoquinone alleviates the experimental diabetic peripheral neuropathy by modulation of inflammation. Scientific Reports 6: 1–11. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31656.
Oh, Yoon. 2016. Bioactive compounds and their Neuroprotective effects in diabetic complications. Nutrients 8: 1–20. https://doi.org/10.3390/nu8080472.
Vincent, Andrea M., Brian C. Callaghan, Andrea L. Smith, and Eva L. Feldman. 2011. Diabetic neuropathy: Cellular mechanisms as therapeutic targets. Nature Reviews Neurology 7: 573–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrneurol.2011.137.
Oyenihi, Ayodeji Babatunde, Ademola Olabode Ayeleso, Emmanuel Mukwevho, and Bubuya Masola. 2015. Antioxidant strategies in the management of diabetic neuropathy. BioMed Research International. Hindawi: 1–15. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/515042.
Zangiabadi, Nasser, Vahid Sheibani, Majid Asadi-Shekaari, Mohammad Shabani, Mandana Jafari, Ali Reza Asadi, Haleh Tajadini, and Morteza Jarahi. 2011. Effects of melatonin in prevention of neuropathy in STZ-induced diabetic rats. American Journal of Pharmacology and Toxicology 6: 59–67. https://doi.org/10.3844/ajptsp.2011.59.67.
Yagihashi, Soroku, Hiroki Mizukami, and Kazuhiro Sugimoto. 2011. Mechanism of diabetic neuropathy: Where are we now and where to go? Journal of Diabetes Investigation 2: 18–32. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2040-1124.2010.00070.x Wiley-Blackwell.
Edwards, James L., Andrea M. Vincent, Hsinlin T. Cheng, and Eva L. Feldman. 2008. Diabetic neuropathy: Mechanisms to management. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 120: 1–34. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2008.05.005 NIH Public Access.
Ramasamy, Ravichandran, Shi Fang Yan, Kevan Herold, Raphael Clynes, and Ann Marie Schmidt. 2008. Receptor for advanced glycation end products: Fundamental roles in the inflammatory response: Winding the way to the pathogenesis of endothelial dysfunction and atherosclerosis. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences 1126: 7–13. https://doi.org/10.1196/annals.1433.056 NIH Public Access.
Creager, M.A., Thomas F. Lüscher, Francesco Cosentino, and Joshua A. Beckman. 2003. Diabetes and vascular disease: Pathophysiology, clinical consequences, and medical therapy: Part I. Circulation 108: 1527–1532. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000091257.27563.32.
Eid, Ahmed H., Noha F. Abdelkader, Ola M. Abd El-Raouf, Hala M. Fawzy, and Ezz-El-Din S. El-Denshary. 2016. Carvedilol alleviates testicular and spermatological damage induced by cisplatin in rats via modulation of oxidative stress and inflammation. Archives of Pharmacal Research 39: 1693–1702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12272-016-0833-6.
Parkar, N., and V. Addepalli. 2014. Effect of nobiletin on diabetic neuropathy in experimental rats. Austin Journal of Pharmacology and Therapeutics. 2: 2–5.
Ji, Ru-Rong, Zhen-Zhong Xu, Xiaoying Wang, and Eng H. Lo. 2009. Matrix metalloprotease regulation of neuropathic pain. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 30: 336–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tips.2009.04.002 NIH Public Access.
Kawasaki, Yasuhiko, Zhen-Zhong Xu, Xiaoying Wang, Jong Yeon Park, Zhi-Ye Zhuang, Ping-Heng Tan, Yong-Jing Gao, et al. 2008. Distinct roles of matrix metalloproteases in the early- and late-phase development of neuropathic pain. Nature Medicine 14: 331–336. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm1723 Nature Publishing Group.
Opris, Razvan, Corina Tatomir, Diana Olteanu, Remus Moldovan, Bianca Moldovan, Luminita David, Andras Nagy, Nicoleta Decea, Mihai Ludovic Kiss, and Gabriela Adriana Filip. 2017. The effect of Sambucus nigra L. extract and phytosinthesized gold nanoparticles on diabetic rats. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces 150: 192–200. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfb.2016.11.033.
Nunez, O., A. Fernández-Martínez, P.L. Majano, A. Apolinario, M. Gómez-Gonzalo, I. Benedicto, M. López-Cabrera, et al. 2004. Increased intrahepatic cyclooxygenase 2, matrix metalloproteinase 2, and matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression is associated with progressive liver disease in chronic hepatitis C virus infection: Role of viral core and NS5A proteins. Gut 53: 1665–1672. https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2003.038364.
Kowluru, Renu A., and Mamta Kanwar. 2009. Oxidative stress and the development of diabetic retinopathy: Contributory role of matrix metalloproteinase-2. Free Radical Biology and Medicine 46: 1677–1685. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2009.03.024.
Kaufman-Szymczyk, Agnieszka, Grzegorz Majewski, Katarzyna Lubecka-Pietruszewska, and Krystyna Fabianowska-Majewska. 2015. The role of sulforaphane in epigenetic mechanisms, including interdependence between histone modification and DNA methylation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 16: 29732–29743. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms161226195.
Tarozzi, Andrea, Cristina Angeloni, Marco Malaguti, Fabiana Morroni, Silvana Hrelia, and Patrizia Hrelia. 2013. Sulforaphane as a potential protective phytochemical against neurodegenerative diseases. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2013: 415078. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/415078 Hindawi.
Benedict, Andrea L., Andrea Mountney, Andres Hurtado, Kelley E. Bryan, Ronald L. Schnaar, Albena T. Dinkova-Kostova, and Paul Talalay. 2012. Neuroprotective effects of sulforaphane after contusive spinal cord injury. Journal of Neurotrauma 29: 2576–2586. https://doi.org/10.1089/neu.2012.2474.
Sita, Giulia, Patrizia Hrelia, Andrea Tarozzi, and Fabiana Morroni. 2016. Isothiocyanates are promising compounds against oxidative stress, neuroinflammation and cell death that may benefit neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 17: 63–71. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17091454.
Song, Mi-Young, Eun-Kyung Kim, Woo-Sung Moon, Jin-Woo Park, Hyung-Jin Kim, Hong-Seob So, Raekil Park, Kang-Beom Kwon, and Byung-Hyun Park. 2009. Sulforaphane protects against cytokine- and streptozotocin-induced β-cell damage by suppressing the NF-κB pathway. Toxicology and Applied Pharmacology 235: 57–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.taap.2008.11.007.
Zhang, Rui, Jingzhu Zhang, Lingduo Fang, Xi Li, Yue Zhao, Wanying Shi, and Li An. 2014. Neuroprotective effects of sulforaphane on cholinergic neurons in mice with Alzheimer’s disease-like lesions. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 15: 14396–14410. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms150814396.
Sun, Y., T. Yang, L. Mao, and F. Zhang. 2017. Sulforaphane protects against brain diseases: roles of cytoprotective. Enzyme 4: 1–7.
Zhou, Qian, Bin Chen, Xindong Wang, Lixin Wu, Yang Yang, Xiaolan Cheng, Zhengli Hu, et al. 2016. Sulforaphane protects against rotenone-induced neurotoxicity in vivo: Involvement of the mTOR, Nrf2 and autophagy pathways. Scientific Reports 6: 32206. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep32206.
Yu, Chang, He Qi, Jing Zheng, Ling Yu Li, Yang Hao Hou, and Fang Zhou Song. 2017. Sulforaphane improves outcomes and slows cerebral ischemic/reperfusion injury via inhibition of NLRP3 inflammasome activation in rats. International Immunopharmacology 45: 74–78. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.intimp.2017.01.034.
Ghasemi, Asghar, S. Khalifi, and S. Jedi. 2014. Streptozotocin-nicotinamide-induced rat model of type 2 diabetes (review). Acta Physiologica Hungarica 101: 408–420. https://doi.org/10.1556/APhysiol.101.2014.4.2.
Mikaili, P., A.A. Hemmati, M.J. Khodayar, M. Ghafurian, and I. Rashidi. 2011. Evaluation of the effects of nicotinamide on the blemycin-induced pulmonary fibroses in rat. International Journal of Animal and Veterinary 3: 330–336 Maxwell Scientific Organization.
El-Marasy, Salma A., Heba M.I. Abdallah, Siham M. El-Shenawy, Aiman S. El-Khatib, Osama A. El-Shabrawy, and Sanaa A. Kenawy. 2014. Anti-depressant effect of hesperidin in diabetic rats. Canadian Journal of Physiology and Pharmacology 92: 945–952. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjpp-2014-0281 NRC Research Press.
Kamble, Hemant Vinayak, and Subhash Laxmanrao Bodhankar. 2014. Concomitant administration of trigonelline and sitagliptin attenuates nicotinamide-streptozotocin induced diabetic neuropathy in wistar rats. Journal of Chemical and Pharmaceutical Research 6: 616–624.
Souza, de, Carolina Guerini, José Augusto Sattler, Adriano Martimbianco de Assis, Anderson Rech, Marcos Luiz Santos Perry, and Diogo Onofre Souza. 2012. Metabolic effects of sulforaphane oral treatment in streptozotocin-diabetic rats. Journal of Medicinal Food 15: 795–801. https://doi.org/10.1089/jmf.2012.0016.
Rocha-González, Héctor Isaac, Magali Ramírez-Aguilar, Vinicio Granados-Soto, Juan Gerardo Reyes-García, Jorge Elías Torres-López, Juan Carlos Huerta-Cruz, and Andrés Navarrete. 2014. Antineuropathic effect of 7-hydroxy-3,4-dihydrocadalin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rodents. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 14: 2–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-129.
Lundblad, M., E. Vaudano, and M.A. Cenci. 2003. Cellular and behavioural effects of the adenosine A2a receptor antagonist KW-6002 in a rat model of l-DOPA-induced dyskinesia. Journal of Neurochemistry 84: 1398–1410. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1471-4159.2003.01632.x.
Liepinsh, Edgars, Reinis Vilskersts, Liga Zvejniece, Baiba Svalbe, Elina Skapare, Janis Kuka, Helena Cirule, Solveiga Grinberga, Ivars Kalvinsh, and Maija Dambrova. 2009. Protective effects of mildronate in an experimental model of type 2 diabetes in Goto-Kakizaki rats. British Journal of Pharmacology 157: 1549–1556. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1476-5381.2009.00319.x.
Ameyaw, E.O., J.N. Boampong, K.E. Kukuia, P. Amoateng, E. Obese, C. Osei-Sarpong, and E. Woode. 2014. Effect of xylopic acid on paclitaxel-induced neuropathic pain in rats. Journal of Medical and Biomedical Sciences 2: 6–12. https://doi.org/10.4314/jmbs.v2i4.2 School of Medicine and Health Sciences, University for Development Studies.
Lee, Ji-Hye, Dong Xing Li, Heera Yoon, Donghyun Go, Fu Shi Quan, Byung-Il Min, and Sun Kwang Kim. 2014. Serotonergic mechanism of the relieving effect of bee venom acupuncture on oxaliplatin-induced neuropathic cold allodynia in rats. BMC Complementary and Alternative Medicine 14: 2–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/1472-6882-14-471.
Ruiz-Larrea, M.B., A.M. Leal, M. Liza, M. Lacort, and H. de Groot. 1994. Antioxidant effects of estradiol and 2-hydroxyestradiol on iron-induced lipid peroxidation of rat liver microsomes. Steroids 59: 383–388. https://doi.org/10.1016/0039-128X(94)90006-X.
Sastry, K.V.H., R.P. Moudgal, J. Mohan, J.S. Tyagi, and G.S. Rao. 2002. Spectrophotometric determination of serum nitrite and nitrate by copper–cadmium alloy. Analytical Biochemistry 306: 79–82. https://doi.org/10.1006/abio.2002.5676.
Gibb, R.K., D.D. Taylor, T. Wan, D.M. O’Connor, D.L. Doering, and C. Gerçel-Taylor. 1997. Apoptosis as a measure of chemosensitivity to cisplatin and taxol therapy in ovarian cancer cell lines. Gynecologic Oncology 65: 13–22. https://doi.org/10.1006/gyno.1997.4637.
Tasci, Ilker, Mehmet Refik Mas, Sevil Atalay Vural, Salih Deveci, Bilgin Comert, Gunay Alcigir, Nuket Mas, C. Akay, M. Bozdayi, C. Yurdaydin, H. Bozkaya, O. Uzunalimoglu, A.T. Isik, and H.M. Said. 2007. Pegylated interferon-alpha plus taurine in treatment of rat liver fibrosis. World Journal of Gastroenterology 13: 3237–3244. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v13.i23.3237.
Shi, Guang, Dong Li, Jinling Fu, Yan Sun, Yarong Li, Rongfeng Qu, Xin Jin, and Dongfu Li. 2015. Upregulation of cyclooxygenase-2 is associated with activation of the alternative nuclear factor kappa B signaling pathway in colonic adenocarcinoma. American Journal of Translational Research 7: 1612–1620.
Ahangarpour, Akram, Hamid Heidari, Ali Akbar Oroojan, Farhang Mirzavandi, Khalil Nasr Esfehani, and Zeinab Dehghan Mohammadi. 2017. Antidiabetic, hypolipidemic and hepatoprotective effects of Arctium lappa root’s hydro-alcoholic extract on nicotinamide-streptozotocin induced type 2 model of diabetes in male mice. Avicenna Journal of Phytomedicine 7: 169–179 Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Ghamarian, Abdolreza, Mohammad Abdollahi, Xiaogang Su, Azita Amiri, Ali Ahadi, and Azin Nowrouzi. 2012. Effect of chicory seed extract on glucose tolerance test (GTT) and metabolic profile in early and late stage diabetic rats. DARU Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 20: 2–9. https://doi.org/10.1186/2008-2231-20-56.
Saravanan, Ramalingam, and Leelavinothan Pari. 2008. Effect of succinic acid monoethyl ester on hemoglobin glycation and tail tendon collagen properties in type 2 diabetic rats. Fundamental & Clinical Pharmacology 22: 291–298. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00581.x.
Yilmaz, Okkes, Yasemin Ersan, Ayse Dilek Ozsahin, Ali Ihsan Ozturk, and Yusuf Ozkan. 2013. Consequences of the combined α-tocopherol, ascorbic acid and α-lipoic acid on the glutathione, cholesterol and fatty acid composition in muscle and liver of diabetic rats. Iranian Journal of Basic Medical Sciences 16: 165–172 Mashhad University of Medical Sciences.
Balamurugan, Rangachari, and Savarimuthu Ignacimuthu. 2011. Antidiabetic and hypolipidemic effect of methanol extract of Lippia nodiflora L. in streptozotocin induced diabetic rats. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine 1: S30–S36. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2221-1691(11)60117-2.
Sun, Chengcao, Cuili Yang, Ruilin Xue, Shujun Li, Ting Zhang, Lei Pan, Xuejiao Ma, Liang Wang, and Dejia Li. 2015. Sulforaphane alleviates muscular dystrophy in mdx mice by activation of Nrf2. Journal of Applied Physiology 118: 224–237. https://doi.org/10.1152/japplphysiol.00744.2014.
Pandhare, Ramdas B., B. Sangameswaran, Popat B. Mohite, and Shantaram G. Khanage. 2012. Attenuating effect of seeds of Adenanthera pavonina aqueous extract in neuropathic pain in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats: an evidence of neuroprotective effects. Revista Brasileira de Farmacognosia 22: 428–435. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0102-695X2012005000008 Sociedade Brasileira de Farmacognosia.
Solanki, Nilay D., and Shailesh K. Bhavsar. 2015. An evaluation of the protective role of Ficus racemosa Linn. in streptozotocin-induced diabetic neuropathy with neurodegeneration. Indian Journal of Pharmacology 47: 610–615. https://doi.org/10.4103/0253-7613.169579.
Sharma, Ashish Kumar, Akash Sharma, Rita Kumari, Kunal Kishore, Divya Sharma, Bharthu Parthsarthi Srinivasan, Ashok Sharma, S.K. Singh, S. Gaur, V.S. Jatav, P. Sharma, V. Srivastava, S. Joshi, M. Joshi, P.K. Dhakad, D.S. Kanawat, A. Mishra, A. Sharma, D. Singh, R.P. Singh, H.S. Chawda, R. Singh, S.K. Raikwar, M.K. Kurmi, P. Khatri, A. Agarwal, and A. Munajjam. 2012. Sitagliptin, sitagliptin and metformin, or sitagliptin and amitriptyline attenuate streptozotocin-nicotinamide induced diabetic neuropathy in rats. Journal of Biomedical Research 26: 200–210. https://doi.org/10.7555/JBR.26.20110054.
Al-Rejaie, Salim S., Hatem M. Abuohashish, Mohammed M. Ahmed, Aws S. Arrejaie, Abdulaziz M. Aleisa, and Shakir D. AlSharari. 2015. Telmisartan inhibits hyperalgesia and inflammatory progression in a diabetic neuropathic pain model of Wistar rats. Neurosciences (Riyadh, Saudi Arabia) 20: 115–123. https://doi.org/10.17712/nsj.2015.2.20140511.
Morroni, Fabiana, Andrea Tarozzi, Giulia Sita, Cecilia Bolondi, Juan Manuel Zolezzi Moraga, Giorgio Cantelli-Forti, and Patrizia Hrelia. 2013. Neuroprotective effect of sulforaphane in 6-hydroxydopamine-lesioned mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Neurotoxicology 36: 63–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuro.2013.03.004.
Chen, Long, Bing Li, Biqin Chen, Yiye Shao, Qiong Luo, Xiaohong Shi, and Yinghui Chen. 2016. Thymoquinone alleviates the experimental diabetic peripheral neuropathy by modulation of inflammation. Scientific Reports 6: 31656. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep31656 Nature Publishing Group.
Bender, Gregor, Jeffry A. Florian, Stephen Bramwell, Mark J. Field, Keith K.C. Tan, Scott Marshall, Joost DeJongh, Robert.R. Bies, and Meindert Danhof. 2010. Pharmacokinetic–pharmacodynamic analysis of the static allodynia response to pregabalin and sildenafil in a rat model of neuropathic pain. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 334: 599–608.
Sandireddy, Reddemma, Veera Ganesh Yerra, Aparna Areti, Prashanth Komirishetty, and Ashutosh Kumar. 2014. Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in diabetic neuropathy: futuristic strategies based on these targets. International Journal of Endocrinology 2014: 674987. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/674987 Hindawi.
Karin, Michael, Yumi Yamamoto, and Q. May Wang. 2004. The IKK NF-κB system: A treasure trove for drug development. Nature Reviews Drug Discovery 3: 17–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrd1279.
Guerrero-Beltrán, Carlos Enrique, Mariel Calderón-Oliver, José Pedraza-Chaverri, and Yolanda Irasema Chirino. 2012. Protective effect of sulforaphane against oxidative stress: Recent advances. Experimental and Toxicologic Pathology 64: 503–508. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etp.2010.11.005.
Itoh, Ken, Junsei Mimura, and Masayuki Yamamoto. 2010. Discovery of the negative regulator of Nrf2, Keap1: A historical overview. Antioxidants & Redox Signaling 13: 1665–1678. https://doi.org/10.1089/ars.2010.3222.
Xue, M., Q. Qian, A. Adaikalakoteswari, N. Rabbani, R. Babaei-Jadidi, and P.J. Thornalley. 2008. Activation of NF-E2-related factor-2 reverses biochemical dysfunction of endothelial cells induced by hyperglycemia linked to vascular disease. Diabetes 57: 2809–2817. https://doi.org/10.2337/db06-1003.
González-Ramos, Reinaldo, Jacques Donnez, Sylvie Defrère, Isabelle Leclercq, Jean Squifflet, Jean Christophe Lousse, and Anne Van Langendonckt. 2007. Nuclear factor-kappa B is constitutively activated in peritoneal endometriosis. Molecular Human Reproduction 13: 503–509. https://doi.org/10.1093/molehr/gam033.
Thiagarajan, Venkata R.K., Palanichamy Shanmugam, Uma M. Krishnan, and Arunachalam Muthuraman. 2014. Ameliorative potential of Vernonia cinerea on chronic constriction injury of sciatic nerve induced neuropathic pain in rats. Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciencias 86: 1436–1449.
Park, Seyeon, Eun Sook Ahn, Dong Woo Han, Jong Hwa Lee, Kyung Tae Min, Hyunkyung Kim, and Yong-Woo Hong. 2008. Pregabalin and gabapentin inhibit substance P-induced NF-κB activation in neuroblastoma and glioma cells. Journal of Cellular Biochemistry 105: 414–423. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcb.21837.
Kumar, Ashutosh, Ravinder K. Kaundal, Seethalakshmi Iyer, and Shyam S. Sharma. 2007. Effects of resveratrol on nerve functions, oxidative stress and DNA fragmentation in experimental diabetic neuropathy. Life Sciences 80: 1236–1244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lfs.2006.12.036.
Angeloni, Cristina, Emanuela Leoncini, Marco Malaguti, Sabrina Angelini, Patrizia Hrelia, and Silvana Hrelia. 2009. Modulation of phase II enzymes by sulforaphane: Implications for its cardioprotective potential. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 57: 5615–5622. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf900549c.
Zangiabadi, Nasser, Hossein Mohtashami, Mahboobeh Hojatipour, Mandana Jafari, Majid Asadi-Shekaari, and Mohammad Shabani. 2014. The effect of Angipars on diabetic neuropathy in STZ-induced diabetic male rats: A study on behavioral, electrophysiological, sciatic histological and ultrastructural indices. The Scientific World Journal 2014: 1–8. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/721547.
Martin, Alexandra, Michael R. Komada, and David C. Sane. 2003. Abnormal angiogenesis in diabetes mellitus. Medicinal Research Reviews 23: 117–145. https://doi.org/10.1002/med.10024.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Dr. Adel Bakeir (Histology Department, Faculty of Veterinary Medicine, Cairo University, Cairo, Egypt) for carrying out the histopathological and immunohistochemical examinations of this study.
Funding
This study was funded by the National Research Centre, Cairo, Egypt.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study conforms with the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals published by the US National Institutes of Health (NIH Publication No. 85-23, revised 1996) and was approved by the Ethics Committees of Faculty of Pharmacy, Cairo University (permit number 1393) and National Research Centre (permit number 15/047).
Conflict of Interest
The authors affirm that there were no conflicts of interest associated with this research work.
Additional information
Highlights
• Sulforaphane is neuroprotective against diabetic peripheral neuropathy
• Sulforaphane has anti-hyperglycemic, anti-oxidant, anti-inflammatory activities
• Sulforaphane suppressed matrix metalloproteinases involved in the neuropathic pain
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moustafa, P.E., Abdelkader, N.F., El Awdan, S.A. et al. Extracellular Matrix Remodeling and Modulation of Inflammation and Oxidative Stress by Sulforaphane in Experimental Diabetic Peripheral Neuropathy. Inflammation 41, 1460–1476 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0792-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-018-0792-9