Abstract
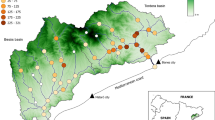
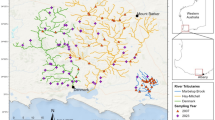
Summer rainfall shortage and low or no flows in Mediterranean rivers make it difficult for fish to attain their final preferenda and hinder the assembling of fish communities. We investigated in this study the degree to which large-scale features of the watersheds and reach-scale habitats correlated with a non-random structure of fish species' richness, composition and distribution under these conditions by intensively sampling a river system during summer and using Geographical Information Systems data. The results of multivariate ordination and association analyses showed that multi-scale factors were hierarchically related and that they correlated with non-random fish distributions and assemblage structure. They also highlighted large-scale factors shaping reach-scale water availability for fish during summer. Fish species' richness, composition and distribution varied along a gradient of water shortage and connectivity loss which were more severe with the smaller drainage area into the reaches upstream. Fish species' distributions along these gradients were strongly correlated with both life-history traits (adult size) and biogeographical origin (native vs. exotic). The results for the summer environmental segregation of exotic versus small endemic richness characteristics indicate strong species' interactions forcing the latter into the upstream, harsher seasonal habitats. Special fitness costs are to be expected in drought years, in regulated rivers, and in general, in a climate change scenario in Mediterranean river networks. The study emphasizes that the conservation of the threatened Mediterranean freshwater fish faunas requires operating at the proper spatial scale. In particular, reach-scale habitat improvements are adequate but not enough during the summer in fragmenting river networks, unless there is proper watershed-scale management of the flow regimes.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almaça, C., 1967. Estudo das populações portuguesas do Gen. Barbus Cuvier, 1817 (Pisces, Cyprinidae). Revista da Faculdade de Ciências de Lisboa 14: 151–400.
Almaça, C., 1995. Fish Species and Varieties Introduced into Portuguese Inland Waters. Publicaçoes Avulsas do Museu Bocage, Lisboa: 29.
Angermeier, P. L. & J. R. Karr, 1983. Fish communities along environmental gradients in a system of tropical streams. Environmental Biology of Fishes 9: 117–135.
Banarescu, P. & H. J. Paepke, 2001. The Freshwater Fishes of Europe. Cyprinidae-2, Vol. 5. AULA-Verlag GmbH, Wiebelsheim.
Benejam, L., P. L. Angermeier, A. Munné & E. García-Berthou, 2010. Assessing effects of water abstraction on fish assemblages in Mediterranean streams. Freshwater Biology 55: 628–642.
Beugly, J. & M. Pyron, 2010. Temporal and spatial variation in the long-term functional organization of fish assemblages in a large river. Hydrobiologia 654: 215–226.
Boix, D., E. García-Berthou, S. Gascón, L. Benejam, E. Tornés, J. Sala, J. Benito, A. Munné, C. Solá & S. Sabater, 2010. Response of community structure to sustained drought in Mediterranean rivers. Journal of Hydrology 383: 135–146.
Borcard, D., P. Legendre & P. Drapeau, 1992. Partialling out the spatial component of ecological variation. Ecology 73: 1045–1055.
Clavero, M. & V. Hermoso, 2011. Reservoirs promote the taxonomic homogenization of fish communities within river basins. Biodiversity Conservation 20: 41–57.
Collares-Pereira, M. J., M. F. Magalhães, A. M. Geraldes & M. M. Coelho, 1995. Riparian ecotones and spatial variation of fish assemblages in Portuguese lowland streams. Hydrobiologia 303: 93–101.
Corbacho, C. & J. M. Sánchez, 2001. Patterns of species richness and introduced species in native freshwater fish faunas of a Mediterranean-type basin: the Guadiana River (southwest Iberian Peninsula). Regulated Rivers-Research and Management 17: 699–707.
Davey, A. J. H. & D. J. Kelly, 2007. Fish community responses to drying disturbances in an intermittent stream: a landscape perspective. Freshwater Biology 52: 1719–1733.
Dekar, M. P. & D. D. Magoulick, 2007. Factors affecting fish assemblage structure during seasonal stream drying. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 16: 335–342.
Doadrio, I., 1988. Sobre la taxonomía de Barbus comiza Steindachner, 1865 (Ostariophysi: Cyprinidae). Doñana Acta Vertebrata 15: 19–28.
Doadrio, I., 2001. Atlas y Libro Rojo de los peces continentales de España. Ministerio de Medio Ambiente, Madrid.
Elvira, B., 1995. Conservation status of endemic freshwater fish in Spain. Biological Conservation 72: 129–136.
Elvira, B., A. Almodóvar & G. G. Nicola, 1998. Fish communities of the middle-upper Tagus River (central Spain): a story of river regulation and exotic introductions. Polskie Archiwum Hydrobiologii 45: 167–171.
Esguícero, A.L.H. & M.S. Arcifa, 2010. Fragmentation of a Neotropical migratory fish population by a century-old dam. Hydrobiologia 638: 41–53.
Esselman, P. C. & J. D. Allan, 2010. Relative influences of catchment- and reach-scale abiotic factors on freshwater fish communities in rivers of northeastern Mesoamerica. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 19: 439–454.
Fernández Yuste, F. & C. Martínez, 2010. Índices de Alteración Hidrológica en Ríos (IAHRIS). Régimen Ambiental de Caudales: Manual de Referencia Metodológica Versión 2.2. Universidad Politécnica de Madrid, Madrid.
Ferreira, M. T., L. Sousa, J. M. Santos, L. Reino, J. Oliveira, P. R. Almeida & R. V. Cortes, 2007. Regional and local environmental correlates of Iberian fish fauna. Environmental Biology of Fish 16: 504–514.
Filipe, A. F., M. F. Magalhães & M. J. Collares-Pereira, 2010. Native and introduced fish species richness in Mediterranean streams: the role of multiple landscape influences. Diversity and Distributions 16: 773–785.
Fisher, J. R. & C. P. Paukert, 2008. Habitat relationships with fish assemblages in minimally disturbed Great Plains regions. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 17: 597–609.
Frissell, C. A., W. J. Liss, C. E. Warren & M. D. Hurley, 1986. A hierarchical framework for stream habitat classification: viewing streams in a watershed context. Environmental Management 10: 199–214.
Gasith, A. & V. H. Resh, 1999. Streams in Mediterranean climate regions: abiotic influences and biotic responses to predictable seasonal events. Annual Review of Ecology and Systematics 30: 51–81.
Godinho, F. N. G. & M. T. Ferreira, 1998. The relative influences of exotic species and environmental factors on an Iberian native fish community. Environmental Biology of Fishes 51: 41–51.
Godinho, F. N., M. T. Ferreira & R. V. Cortes, 1997. Composition and spatial organization of fish assemblages in the lower Guadiana basin, southern Iberia. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 6: 134–143.
Godinho, F. N., M. T. Ferreira & J. M. Santos, 2000. Variation in fish community composition along an Iberian river basin from low to high discharge: relative contributions of environmental and temporal variables. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 9: 22–29.
Gorman, O. T. & J. R. Karr, 1978. Habitat structure and stream fish communities. Ecology 59: 507–515.
Grenouillet, G., D. Pont & C. Hérissé, 2004. Within-basin fish assemblage structure: the relative influence of habitat versus stream spatial position on local species richness. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 61: 93–102.
Hermoso, V., S. Linke & J. Prenda, 2009a. Identifying priority sites for the conservation of freshwater fish biodiversity in a Mediterranean basin with a high degree of threatened endemics. Hydrobiologia 623: 127–140.
Hermoso, V., M. Clavero, F. Blanco-Garrido & J. Prenda, 2009b. Assessing freshwater fish sensitivity to different sources of perturbation in a Mediterranean basin. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 18: 269–281.
Hermoso, V., M. Clavero, F. Blanco-Garrido & J. Prenda, 2011. Invasive species and habitat degradation in Iberian streams: an analysis of their role in freshwater fish diversity loss. Ecological Applications 21: 175–188.
Holtrop, A. M., Y. Cao & C. R. Dolan, 2010. Estimating sampling effort required for characterizing species richness and site-to-site similarity in fish assemblage surveys of wadeable Illinois streams. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 139: 1421–1435.
Ibarra, A. A., Y. S. Park, S. Brosse, Y. Reyjol, P. Lim & S. Lek, 2005. Nested patterns of spatial diversity revealed for fish assemblages in a west European river. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 14: 233–242.
Jackson, D. A., 1995. PROTEST: a PROcrustean Randomization TEST of community environment concordance. Ecoscience 2: 297–303.
Jackson, D. A., P. R. Peres-Neto & J. Olden, 2001. What controls who is where in freshwater fish communities—the roles of biotic, abiotic and spatial factors. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 58: 157–170.
Jenkins, R. E. & C. A. Freeman, 1972. Longitudinal distribution and habitat of the fishes of Mason Creek, an upper Roanoke River drainage tributary, Virginia. Virginia Journal of Science 23: 194–202.
Johnson, P. T. J., J. D. Olden & M. J. Vander Zanden, 2008. Dam Invaders: impoundments facilitate biological invasions into freshwaters. Frontiers in Ecology and the Environment 6: 357–363.
Jongman, R. H. G., C. J. F. Ter Braak & O. F. R. van Tongeren, 1995. Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Pudoc Wageningen.
Kondolf, G. M. & R. J. Batalla, 2005. Hydrological effects of dams and water diversions on rivers of Mediterranean-climate regions: examples from California. In García, C. & J. Batalla (eds), Catchment Dynamics and River Processes: Mediterranean and Other Climate Regions. Elsevier, Amsterdam.
Ladero-Álvarez, M., 1987. España Luso-Extremadurense. In Lorca M. P. & S. Rivas-Martínez (eds), La Vegetación de España. Servicio de Publicaciones de la Universidad de Alcalá de Henares: 453–486.
Lake, P. S., 2003. Ecological effects of perturbation by drought in flowing waters. Freshwater Biology 48: 1161–1172.
Levin, S. A., 1992. The problem of pattern and scale in ecology. Ecology 73: 1943–1967.
Magalhães, M. F., D. C. Batalha & M. J. Collares-Pereira, 2002a. Gradients in stream fish assemblages across a Mediterranean landscape: contributions of environmental factors and spatial structure. Freshwater Biology 47: 1015–1031.
Magalhães, M. F., P. Beja, C. Canas & M. J. Collares-Pereira, 2002b. Functional heterogeneity of dry-season refugia across a Mediterranean catchment: the role of habitat and predation. Freshwater Biology 47: 1919–1934.
Magalhães, M. F., P. Beja, I. J. Schlosser & M. J. Collares-Pereira, 2007. Effects of multi-year droughts on fish assemblages of seasonally drying Mediterranean streams. Freshwater Biology 52: 1494–1510.
Mas-Martí, E., E. García-Berthou, S. Sabater, S. Tomanova & I. Muñoz, 2010. Comparing fish assemblages and trophic ecology of permanent and intermittent reaches in a Mediterranean stream. Hydrobiologia 657: 167–180.
Matthews, W. J., 1998. Patterns in Freshwater Fish Ecology. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht.
Matthews, W. J. & E. Marsh-Matthews, 2003. Effects of drought on fish across axes of space, time and ecological complexity. Freswater Biology 48: 1232–1253.
Meador, R. M., L. R. Brown & T. Short, 2003. Relations between introduced fish and environmental conditions at large geographic scales. Ecological Indicators 3: 81–92.
Mesquita, N., M. M. Coelho & M. F. Magalhães, 2006. Spatial variation in fish assemblages across small Mediterranean drainages: effects of habitat and landscape context. Environmental Biology of Fish 77: 105–120.
Morán-López, R., J. L. Pérez-Bote, E. Da Silva Rubio & C. Corbacho Amado, 2005. Summer habitat relationships of barbels in south-west Spain. Journal of Fish Biology 67: 66–82.
Morán-López, R., E. Da Silva Rubio, J. L. Pérez-Bote & C. Corbacho Amado, 2006. Associations between fish assemblages and environmental factors for Mediterranean-type rivers during summer. Journal of Fish Biology 69: 1552–1569.
Moyle, P. B. & T. Light, 1996. Fish invasions in California: do abiotic factors determine success? Ecology 77: 1666–1670.
Mueller, M., J. Pander & J. Geist, 2011. The effects of weirs on structural stream habitat and biological communities. Journal of Applied Ecology 48: 1450–1461.
Mugodo, J., M. Kenard, P. Liston, S. Nichols, S. Linke, R. H. Norris & M. Lintermans, 2006. Local stream habitat variables predicted from catchment scale characteristics are useful for predicting fish distribution. Hydrobiologia 572: 59–70.
Nislow, K. H., M. Hudy, B. H. Letcher & E. P. Smith, 2011. Variation in local abundance and species richness of stream fishes in relation to dispersal barriers: implications for management and conservation. Freshwater Biology 56: 2135–2144.
Oberdorff, T., D. Pont, B. Hugueny & D. Chessel, 2001. A probabilistic model characterizing fish assemblages of French rivers: a framework for environmental assessment. Freshwater Biology 46: 399–415.
Pegg, M. A. & M. A. McClelland, 2004. Spatial and temporal patterns in fish communities along the Illinois River. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 13: 125–135.
Peres-Neto, P. R. & D. A. Jackson, 2001. How well do multivariate data sets match? The advantages of Procrustean superimposition approach over the Mantel test. Oecologia 129: 169–178.
Petts, G. E., 2000. A perspective on the abiotic processes sustaining the ecological integrity of running Waters. Hydrobiologia 422(423): 15–27.
Pires, A. M., I. G. Cowx & M. M. Coelho, 1999. Seasonal changes in fish community structure of intermittent streams in the middle reaches of the Guadiana basin, Portugal. Journal of Fish Biology 54: 235–249.
Pires, D. F., A. M. Pires, M. J. Collares-Pereira & M. F. Magalhães, 2010. Variation in fish assemblages across dry-season pools in a Mediterranean stream: effects of pool morphology, physicochemical factors and spatial context. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 19: 74–86.
Poff, L. J., J. D. Allan & M. B. Bain, 1997. The natural flow regime: a paradigm for river conservation and restoration. BioScience 47: 749–784.
Pont, D., B. Hugueny & T. Oberdorff, 2005. Modelling habitat requirement of European fishes: do species have similar responses to local and regional environmental constraints? Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 62: 163–173.
Quist, M. C., F. J. Rahel & W. A. Hubert, 2005. Hierarchical faunal filters: an approach to assessing effects of habitat and nonnative species on native fishes. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 14: 24–39.
Ribeiro, F. & M. J. Collares-Pereira, 2010. Life-history variability of non-native centrarchids in regulated river systems of the lower River Guadiana drainage (south-west Iberian Peninsula). Journal of Fish Biology 76: 522–537.
Ribeiro, F. B., B. Elvira, M. J. Collares-Pereira & P. B. Moyle, 2008. Life-history traits of non-native fishes in Iberian watersheds across several invasion stages: a first approach. Biological Invasions 10: 89–102.
Rifflart, R., G. Carrel, Y. Le Coarer & B. N. The Fontez, 2009. Spatio-temporal patterns of fish assemblages in a large regulated alluvial river. Freshwater Biology 54: 1544–1559.
Schlosser, I. J., 1982. Fish community structure and function along two habitat gradients in a headwater stream. Ecological Monographs 52: 395–414.
Segurado, P., M.T. Ferreira, D. García, J. Gortazar, P. Pinheiro & J.M. Santos, 2008. EFI+-Improvement and spatial extension of the European Fish Index. WP3, Subtask 7 – Mediterranean River Assessment. Available at: http://efi-plus.boku.ac.at/ (accessed January 2010).
Smogor, R. A., P. L. Angermeier & C. K. Gaylord, 1995. Distribution and abundance of American eels in Virginia streams: tests of null models across spatial scales. Transactions of the American Fisheries Society 124: 789–803.
Ter Braak, C. J. F., 1986. Canonical correspondence analysis: a new eigenvector technique for multivariate direct gradient analysis. Ecology 67: 1167–1179.
Ter Braak, C. F. J., 1995. Ordination. In Jongman, R., C. Ter Braak & O. Van Tongeren (eds), Data Analysis in Community and Landscape Ecology. Cambridge University Press, Pudoc Wageningen: 91–173.
Ter Braak, C. F. J. & P. F. M. Verdonschot, 1995. Canonical correspondence analysis and related multivariate methods in aquatic ecology. Aquatic Science 57: 255–289.
Vila-Gispert, A., E. García-Berthou & R. Moreno-Amich, 2002. Fish zonation in a Mediterranean stream: effects of human disturbances. Aquatic Sciences 64: 163–170.
Wang, L., J. Lyons, P. Rasmussen, P. Seelbach, T. Simon, M. Wiley, P. Kanehl, E. Baker, S. Niemela & P. M. Stewart, 2003. Watershed, reach, and riparian influences on stream fish assemblages in the Northern Lakes and Forest Ecoregion, U.S.A. Canadian Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Sciences 60: 491–505.
Wiens, J. A., 1989. Spatial scaling in ecology. Functional Ecology 3: 385–397.
Wiley, M., S. Kohler & P. Seelbach, 1997. Reconciling landscape and local views of aquatic communities: lessons from Michigan trout streams. Freshwater Biology 37: 133–148.
Wootton, R. J., 1990. Ecology of Teleost Fishes. Chapman & Hall, London.
Yan, Y., X. Xiang, L. Chu, Y. Zhan & C. Fu, 2011. Influences of local habitat and stream spatial position on fish assemblages in a dammed watershed, the Qingyi Stream, China. Ecology of Freshwater Fish 20: 199–208.
Zamora Cabanillas, J. F., 1987. El Río Guadiana (Fisiografía, Geoquímica y Contaminación). Departamento de Publicaciones, Diputación de Badajoz, Badajoz.
Zardoya, R. & I. Doadrio, 1998. Phylogenetic relationships of Iberian cyprinids: systematic and biogeographical implications. Proceedings of the Royal society of London 265: 1365–1372.
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank those persons who all assisted in the field and compilation of data. The authors are grateful to the regional environmental authorities, Dirección General del Medio Natural (Junta de Extremadura) for providing sampling permissions, and to the private individuals who allowed us access to their estates. D.A. Jackson provided helpful recommendations on Procrustes methods. The study was funded under a contract with the Confederación Hidrográfica del Guadiana, Ministerio de Medio Ambiente Rural y Marino. The Consejería de Economía, Comercio e Innovación (Junta de Extremadura) funded the translation of the manuscript (GR10174). Two anonymous referees gave useful suggestions which improved the article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Handling editor: Koen Martens
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Morán-López, R., Pérez-Bote, J.L., Da Silva, E. et al. Hierarchical large-scale to local-scale influence of abiotic factors in summer-fragmented Mediterranean rivers: structuring effects on fish distributions, assemblage composition and species richness. Hydrobiologia 696, 137–158 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1189-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-012-1189-7