Abstract
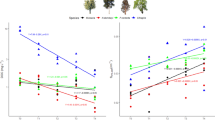
In shallow aquatic systems, the majority of organic matter mineralization occurs in the sediments. Several factors including temperature control mineralization rates, however, the underlying causes of the effects are not well understood in subtropical lakes. In this study, we determined the influence of temperature on organic matter degradation by taking sediments from four sites in a subtropical large shallow freshwater lake, and monitoring organic matter composition and enzymes in microcosm experiments at five temperatures from 5 to 40°C. Following a three-month incubation, it was found that the mineralization of submerged plants in sediments was strongly influenced by temperature. Removal efficiency of total organic carbon in sediments ranged from 4.3 to 22.6% at 5°C, and reached 46.7–55.5% at 40°C. In addition, the removal efficiency of organic matter and the relative recalcitrant carbon decomposition depended on sediment type. For sediments in the site located in the lake center, recalcitrant and labile carbon decomposition had equivalent responses to the different temperatures. For sediments with dominance of submerged macrophytes, the humic acids were low even at high temperature. Thus, the annual deposition of plant litter in sediments favored organic carbon decomposition rather than humification.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baldwin, D. S. & A. Mitchell, 2012. Impact of sulfate pollution on anaerobic biogeochemical cycles in a wetland sediment. Water Research 46: 965–974.
Bastviken, D., L. J. Tranvik, J. A. Downing, P. M. Crill & A. Enrich-Prast, 2011. Freshwater methane emissions offset the continental carbon sink. Science 331: 50.
Benner, R., M. A. Moran & R. E. Hodson, 1986. Biogeochemical cycling of lignocellulosic carbon in marine and freshwater ecosystems: relative contributions of procaryotes and eucaryotes. Limnology and Oceanography 31: 89–100.
Bergström, I., P. Kortelainen, J. Sarvala & K. Salonen, 2010. Effects of temperature and sediment properties on benthic CO2 production in an oligotrophic boreal lake. Freshwater Biology 55: 1747–1757.
Buesing, N. & M. O. Gessner, 2006. Benthic bacterial and fungal productivity and carbon turnover in a freshwater marsh. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 72: 596–605.
Canfield, D. E., B. B. Jørgensen, H. Fossing, R. Glud, J. Gundersen, N. B. Ramsing, B. Thamdrup, J. W. Hansen, L. P. Nielsen & P. O. J. Hall, 1993. Pathways of organic-carbon oxidation in three continental-margin sediments. Marine Geology 113: 27–40.
Cole, J. J., Y. T. Prairie, N. F. Caraco, W. H. McDowell, L. J. Tranvik, R. G. Striegl, C. M. Duarte, P. Kortelainen, J. A. Downing, J. J. Middelburg & J. Melack, 2007. Plumbing the global carbon cycle: integrating inland waters into the terrestrial carbon budget. Ecosystems 10: 172–184.
Dean, W. E. & E. Gorham, 1998. Magnitude and significance of carbon burial in lakes, reservoirs, and peatlands. Geology 26: 535–538.
de Boer, W., L. B. Folman, R. C. Summerbell & L. Boddy, 2005. Living in a fungal world: impact of fungi on soil bacterial niche development. FEMS Microbiology Reviews 29: 795–811.
den Heyer, C. & J. Kalff, 1998. Organic matter mineralization rates in sediments: a within- and among-lake study. Limnology and Oceanography 43: 695–705.
Dong, X. H., N. J. Anderson, X. D. Yang, X. Chen & J. Shen, 2012. Carbon burial by shallow lakes on the Yangtze floodplain and its relevance to regional carbon sequestration. Global Chang Biology 18: 2205–2217.
Dubois, M., K. A. Gilles, J. K. Hamilton, P. A. Rebers & F. Smith, 1956. Colorimetric method for determination of sugars and related substances. Analytic Chemistry 28: 350–356.
Finke, N. & B. B. Jørgensen, 2008. Response of fermentation and sulfate reduction to experimental temperature changes in temperate and Arctic marine sediments. ISME Journal 2: 815–829.
Ghose, T. K., 1987. Measurement of cellulase activities. Pure and Applied Chemistry 59: 257–268.
Giovanela, M., E. Parlanti, E. J. Soriano-Sierra, M. S. Soldi & M. M. D. Sierra, 2004. Elemental compositions, FT-IR spectra and thermal behavior of sedimentary fulvic and humic acids from aquatic and terrestrial environments. Geochemical Journal 38: 255–264.
Gudasz, C., D. Bastviken, K. Steger, K. Premke, S. Sobek & L. J. Tranvik, 2010. Temperature-controlled organic carbon mineralization in lake sediments. Nature 466: 478–481.
Gudasz, C., D. Bastviken, K. Premke, K. Steger & L. J. Tranvik, 2012. Constrained microbial processing of allochthonous organic carbon in boreal lake sediments. Limnology and Oceanography 57: 163–175.
Hong, S. W., H. S. Kim & T. H. Chung, 2010. Alteration of sediment organic matter in sediment microbial fuel cells. Environmental Pollution 158: 185–191.
Hu, W. P., S. E. Jørgensen & F. B. Zhang, 2006. A vertical-compressed three-dimensional ecological model in Lake Taihu, China. Ecological Modelling 190: 367–398.
Hungate, R. E., 1950. The anaerobic mesophilic cellulolytic bacteria. Bacteriological reviews 14: 1–49.
Hupfer, M. & J. Lewandowski, 2008. Oxygen controls the phosphorus release from lake sediments—a long-lasting paradigm in limnology. International Review of Hydrobiology 93: 415–432.
Jin, X. C., S. R. Wang, Y. Pang & F. C. Wu, 2006. Phosphorus fractions and the effect of pH on the phosphorus release of the sediments from different trophic areas in Taihu Lake, China. Environmental Pollution 139: 288–295.
Kourtev, P. S., J. G. Ehrenfeld & W. Z. Huang, 2002. Enzyme activities during litter decomposition of two exotic and two native plant species in hardwood forests of New Jersey. Soil Biology & Biochemistry 34: 1207–1218.
Kristensen, E., S. I. Ahmed & A. H. Devol, 1995. Aerobic and anaerobic decomposition of organic matter in marine sediment: which is fastest? Limnology and Oceanography 40: 1430–1437.
Laas, A., P. Noges, T. Koiv & T. Noges, 2012. High-frequency metabolism study in a large and shallow temperate lake reveals seasonal switching between net autotrophy and net heterotrophy. Hydrobiologia 694: 57–74.
Larmola, T., J. Alm, S. Juutinen, D. Koppisch, J. Augustin, P. J. Martikainen & J. Silvola, 2006. Spatial patterns of litter decomposition in the littoral zone of boreal lakes. Freshwater Biology 51: 2252–2264.
Liikanen, A., T. Murtoniemi, H. Tanskanen, T. Vaisanen & P. J. Martikainen, 2002. Effects of temperature and oxygen availability on greenhouse gas and nutrient dynamics in sediment of a eutrophic mid-boreal lake. Biogeochemistry 59: 269–286.
Liikanen, A., J. T. Huttunen, T. Murtoniemi, H. Tanskanen, T. Vaisanen, J. Silvola, J. Alm & P. J. Martikainen, 2003. Spatial and seasonal variation in greenhouse gas and nutrient dynamics and their interactions in the sediments of a boreal eutrophic lake. Biogeochemistry 65: 83–103.
Longhi, D., M. Bartoli & P. Viaroli, 2008. Decomposition of four macrophytes in wetland sediments: organic matter and nutrient decay and associated benthic processes. Aquatic Botany 89: 303–310.
Lovley, D. R. & E. J. P. Phillips, 1988. Novel mode of microbial energy metabolism: organic carbon oxidation coupled to dissimilatory reduction of iron or manganese. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 54: 1472–1480.
McKinley, V. L. & J. R. Vestal, 1992. Mineralization of glucose and lignocellulose by four arctic freshwater sediments in response to nutrient enrichment. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 58: 1554–1563.
Pace, M. L. & Y. T. Prairie, 2005. Respiration in lakes. In del Giorgio, P. A. & P. J. Le B. Williams (eds), Respiration in Aquatic Ecosystems. Oxford University Press, New York: 103–121.
Paerl, H. W., H. Xu, M. J. McCarthy, G. W. Zhu, B. Q. Qin, Y. P. Li & W. S. Gardner, 2011. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): the need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Research 45: 1973–1983.
Prairie, Y. T., C. de Montigny & P. A. del Giorgio, 2001. Anaerobic phosphorus release from sediments: a paradigm revisited. Verhandlungen der Internationale Vereinigung für theoretische und angewandte Limnologie 27: 4013–4020.
Prescott, C. E., 2010. Litter decomposition: what controls it and how can we alter it to sequester more carbon in forest soils? Biogeochemistry 101: 133–149.
Qin, B. Q., P. Z. Xu, Q. L. Wu, L. C. Luo & Y. L. Zhang, 2007. Environmental issues of Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581: 3–14.
Rovira, P. & V. R. Vallejo, 2002. Labile and recalcitrant pools of carbon and nitrogen in organic matter decomposing at different depths in soil: an acid hydrolysis approach. Geoderma 107: 109–141.
Schneider, T., K. M. Keiblinger, E. Schmid, K. Sterflinger-Gleixner, G. Ellersdorfer, B. Roschitzki, A. Richter, L. Eberl, S. Zechmeister-Boltenstern & K. Riedel, 2011. Who is who in litter decomposition? Metaproteomics reveals major microbial players and their biogeochemical functions. ISME Journal 6: 1749–1762.
Shao, K., G. Gao, B. Qin, X. Tang, Y. Wang, K. Chi & J. Dai, 2011. Comparing sediment bacterial communities in the macrophyte-dominated and algae-dominated areas of eutrophic Lake Taihu, China. Canadian Journal of Microbiology 57: 263–272.
Sinsabaugh, R. L., 2010. Phenol oxidase, peroxidase and organic matter dynamics of soil. Soil Biology & Biochemistry 42: 391–404.
Sizova, M. V., J. A. Izquierdo, N. S. Panikov & L. R. Lynd, 2011. Cellulose- and xylan-degrading thermophilic anaerobic bacteria from biocompost. Applied and Environmental Microbiology 77: 2282–2291.
Sobek, S., E. Durisch-Kaiser, R. Zurbrügg, N. Wongfun, M. Wessels, N. Pasche & B. Wehrli, 2009. Organic carbon burial efficiency in lake sediments controlled by oxygen exposure time and sediment source. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 2243–2254.
Song, T. S., H. Y. Cai, Z. S. Yan, Z. W. Zhao & H. L. Jiang, 2012. Various voltage productions by microbial fuel cells with sedimentary inocula taken from different sites in one freshwater lake. Bioresource Technology 108: 68–75.
Song, N., H. Y. Cai, Z. S. Yan & H. L. Jiang, 2013. Cellulose degradation by one mesophilic strain Caulobacter sp. FMC1 under both aerobic and anaerobic conditions. Bioresource Technology 131: 281–287.
Stookey, L. L., 1970. Ferrozine: a new spectrophotometric regent for iron. Analytic Chemistry 42: 779–781.
Thomsen, U., B. Thamdrup, D. A. Stahl & D. E. Canfield, 2004. Pathways of organic carbon oxidation in a deep lacustrine sediment, Lake Michigan. Limnology and Oceanography 49: 2046–2057.
Tranvik, L. J., J. A. Downing, J. B. Cotner, S. A. Loiselle, R. G. Striegl, T. J. Ballatore, P. Dillon, K. Finlay, K. Fortino, et al., 2009. Lakes and reservoirs as regulators of carbon cycling and climate. Limnology and Oceanography 54: 2298–2314.
von Lützow, M. & I. Kögel-Knabner, 2009. Temperature sensitivity of soil organic matter decomposition—what do we know? Biology and Fertility of Soils 46: 1–15.
Walkley, A. & I. A. Black, 1934. An examination of the Degtjareff method for determining soil organic matter and a proposed modification of the chromic acid titration method. Soil Science 37: 29–38.
Weston, N. B. & S. B. Joye, 2005. Temperature-driven decoupling of key phases of organic matter degradation in marine sediments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 102: 17036–17040.
Wetterstedt, J. Ǻ. M., T. Persson & G. I. Ǻgren, 2010. Temperature sensitivity and substrate quality in soil organic matter decomposition: results of an incubation study with three substrates. Global Chang Biology 16: 1806–1819.
Wissel, H., C. Mayr & A. Lücke, 2008. A new approach for the isolation of cellulose from aquatic plant tissue and freshwater sediments for stable isotope analysis. Organic Geochemistry 39: 1545–1561.
Woomer, P., J. Bennett & R. Yost, 1990. Overcoming the inflexibility of most-probable-number procedures. Agronomy Journal 82: 349–353.
Wu, T. F., B. Q. Qin, G. W. Zhu, Y. Q. Ding, Y. P. Wang, L. C. Luo, W. Li & W. M. Zhang, 2012. Flume simulation of wave-induced release of internal dissolved nitrogen in Taihu Lake, China. Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 30: 796–805.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank anonymous reviewers and the associate editor Dr Mariana Meerhoff for their valuable comments, and Prof Lee R Krumholz in University of Oklahoma, USA, for help in language modification for the manuscript,. This work was supported by grants from Innovation Program of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (KZCX2-EW-314), and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (51079139 and 40971279).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Mariana Meerhoff
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, N., Yan, ZS., Cai, HY. et al. Effect of temperature on submerged macrophyte litter decomposition within sediments from a large shallow and subtropical freshwater lake. Hydrobiologia 714, 131–144 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1529-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-013-1529-2