Abstract
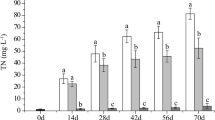
While considerable research has addressed the influence of sediment resuspension on shallow lake ecosystems, little attention has been paid to its potential impact on phytoplankton responses to nutrient loading. A factorial experiment was designed using field mesocosms to investigate the impacts of resuspension, nutrient loading and the interactions between them on standing crops of phytoplankton and community structure dynamics. Results showed that phytoplankton biomass increased with nutrient loading when no sediment resuspension occurred, but there was no significant biomass response to nutrient loading in treatments with strong sediment resuspension. The results also showed both sediment resuspension and nutrient loading to have significant effects on the structural dynamics of phytoplankton communities. Our results suggest that strong sediment resuspension can dampen the response of phytoplankton to nutrient loading in lakes such as Lake Taihu which experiences strong sediment resuspension due to wind action. These findings also suggest that in shallow eutrophic lakes with high nutrient concentrations or external loadings, measures aimed at reducing sediment resuspension are unlikely to be effective in aiding the re-establishment of macrophytes, because of the side effect of enhanced phytoplankton growth.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
APHA, 1998. Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater. American Public Health Association, Washington, DC.
Bachmann, R. W., M. V. Hoyer & D. E. Canfield Jr, 1999. The restoration of Lake Apopka in relation to alternative stable states. Hydrobiologia 394: 219–232.
Bloesch, J., 1995. Mechanisms, measurement and importance of sediment resuspension in lakes. Marine and Freshwater Research 46: 295–304.
Blom, G., E. van Duin & L. Lijklema, 1994. Sediment resuspension and light conditions in some shallow Dutch lakes. Water Science and Technology 30: 243–252.
Chen, Y., B. Qin, K. Teubner & M. T. Dokulil, 2003. Long-term dynamics of phytoplankton assemblages: Microcystis-domination in Lake Taihu, a large shallow lake in China. Journal of Plankton Research 25: 445–453.
Diehl, S., S. Berger, R. Ptacnik & A. Wild, 2002. Phytoplankton, light, and nutrients in a gradient of mixing depths: field experiments. Ecology 83: 399–411.
Evans, R. D., 1994. Empirical evidence of the importance of sediment resuspension in lakes. Hydrobiologia 284: 5–12.
Gervais, F., 1997. Light-dependent growth, dark survival, and glucose uptake by Cryptophytes isolated from a freshwater chemocline. Journal of Phycology 33: 18–25.
Gulati, R. D. & E. Van Donk, 2002. Lakes in the Netherlands, their origin, eutrophication and restoration: state-of-the-art review. Hydrobiologia 478: 73–106.
Håkanson, L., 1982. Lake bottom dynamics and morphometry: the dynamic ratio. Water Resources Research 18: 1444–1450.
Håkanson, L. & M. Jansson, 1983. Principles of Lake Sedimentology. Springer-Verlag, Berlin.
Hamilton, D. P. & S. F. Mitchell, 1996. An empirical model for sediment resuspension in shallow lakes. Hydrobiologia 317: 209–220.
Hamilton, D. P. & S. F. Mitchell, 1997. Wave-induced shear stresses, plant nutrients and chlorophyll in seven shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 38: 159–168.
Hellström, T., 1991. The effect of resuspension on algal production in a shallow lake. Hydrobiologia 213: 183–190.
Hu, H., R. Li, Y. Wei, H. Zhu, J. Chen & Z. Shi, 1980. Freshwater Algae in China. Shanghai Science and Technology Press, Shanghai. (in Chinese).
Huang, P. & Z. Liu, 2009. The effect of wave-reduction engineering on sediment resuspension in a large, shallow, eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu). Ecological Engineering 35: 1619–1623.
Huisman, J. & F. J. Weissing, 1994. Light-limited growth and competition for light in well-mixed aquatic environments: an elementary model. Ecology 75: 507–520.
Jäger, C., S. Diehl & G. M. Schmidt, 2008. Influence of water-column depth and mixing on phytoplankton biomass, community composition, and nutrients. Limnology and Oceanography 53: 2361–2373.
James, R. T., K. Havens, G. Zhu & B. Qin, 2009. Comparative analysis of nutrients, chlorophyll and transparency in two large shallow lakes (Lake Taihu, P. R. China and Lake Okeechobee, USA). Hydrobiologia 627: 211–231.
Jansson, M., P. Blomqvist, A. Josson & A. K. Bergstrom, 1996. Nutrient limitation of bacterioplankton, autotrophic and mixotrophic phytoplankton, and heterotrophic nanoflagellates in Lake Örträsket. Limnology and Oceanography 41: 1552–1559.
Jeppesen, E., P. Kristensen, J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard, E. Mortensen & T. Lauridsen, 1991. Recovery resilience following a reduction in external phosphorus loading of shallow, eutrophic Danish lakes: duration, regulating factors and methods for overcoming resilience. Memorie dell’istituto italiano di idrobiologia dott Marco de Marchi 48: 127–148.
Jeppesen, E., J. P. Jensen, M. Søndergaard & T. Lauridsen, 1999. Trophic dynamics in turbid and clearwater lakes with special emphasis on the role of zooplankton for water clarity. Hydrobiologia 408: 217–231.
Jeppesen, E., M. Meerhoff, B. A. Jacobsen, R. S. Hansen, M. Søndergaard, J. P. Jensen, T. L. Lauridsen, N. Mazzeo & C. W. C. Branco, 2007. Restoration of shallow lakes by nutrient control and biomanipulation—the successful strategy varies with lake size and climate. Hydrobiologia 581: 269–285.
Jiang, W., Z. Liu, L. Guo, F. Chen & X. Song, 2010. Experimental study on the effect of sediment resuspension on zooplankton community. Journal of Lake Sciences 22: 557–562. (in Chinese).
Jin, X. & Q. Tu, 1990. The Standard Methods for Observation and Analysis in Lake Eutrophication, 2nd ed. Environmental Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese).
Kristensen, P., M. Søndergaard & E. Jeppesen, 1992. Resuspension in a shallow eutrophic lake. Hydrobiologia 228: 101–109.
Li, W. C., 1996. Biological and environmental succession in Wuli Bay of Taihu Lake along with the eutrophication processes. Journal of Lake Science 8(Suppl): 37–45. (in Chinese with English abstract).
McCarthy, M. J., P. J. Lavrentyev, L. Yang, L. Zhang, Y. Chen, B. Qin & W. S. Gardner, 2007. Nitrogen dynamics and microbial food web structure during a summer cyanobacterial bloom in a subtropical, shallow, well-mixed, eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China). Hydrobiologia 581: 195–207.
Meijer, M. L., E. Lammens, A. J. P. Raat, M. P. Grimm & S. H. Hosper, 1990. Impact of cyprinids on zooplankton and algae in ten drainable ponds. Hydrobiologia 191: 275–284.
Ogilvie, B. G. & S. F. Mitchell, 1998. Does sediment resuspension have persistent effects on phytoplankton? Experimental studies in three shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 40: 51–63.
Paerl, H. W., H. Xu, M. J. McCarthy, G. Zhu, B. Qin, Y. Li & W. S. Gardner, 2010. Controlling harmful cyanobacterial blooms in a hyper-eutrophic lake (Lake Taihu, China): The need for a dual nutrient (N & P) management strategy. Water Research 45: 1973–1983.
Penning, W. E., M. Genseberger, R. Uittenbogaard, & J. C. Cornelisse, 2012. Quantifying measures to limit wind driven resuspension of sediments for improvement of the ecological quality in some shallow Dutch lakes. Hydrobiologia, this volume.
Qin, B., Z. Liu & K. Havens, 2007. Eutrophication of shallow lakes with special reference to Lake Taihu. Hydrobiologia 581.
Reynolds, C. S., 1984. The Ecology of Freshwater Phytoplankton. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge.
Reynolds, C. S., 1998. What factors influence the species composition of phytoplankton in lakes of different trophic status? Hydrobiologia 369: 11–26.
Reynolds, C. S. & S. W. Wiseman, 1982. Sinking losses of phytoplankton in closed limnetic systems. Journal of Plankton Research 4: 489–522.
Roozen, F. C. J. M., M. Lürling, H. Vlek, K. Van der Pouw, B. Ibelings & M. Scheffer, 2007. Resuspension of algal cells by benthivorous fish boosts phytoplankton biomass and alters community structure in shallow lakes. Freshwater Biology 52: 977–987.
Schallenberg, M. & C. W. Burns, 2004. Effects of sediment resuspension on phytoplankton production: teasing apart the influences of light, nutrients and algal entrainment. Freshwater Biology 49: 143–159.
Scheffer, M., 1998. Ecology of Shallow Lakes. Chapman and Hall, New York.
Schelske, C. L., H. J. Carrick & F. J. Aldridge, 1995. Can wind-induced resuspension of meroplankton affect phytoplankton dynamics? Journal of the North American Benthological Society 14: 616–630.
SEPA, 2002. Analytical Methods for Water and Wasterwater Monitor, 4th ed. Chinese Enviromental Science Press, Beijing.
Song, X., Z. Liu, G. Yang & Y. Chen, 2010. Effects of resuspension and eutrophication level on summer phytoplankton dynamics in two hypertrophic areas of Lake Taihu, China. Aquatic Ecology 44: 41–54.
Stephen, D., D. Balayla, E. Bécares, S. Collings, C. Fernández-Aláez, M. Fernández-Aláez, C. Ferriol, P. García, J. Gomá, M. Gyllström, L.-A. Hasson, J. Hietala, T. Kairesalo, M. Miracle, S. Romo, J. Rueda, A. Ståhl-Delbanco, M. Svensson, K. Vakkilainen, M. ValentÍn, W. Van der Bund, E. Van Donk, E. Vicente, M. Villena & B. Moss, 2004. Continental—scale patterns of nutrient and fish effects on shallow lakes: introduction to a pan—European mesocosm experiment. Freshwater Biology 49: 1517–1524.
Wahl, D. H., M. D. Wolfe, V. J. Santucci & J. A. Freedman, 2011. Invasive carp and prey community composition disrupt trophic cascades in eutrophic ponds. Hydrobiologia: 1–15.
Weyhenmeyer, G., 1998. Resuspension in lakes and its ecological impact-a review. Ergebnisse Der Limnologie 51: 185–200.
Wu, Q. L., Y. Chen, K. Xu, Z. Liu & M. W. Hahn, 2007. Intra-habitat heterogeneity of microbial food web structure under the regime of eutrophication and sediment resuspension in the large subtropical shallow Lake Taihu, China. Hydrobiologia 581: 241–254.
Zhang, Z. S. & X. F. Huang, 1991. Methods in Freshwater Plankton Study. Science Press, Beijing. (in Chinese).
Zhang, Y., B. Qin, W. Chen & L. Luo, 2004. A study on total suspended matter in Lake Taihu. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin 13: 266–271.
Zhang, Y. L., B. Q. Qin, W. P. Hu, S. Wang, Y. W. Chen & W. M. Chen, 2006. Temporal-spatial variations of euphotic depth of typical lake regions in Lake Taihu and its ecological environmental significance Science in China Series D: Earth. Sciences 49: 431–442.
Zhu, G., B. Qin & G. Gao, 2005. Direct evidence of phosphorus outbreak release from sediment to overlying water in a large shallow lake caused by strong wind wave disturbance. Chinese Science Bulletin 50: 577–582.
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express our special gratitude to professors Erik Jeppesen and Kuanyi Li, their views and suggestions have been of great importance for the final content and framing of this manuscript. The authors also thank Liang Guo, Hu He, Liu Yang, Weiwei Jiang and Ke Li for field and laboratory support, and Anne Mette and Amy-Jane Beer for the English improvements of this manuscript. This study was supported by the National Basic Research Program of China (No. 2012CB956100), the National Science Foundation of China (No. 31070419 and 41073057) and the National Key Technology Research and Development Program of China (No. 2007BAC26B02).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Guest editors: Zhengwen Liu, Bo-Ping Han & Ramesh D. Gulati / Conservation, management and restoration of shallow lake ecosystems facing multiple stressors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kang, Y., Song, X. & Liu, Z. Sediment resuspension dampens the effect of nutrient inputs on the phytoplankton community: a mesocosm experiment study. Hydrobiologia 710, 117–127 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1221-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1221-y