Abstract
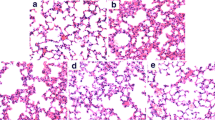
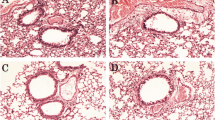
Angelicin, a furocoumarin found in Psoralea corylifolia L. fruit, has been reported to have anti-inflammatory activity. The purpose of this study was to determine the protective effects of angelicin on allergic asthma induced by ovalbumin (OVA) in mice. Mice were sensitized to OVA (on days 0 and 14) and challenged with OVA three times (on days 21 to 23). Angelicin (2.5, 5, 10 mg/kg) was given intraperitoneally 1 h before OVA treatment after the initial OVA sensitization. The production of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 in BALF and IgE in the serum were measured by ELISA. Lung histological changes were detected by using hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) stain. The results showed that angelicin significantly inhibited inflammatory cells infiltration into the lungs. Histological studies showed that angelicin significantly attenuated OVA-induced lung injury. Meanwhile, treatment of angelicin dose-dependently inhibited OVA-induced the production of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 in BALF and IgE in the serum. Furthermore, angelicin was found to inhibit airway hyperresponsiveness and NF-kB activation. In conclusion, our results suggested that angelicin inhibited allergic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness by inhibiting NF-kB activation.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bousquet, J., P.K. Jeffery, W.W. Busse, M. Johnson, and A.M. Vignola. 2000. Asthma. From bronchoconstriction to airways inflammation and remodeling. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 161(5): 1720–1745.
Larché, M., D.S. Robinson, and A.B. Kay. 2003. The role of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 111(3): 450–463.
Romagnani, S. 2000. The role of lymphocytes in allergic disease. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 105(3): 399–408.
Bradding, P., J. Roberts, K. Britten, S. Montefort, R. Djukanovic, R. Mueller, C. Heusser, P. Howarth, and S. Holgate. 1994. Interleukin-4,-5, and-6 and tumor necrosis factor-alpha in normal and asthmatic airways: evidence for the human mast cell as a source of these cytokines. American Journal of Respiratory Cell and Molecular Biology 10(5): 471–480.
Advenier, C., V. Lagente, and E. Boichot. 1997. The role of tachykinin receptor antagonists in the prevention of bronchial hyperresponsiveness, airway inflammation and cough. European Respiratory Journal 10(8): 1892–1906.
Holgate, S., T. Casale, S. Wenzel, J. Bousquet, Y. Deniz, and C. Reisner. 2005. The anti-inflammatory effects of omalizumab confirm the central role of IgE in allergic inflammation. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 115(3): 459–465.
Cho, H.J., S.G. Jeong, J.E. Park, J.A. Han, H.R. Kang, D. Lee, and M.J. Song. 2013. Antiviral activity of angelicin against gammaherpesviruses. Antiviral Research 100(1): 75–83.
Liu, F., G.-Q. Sun, H.-Y. Gao, R.-S. Li, L.-W. Soromou, N. Chen, Y.-H. Deng, and H.-H. Feng. 2013. Angelicin regulates LPS-induced inflammation via inhibiting MAPK/NF-kB pathways. Journal of Surgical Research 185(1): 300–309.
Wang, C.C., J.E. Lai, L.G. Chen, K.Y. Yen, and L.L. Yang. 2000. Inducible nitric oxide synthase inhibitors of Chinese herbs. Part 2: naturally occurring furanocoumarins. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 8(12): 2701–2707.
Zosky, G.R., and P.D. Sly. 2007. Animal models of asthma. Clinical and Experimental Allergy 37(7): 973–988.
Ackerman, K.G., H. Huang, H. Grasemann, C. Puma, J.B. Singer, A.E. Hill, E. Lander, J.H. Nadeau, G.A. Churchill, J.M. Drazen, and D.R. Beier. 2005. Interacting genetic loci cause airway hyperresponsiveness. Physiological Genomics 21(1): 105–111.
Song, C., L. Luo, Z. Lei, B. Li, Z. Liang, G. Liu, D. Li, G. Zhang, B. Huang, and Z.-H. Feng. 2008. IL-17-producing alveolar macrophages mediate allergic lung inflammation related to asthma. The Journal of Immunology 181(9): 6117–6124.
Kapp, A. 1993. The role of eosinophils in the pathogenesis of atopic dermatitis-eosinophil granule proteins as markers of disease activity. Allergy 48(1): 1–5.
Hamid, Q., M.K. Tulic, M.C. Liu, and R. Moqbel. 2003. Inflammatory cells in asthma: mechanisms and implications for therapy. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 111(1): S5–S17.
Chung, K. 1986. Role of inflammation in the hyperreactivity of the airways in asthma. Thorax 41(9): 657–662.
Wakashin, H., K. Hirose, Y. Maezawa, S.-I. Kagami, A. Suto, N. Watanabe, Y. Saito, M. Hatano, T. Tokuhisa, and Y. Iwakura. 2008. IL-23 and Th17 cells enhance Th2-cell-mediated eosinophilic airway inflammation in mice. American Journal of Respiratory and Critical Care Medicine 178(10): 1023–1032.
Renauld, J.-C. 2001. New insights into the role of cytokines in asthma. Journal of Clinical Pathology 54(8): 577–589.
Lebman, D.A., and R.L. Coffman. 1988. Interleukin 4 causes isotype switching to IgE in T cell-stimulated clonal B cell cultures. The Journal of Experimental Medicine 168(3): 853–862.
Carballido, J.M., D. Schols, R. Namikawa, S. Zurawski, G. Zurawski, M.-G. Roncarolo, and J. De Vries. 1995. IL-4 induces human B cell maturation and IgE synthesis in SCID-hu mice. Inhibition of ongoing IgE production by in vivo treatment with an IL-4/IL-13 receptor antagonist. The Journal of Immunology 155(9): 4162–4170.
O’Byrne, P.M., M.D. Inman, and K. Parameswaran. 2001. The trials and tribulations of IL-5, eosinophils, and allergic asthma. Journal of Allergy and Clinical Immunology 108(4): 503–508.
Huffnagle, G.B., M.B. Boyd, N.E. Street, and M.F. Lipscomb. 1998. IL-5 is required for eosinophil recruitment, crystal deposition, and mononuclear cell recruitment during a pulmonary Cryptococcus neoformans infection in genetically susceptible mice (C57BL/6). The Journal of Immunology 160(5): 2393–2400.
Kuperman, D.A., X. Huang, L.L. Koth, G.H. Chang, G.M. Dolganov, Z. Zhu, J.A. Elias, D. Sheppard, and D.J. Erle. 2002. Direct effects of interleukin-13 on epithelial cells cause airway hyperreactivity and mucus overproduction in asthma. Nature Medicine 8(8): 885–889.
Yang, G., A. Volk, T. Petley, E. Emmell, J. Giles-Komar, X. Shang, J. Li, A.M. Das, D. Shealy, and D.E. Griswold. 2004. Anti-IL-13 monoclonal antibody inhibits airway hyperresponsiveness, inflammation and airway remodeling. Cytokine 28(6): 224–232.
Wills‐Karp, M. 2004. Interleukin-13 in asthma pathogenesis. Immunological Reviews 202(1): 175–190.
Wills-Karp, M., J. Luyimbazi, X. Xu, B. Schofield, T.Y. Neben, C.L. Karp, and D.D. Donaldson. 1998. Interleukin-13: central mediator of allergic asthma. Science 282(5397): 2258–2261.
Webb, D.C., A.N. McKenzie, A.M. Koskinen, M. Yang, J. Mattes, and P.S. Foster. 2000. Integrated signals between IL-13, IL-4, and IL-5 regulate airways hyperreactivity. The Journal of Immunology 165(1): 108–113.
Huang, C.S., A.H. Lin, T.C. Yang, K.L. Liu, H.W. Chen, and C.K. Lii. 2015. Shikonin inhibits oxidized LDL-induced monocyte adhesion by suppressing NFkappaB activation via up-regulation of PI3K/Akt/Nrf2-dependent antioxidation in EA.hy926 endothelial cells. Biochemical Pharmacology 93(3): 352–361.
Rai, A., S. Kapoor, S. Singh, B.P. Chatterji, and D. Panda. 2015. Transcription factor NF-kappaB associates with microtubules and stimulates apoptosis in response to suppression of microtubule dynamics in MCF-7 cells. Biochemical Pharmacology 93(3): 277–289.
Zhao, Z.Z., X.F. Tang, X.H. Zhao, M.H. Zhang, W.J. Zhang, S.H. Hou, W.F. Yuan, H.F. Zhang, L.J. Shi, H. Jia, L. Liang, Z. Lai, J.F. Gao, K.Y. Zhang, L. Fu, and W. Chen. 2014. Tylvalosin exhibits anti-inflammatory property and attenuates acute lung injury in different models possibly through suppression of NF-kappa B activation. Biochemical Pharmacology 90(1): 73–87.
Bureau, F., S. Delhalle, G. Bonizzi, L. Fiévez, S. Dogné, N. Kirschvink, A. Vanderplasschen, M.-P. Merville, V. Bours, and P. Lekeux. 2000. Mechanisms of persistent NF-kB activity in the bronchi of an animal model of asthma. The Journal of Immunology 165(10): 5822–5830.
Acknowledgments
The project received the financial support from the Science and Technology Bureau of Wenzhou (Y20140253), Zhejiang Province, China.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wei, Dz., Guo, Xy., Lin, Ln. et al. Effects of Angelicin on Ovalbumin (OVA)-Induced Airway Inflammation in a Mouse Model of Asthma. Inflammation 39, 1876–1882 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0423-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-016-0423-2