Abstract
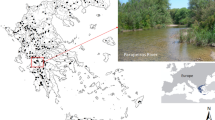
Anthropogenic changes to the temperature regimes of rivers, whether through thermal pollution, removal of shade, or climate change, could affect community stability and cause phenological changes in aquatic species. This study examines the impact of a thermal discharge from a power station on the diversity and composition of the aquatic macroinvertebrate community in the River Severn, UK. Daily temperatures up to 2 km downstream of the thermal discharge averaged 4.5°C above ambient. Abundance and taxon richness metrics were reduced at a site approximately 0.5 km downstream of the power station outfall, but were largely unaffected at a second site about 2 km downstream. The majority of the macroinvertebrate taxa observed were recorded at both control and heated sites, suggesting species were below their thermal tolerance threshold or had developed adaptations to survive increased temperatures. However, indicator species analysis suggests certain taxa were associated with particular sites; abundances of Musculium lacustre, Simulium reptans, and Orthocladiinae were greater at the unheated control site, whereas more pollution-tolerant species such Asellus aquaticus and Erpobdella octoculata were more common in the thermally impacted reaches. Overall, the results provide an indication of potential species and community response to future warming under climate change scenarios.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aston, R. J., 1973. Tubificids and water quality: a review. Environmental Pollution 5: 1–10.
Aston, R. J. & D. J. A. Brown, 1975. Local and seasonal variations in populations of the leech Erpobdella octoculata (L) in a polluted river warmed by condenser effluents. Hydrobiologia 47: 347–366.
Aston, R. J. & A. G. P. Milner, 1980. A comparison of populations of the isopod Asellus aquaticus above and below power stations in organically polluted reaches of the River Trent. Freshwater Biology 10: 1–14.
Baker, S. C. & H. F. Sharp, 1998. Evaluation of the recovery of a polluted urban stream using the Ephemeroptera–Plecoptera–Trichoptera index. Journal of Freshwater Ecology 13: 229–234.
Bates, B. C., Z. W. Kundzewicz, S. Wu & J. P. Palutikof, 2008. Climate Change and Water. Technical Paper of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. IPCC Secretariat, Geneva.
Bernotiene, R., 2013. The relationship between blackflies (Diptera: Simuliidae) and some hydrochemical and hydrophysical parameters in large and medium-sized Lithuanian rivers. River Research and Applications. doi:10.1002/rra.2715.
Bolker, B. M., M. E. Brooks, C. J. Clark, S. W. Geange, J. R. Poulsen, M. H. H. Stevens & J.-S. S. White, 2009. Generalized linear mixed models: a practical guide for ecology and evolution. Trends in Ecology & Evolution 24: 127–135.
Brittain, J., 1977. The effect of temperature on the egg incubation period of Taeniopteryx nebulosa (Plecoptera). Oikos 29: 302–305.
Brittain, J., 1990. Life history strategies in Ephemeroptera and Plecoptera. In Campbell, I. C. (ed.), Mayflies and Stoneflies. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht: 1–12.
Broadmeadow, S. B., J. G. Jones, T. E. L. Langford, P. J. Shaw & T. R. Nisbet, 2011. The influence of riparian shade on lowland stream water temperatures in southern England and their viability for brown trout. River Research and Applications 27: 226–237.
Caissie, D., 2006. The thermal regime of rivers: a review. Freshwater Biology 51: 1389–1406.
Chessman, B. C., 2009. Climatic changes and 13-year trends in stream macroinvertebrate assemblages in New South Wales, Australia. Global Change Biology 15: 2791–2802.
Conti, L., A. Schmidt-Kloiber, G. Grenouillet & W. Graf, 2014. A trait-based approach to assess the vulnerability of European aquatic insects to climate change. Hydrobiologia 721: 297–315.
Dallas, H. F. & Z. A. Ketley, 2011. Upper thermal limits of aquatic macroinvertebrates: comparing critical thermal maxima with 96-LT50 values. Journal of Thermal Biology 36: 322–327.
Daufresne, M., M. C. Roger, H. Capra & N. Lamouroux, 2004. Long-term changes within the invertebrate and fish communities of the Upper Rhône River: effects of climatic factors. Global Change Biology 10: 124–140.
De Cáceres, M. & P. Legendre, 2009. Associations between species and groups of sites: indices and statistical inference. Ecology 90: 3566–3574.
De Cáceres, M., P. Legendre & M. Moretti, 2010. Improving indicator species analysis by combining groups of sites. Oikos 119: 1674–1684.
Diamond, S. E., A. M. Frame, R. A. Martin & L. B. Buckley, 2011. Species’ traits predict phenological responses to climate change in butterflies. Ecology 92: 1005–1012.
Domisch, S., M. B. Araújo, N. Bonada, S. U. Pauls, S. C. Jähnig & P. Haase, 2013. Modelling distribution in European stream macroinvertebrates under future climates. Global Change Biology 19: 752–762.
Domisch, S., S. C. Jähnig & P. Haase, 2011. Climate-change winners and losers: stream macroinvertebrates of a submontane region in Central Europe. Freshwater Biology 56: 2009–2020.
Duda, A. M. & M. T. El-Ashry, 2000. Addressing the global water and environment crises through integrated approaches to the management of land, water and ecological resources. Water International 25: 115–126.
Dudgeon, D., A. H. Arthington, M. O. Gessner, Z.-I. Kawabata, D. J. Knowler, C. Lévêque, R. J. Naiman, A.-H. Prieur-Richard, D. Soto, M. L. J. Stiassny & C. A. Sullivan, 2006. Freshwater biodiversity: importance, threats, status and conservation challenges. Biological Reviews 81: 163–182.
Dufrêne, M. & P. Legendre, 1997. Species assemblages and indicator species: the need for a flexible asymmetrical approach. Ecological Monographs 67: 345–366.
Durance, I. & S. J. Ormerod, 2007. Climate change effects on upland stream macroinvertebrates over a 25-year period. Global Change Biology 13: 942–957.
Durance, I. & S. J. Ormerod, 2009. Trends in water quality and discharge confound long-term warming effects on river macroinvertebrates. Freshwater Biology 54: 388–405.
Durrett, C. W. & W. D. Pearson, 1975. Drift of macroinvertebrates in a channel carrying heated water from a power plant. Hydrobiologia 46: 33–43.
Elliott, J. M., 1987. Egg hatching and resource partitioning in stoneflies: the six British Leuctra Spp. (Plecoptera: Leuctridae). Journal of Animal Ecology 56: 415–426.
Fey, J. M., 1977. The heating of a mountain stream and the effects on the zoocenosis demonstrated by the Lenne, Sauerland. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 53: 307–363.
Ficke, A. D., C. A. Myrick & L. J. Hansen, 2007. Potential impacts of global climate change on freshwater fisheries. Reviews in Fish Biology and Fisheries 17: 581–613.
Floury, M., P. Usseglio-Polatera, M. Ferreol, C. Delattre & Y. Souchon, 2013. Global climate change in large European rivers: long-term effects on macroinvertebrate communities and potential local confounding factors. Global Change Biology 19: 1085–1099.
Foster, D., F. Swanson, J. Aber, I. Burke, N. Brokaw, D. Tilman & A. Knapp, 2003. The importance of land-use legacies to ecology and conservation. Bioscience 53: 77–88.
Fournier, D. A., H. J. Skaug, J. Ancheta, J. Ianelli, A. Magnusson, M. N. Maunder, A. Nielsen & J. Sibert, 2012. AD Model Builder: using automatic differentiation for statistical inference of highly parameterized complex nonlinear models. Optimization Methods and Software 27: 233–249.
Fox, J. & S. Weisberg, 2011. An R Companion to Applied Regression, 2nd ed. SAGE Publications, Thousand Oaks, CA.
Freeman, M. C. & P. A. Marcinek, 2006. Fish assemblage responses to water withdrawals and water supply reservoirs in Piedmont streams. Environmental Management 38: 435–450.
Friberg, N. & D. Jacobsen, 1999. Variation in growth of the detritivore-shredder Sericostoma personatum (Trichoptera). Freshwater Biology 42: 625–635.
Frost, S., A. Huni & W. E. Kershaw, 1971. Evaluation of a kicking technique for sampling stream bottom fauna. Canadian Journal of Zoology 49: 167–173.
Furse, M. T., J. F. Wright, P. D. Armitage & D. Moss, 1981. An appraisal of pond-net samples for biological monitoring of lotic macro-invertebrates. Water Research 15: 679–689.
Hahn, T., 2005. Respiration rates in Bithynia tentaculata (L.) (Gastropoda: Bithyniidae) in response to acclimation temperature and acute temperature change. Journal of Molluscan Studies 71: 127–131.
Haidekker, A. & D. Hering, 2008. Relationship between benthic insects (Ephemeroptera, Plecoptera, Coleoptera, Trichoptera) and temperature in small and medium-sized streams in Germany: a multivariate study. Aquatic Ecology 42: 463–481.
Hammond, D. & A. R. Pryce, 2007. Climate Change Impacts and Water Temperature. Environment Agency Science Report SC060017/SR Bristol, UK.
Harding, J. S., E. F. Benfield, P. V. Bolstad, G. S. Helfman & E. B. D. Jones, 1998. Stream biodiversity: the ghost of land use past. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 95: 14843–14847.
Hartigan, J. A. & M. A. Wong, 1979. A k-means clustering algorithm. Applied Statistics 28: 100–108.
Hawkes, H. A., 1956. The biological assessment of pollution in Birmingham streams. Journal of the Institute of Municipal Engineers 82: 425–436.
Heino, J., R. Virkkala & H. Toivonen, 2009. Climate change and freshwater biodiversity: detected patterns, future trends and adaptations in northern regions. Biological Reviews 84: 39–54.
Hering, D., A. Schmidt-Kloiber, J. Murphy, S. Lücke, C. Zamora-Muñoz, M. López-Rodríguez, T. Huber & W. Graf, 2009. Potential impact of climate change on aquatic insects: a sensitivity analysis for European caddisflies (Trichoptera) based on distribution patterns and ecological preferences. Aquatic Sciences 71: 3–14.
Hoang, H., F. Recknagel, J. Marshall & S. Choy, 2006. Elucidation of hypothetical relationships between habitat conditions and macroinvertebrate assemblages in freshwater streams by artificial neural networks. In Recknagel, F. (ed.), Ecological Informatics. Springer, Berlin: 239–251.
Hogg, I. D. & D. D. Williams, 1996. Response of stream invertebrates to a global-warming thermal regime: an ecosystem-level manipulation. Ecology 77: 395–407.
Hogg, I. D., D. D. Williams, J. M. Eadie & S. A. Butt, 1995. The consequences of global warming for stream invertebrates: a field simulation. Journal of Thermal Biology 20: 199–206.
Hothorn, T., F. Bretz & P. Westfall, 2008. Simultaneous inference in general parametric models. Biometrical Journal 50: 346–363.
Howells, G. D., 1983. The effects of power station cooling water discharges on aquatic ecology. Water Pollution Control 19: 10–17.
Hrovat, M. & G. Urbanic, 2012. Life cycle of Rhyacophila fasciata Hagen, 1859 and Hydropsyche saxonica McLachlan, 1884 in a Dinaric karst river system. Aquatic Insects 34: 113–125.
Hulme, M., G. J. Jenkins, X. Lu, J. R. Turnpenny, T. D. Mitchell, R. G. Jones, J. Lowe, J. M. Murphy, D. Hassell, P. Boorman, R. McDonald & S. Hill, 2002. Climate Change Scenarios for the United Kingdom: The UKCIP02 Scientific Report. Tyndall Centre for Climate Change Research, School of Environmental Sciences, University of East Anglia, Norwich.
Hynes, H. B. N., 1960. The Biology of Polluted Waters. Liverpool University Press, Liverpool.
IPCC, 2013. Summary for policymakers. In Stocker, T. F., et al. (eds), Climate Change 2013: The Physical Science Basis Contribution of Working Group I to the Fifth Assessment Report of the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Jenkins, G. J., J. M. Murphy, D. M. H. Sexton, J. A. Lowe, P. Jones & C. G. Kilsby, 2009. UK Climate Projections: Briefing Report. Met Office Hadley Centre, Exeter.
Jenkins, G. J., M. C. Perry & M. J. Prior, 2008. The Climate of the United Kingdom and Recent Trends. Met Office Hadley Centre, Exeter.
Jenkins, M., 2003. Prospects for biodiversity. Science 302: 1175–1177.
Johnson, A. C., M. C. Acreman, M. J. Dunbar, S. W. Feist, A. M. Giacomello, R. E. Gozlan, S. A. Hinsley, A. T. Ibbotson, H. P. Jarvie, J. I. Jones, M. Longshaw, S. C. Maberly, T. J. Marsh, C. Neal, J. R. Newman, M. A. Nunn, R. W. Pickup, N. S. Reynard, C. A. Sullivan, J. P. Sumpter & R. J. Williams, 2009. The British river of the future: how climate change and human activity might affect two contrasting river ecosystems in England. Science of the Total Environment 407: 4787–4798.
Jones, A. F., M. G. Macklin & P. A. Brewer, 2012. A geochemical record of flooding on the upper River Severn, UK, during the last 3750 years. Geomorphology 179: 89–105.
Korhonen, A. I. & K. Y. H. Lagerspetz, 1996. Heat shock response and thermal acclimation in Asellus aquaticus. Journal of Thermal Biology 21: 49–56.
Langford, T., T. Worthington, P. Shaw, P. Kemp, C. Woolgar, A. Ferguson, P. Harding & D. Ottewell, 2012. The unnatural history of the River Trent: 50 years of ecological recovery. In Boon, P. J. & P. J. Raven (eds), River Conservation and Management. Wiley, Chichester: 261–272.
Langford, T. E. L., 1970. The temperature of a British river upstream and downstream of a heated discharge from a power station. Hydrobiologia 35: 353–375.
Langford, T. E. L., 1971. The distribution, abundance and life-histories of stoneflies (Plecoptera) and mayflies (Ephemeroptera) in a British river, warmed by cooling-water from a power station. Hydrobiologia 38: 339–377.
Langford, T. E. L., 1983. Electricity Generation and the Ecology of Natural Waters. Liverpool University Press, Liverpool.
Langford, T. E. L., 1990. Ecological Effects of Thermal Discharges. Elsevier, London.
Langford, T. E. L. & J. R. Daffern, 1975. The emergence of insects from a British river warmed by power station cooling-water. Hydrobiologia 46: 71–114.
Lenat, D. R., 1988. Water quality assessment of streams using a qualitative collection method for benthic macroinvertebrates. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 7: 222–233.
Magurran, A. E. & P. A. Henderson, 2003. Explaining the excess of rare species in natural species abundance distributions. Nature 422: 714–716.
Mouthon, J., 2004. Life cycle of Musculium lacustre (Bivalvia: Sphaeriidae) in the Saône river at Lyon (France): a curious life strategy. Annales de Limnologie – International Journal of Limnology 40: 279–284.
Mouthon, J. & M. Daufresne, 2006. Effects of the 2003 heatwave and climatic warming on mollusc communities of the Saône: a large lowland river and of its two main tributaries (France). Global Change Biology 12: 441–449.
Nordlie, K. J. & J. W. Arthur, 1981. Effect of elevated water temperature on insect emergence in outdoor experimental channels. Environmental Pollution Series A, Ecological and Biological 25: 53–65.
Obrdlík, P., Z. Adámek & J. Zahrádka, 1979. Mayfly fauna (Ephemeroptera) and the biology of the species Potamanthus luteus (L.) in a warmed stretch of the Oslava River. Hydrobiologia 67: 129–140.
Pinheiro, J., D. Bates, S. DebRoy, D. Sarkar & R Development Core Team, 2013. nlme: Linear and Nonlinear Mixed Effects Models. R Package Version 3.1-113.
Poff, N. L. & R. A. Matthews, 1986. Benthic macroinvertebrate community structural and functional group response to thermal enhancement in the Savannah River and a coastal plain tributary. Fundamental and Applied Limnology 106: 119–137.
Poff, N. L., M. I. Pyne, B. P. Bledsoe, C. C. Cuhaciyan & D. M. Carlisle, 2010. Developing linkages between species traits and multiscaled environmental variation to explore vulnerability of stream benthic communities to climate change. Journal of the North American Benthological Society 29: 1441–1458.
R Core Team, 2014. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna. http://www.R-project.org/.
Revenga, C., J. Brunner, N. Henninger, K. Kassem & R. Payne, 2000. Pilot Analysis of Global Ecosystems: Freshwater Systems. World Resources Institute, Washington, DC.
Ricciardi, A. & J. B. Rasmussen, 1999. Extinction rates of North American freshwater fauna. Conservation Biology 13: 1220–1222.
Rotvit, L. & D. Jacobsen, 2013. Temperature increase and respiratory performance of macroinvertebrates with different tolerances to organic pollution. Limnologica – Ecology and Management of Inland Waters 43: 510–515.
Sahin, S. K., 2012. Gastropod species distribution and its relation with some physico-chemical parameters of the Malatya’s streams (East Anatolia, Turkey). Acta Zoologica Bulgarica 64: 129–133.
Sala, O. E., F. Stuart Chapin III, J. J. Armesto, E. Berlow, J. Bloomfield, R. Dirzo, E. Huber-Sanwald, L. F. Huenneke, R. B. Jackson, A. Kinzig, R. Leemans, D. M. Lodge, H. A. Mooney, M. Oesterheld, N. L. Poff, M. T. Sykes, B. H. Walker, M. Walker & D. H. Wall, 2000. Global biodiversity scenarios for the year 2100. Science 287: 1770–1774.
Skaug, H., D. Fournier, A. Nielsen, A. Magnusson & B. Bolker, 2013. glmmADMB: Generalized Linear Mixed Models Using AD Model Builder. R Package Version 0.7.7.
Tixier, G., K. Wilson & D. D. Williams, 2009. Exploration of the influence of global warming on the chironomid community in a manipulated shallow groundwater system. Hydrobiologia 624: 13–27.
Watts, G., R. Batterbee, J. P. Bloomfield, J. Crossman, A. Daccache, I. Durance, J. Elliot, G. Garner, J. Hannaford, D. M. Hannah, T. Hess, C. R. Jackson, A. L. Kay, M. Kernan, J. Knox, J. Mackay, D. T. Monteith, S. Ormerod, J. Rance, M. E. Stuart, A. J. Wade, S. D. Wade, K. Weatherhead, P. G. Whitehead & R. L. Wilby, 2013. Climate Change and Water in the UK: Past Changes and Future Prospects – A Climate Change Report Card for Water: Working Technical Paper. LWEC Partnership.
Wellborn, G. A. & J. V. Robinson, 1996. Effects of a thermal effluent on macroinvertebrates in a central Texas reservoir. The American Midland Naturalist 136: 110–120.
Wilby, R. L., H. Orr, G. Watts, R. W. Battarbee, P. M. Berry, R. Chadd, S. J. Dugdale, M. J. Dunbar, J. A. Elliott, C. Extence, D. M. Hannah, N. Holmes, A. C. Johnson, B. Knights, N. J. Milner, S. J. Ormerod, D. Solomon, R. Timlett, P. J. Whitehead & P. J. Wood, 2010. Evidence needed to manage freshwater ecosystems in a changing climate: turning adaptation principles into practice. Science of the Total Environment 408: 4150–4164.
Wood, S. N., 2003. Thin plate regression splines. Journal of the Royal Statistical Society: Series B (Statistical Methodology) 65: 95–114.
Wood, S. N., 2004. Stable and efficient multiple smoothing parameter estimation for generalized additive models. Journal of the American Statistical Association 99: 673–686.
Woodward, G., D. M. Perkins & L. E. Brown, 2010. Climate change and freshwater ecosystems: impacts across multiple levels of organization. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 365: 2093–2106.
Wright, J. F., D. W. Sutcliffe & M. T. Furse (eds), 2000. Assessing the Biological Quality of Fresh Waters: Rivpacs and other Techniques. Freshwater Biological Association, Ambleside.
Zuur, A. F., 2012. A Beginner’s Guide to Generalized Additive Models with R. Highland Statistics Limited, Newburgh.
Zuur, A. F., E. N. Ieno & C. S. Elphick, 2010. A protocol for data exploration to avoid common statistical problems. Methods in Ecology and Evolution 1: 3–14.
Zuur, A. F., E. N. Ieno, N. Walker, A. A. Saveliev & G. M. Smith, 2009. Mixed Effects Models and Extensions in Ecology with R. Springer, New York.
Acknowledgments
The research was funded by the Esmée Fairbairn Foundation (Grant Number: 091737). The authors wish to thank Dr. R. J. Aston and Dr. D. J. A. Brown for much assistance in the field and the referees for constructive and pertinent comments and suggestions.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Alex Elliott
T. A. Worthington is a visiting researcher within the Department of Biology, University of Maryland.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Worthington, T.A., Shaw, P.J., Daffern, J.R. et al. The effects of a thermal discharge on the macroinvertebrate community of a large British river: implications for climate change. Hydrobiologia 753, 81–95 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2197-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-015-2197-1