Abstract
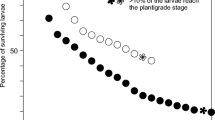
Cyclops vicinus is reported to enter summer diapause triggered by day length in order to survive food scarcity and fish predation. Development ceases and the fourth or fifth copepodid stages persist in the sediment for several weeks. In Lake Søbygård, however, a small eutrophic lake in Denmark, C. vicinus is found in the sediment as well as in the open water throughout the year. We performed laboratory experiments to elucidate the life cycle strategy of this population. In order to find the factors that induce diapause we tested the influence of food composition and light regime on the proportion of copepods entering diapause. Further we examined the diapause pattern of the offspring from diapausing and non-diapausing parents to see whether the co-occurrence of diapausing and non-diapausing copepods results from genetic differentiation within the population. In all experiments some of the copepods developed directly into adults, while others remained at the fourth or fifth copepodid stage and displayed diapause features. The proportion of copepods that developed directly into adults was influenced by food supply. Fewer individuals entered diapause when they received a mixed diet of algae and ciliates or algae, ciliates and seston compared with a pure algal diet. The response to light was different than described in literature: about 30% of the copepods entered diapause under dark conditions, and the diapause frequency was not higher when copepods had been exposed to continuous light. The offspring from diapausing parents showed no higher tendency to enter diapause than the offspring of non-diapausing parents, indicating no genetic differentiation. We conclude that diapause in C. vicinus represents a risk-spreading strategy, modified by food. The simultaneous production of diapausing and non-diapausing offspring ensures survival under harsh conditions; the influence of the food supply on the proportion of individuals entering diapause may adjust the population to the actual environmental condition. This flexible life cycle strategy might contribute to the exclusive dominance of C. vicinus in Lake Søbygård.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
V. R. Alekseev (1998) ArticleTitleBiochemical and physiological characteristics of crustaceans in diapause: the internal mechanism of reactivation Archiv für Hydrobiologie 52 463–476
Alekseev, V. R., K. Djenderedjan & B. Fiks, 2001. Role of summer diapause in success of invasion of a new invertebrate predator into plankton ecosystem of a large mountain lake. Conference Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on the Conservation and Management of Lakes, Biwako, Japan: 217–220
H.-U. Dahms (1995) ArticleTitleDormancy in Copepoda – an overview Hydrobiologia 306 199–211 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00017691
J. B. T. DeStasio (1989) ArticleTitleThe seed bank of a freshwater crustacean: copepodology for the plant ecologist Ecology 70 1377–1389
U. Einsle (1964) ArticleTitleLarvalentwicklung von Cyclopiden und Photoperiodik Naturwissenschaften 14 345
K. Elgmork J. P. Nilssen (1978) ArticleTitleEquivalence of copepod and insect diapause Verhandlungen der Internationalen Vereinigung der Limnologie 20 2511–2517
R. R. L. Guillard C. J. Lorenzen (1972) ArticleTitleYellow-green algae with chlorophyllide c Journal of Phycology 8 10–14 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DyaE38XktFKnsrg%3D
N. G. Hairston SuffixJr. (1996) ArticleTitleZooplankton egg banks as biotic reservoirs in changing environments Limnology & Oceanography 41 1087–1092
N. G. Hairston SuffixJr. E. J. Olds W. R. Munns (1985) ArticleTitleBet-hedging and environmentally cued diapause strategies of diaptomid copepods Verhandlungen der Internationalen Vereinigung für Limnologie 22 3170–3177
A.-M. Hansen (1996) ArticleTitleVariable life history of a cylopoid copepod: role of food availability Hydrobiologia 320 223–227 Occurrence Handle10.1007/BF00016823
A.-M. Hansen E. Jeppesen (1992) ArticleTitleLife cycle of Cyclops vicinus in relation to food availability, predation, diapause and temperature Journal of Plankton Research 14 591–605
A.-M. Hansen B. Santer (1995) ArticleTitleThe influence of food resources on the development, survival and reproduction of the two cyclopoid copepods: Cyclops vicinus and Mesocyclops leuckarti Journal of Plankton Research 17 631–646
A.-M. Hansen B. Santer (2003) ArticleTitleThe life cycle of Cyclops vicinus in Lake Søbygård: new aspects derived from sediment analyses Hydrobiologia 510 17–21 Occurrence Handle10.1023/B:HYDR.0000008472.70663.bb
A.-M. Hansen N. G. Hairston SuffixJr. (1998) ArticleTitleFood limitation in a wild cyclopoid copepod population: direct and indirect life history responses Oecologia 115 320–330 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004420050523
E. Jeppesen M. Søndergaard J. P. Jensen E. Mortensen A.;-M. Hansen T. Jørgensen (1998) ArticleTitleCascading trophic interactions from fish to bacteria and nutrients after reduced sewage loading: an 18-year study of a shallow hypertrophic lake Ecosystem 1 250–326 Occurrence Handle1:CAS:528:DC%2BD3cXptFehsA%3D%3D
F. Kiefer (1978) ArticleTitleFreilebende Copepoda. Die Binnengewässer Schweizerbartsche Verlagsbuchhandlung, Stuttgart 26 1–343
W. Lampert U. Schober (1978) ArticleTitleClimatic conditions and planktonic interactions as factors controlling the regular succession of spring algal bloom and extremely clear water in Lake Constance Verhandlungen der Internationalen Vereinigung für Limnologie 20 969–974
G. Maier (1989) ArticleTitleVariable life cycles in the freshwater copepod Cyclops vicinus (Uljanin 1875): support for the predator avoidance hypothesis? Archiv für Hydrobiologie 115 203–219
B. F. J. Manly (1991) Randomization and Monte Carlo Methods in Biology Chapman and Hall London, New York, Tokyo, Melbourne, Madras
B. Santer (1998) ArticleTitleLife cycle strategy of free-living copepods in fresh waters Journal of Marine Systems 15 327–336 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0924-7963(97)00084-5
B. Santer F. Bosch ParticleVan den (1994) ArticleTitleHerbivorous nutrition of Cyclops vicinus: the effect of a pure algal diet on feeding, development, reproduction and life cycle Journal of Plankton Research 16 171–195
B. Santer W. Lampert (1995) ArticleTitleSummer diapause in cyclopoid copepods: adaptive response to a food bottleneck? Journal of Animal Ecology 64 600–613
K.-D. Spindler (1969) ArticleTitleDie Bedeutung der Photoperiode für die Entwicklung von Cyclops vicinus Verhandlungen der Deutschen zoologischen Gesellschaft, Zoologischer Anzeiger 33 190–195
K.-D. Spindler (1971) ArticleTitleDormanzauslösung und Dormanzcharakteristika beim Süßwassercopepoden Cyclops vicinus Zoologische Jahrbücher der Abteilung für Allgemeine Zoologie und Physiologie der Tiere der Universität Braunschweig (Germany) 76 139–151
T. Weisse N. Karstensen V. C. L. Meyer L. Janke S. Lettner K. Teichgräber (2001) ArticleTitleNiche separation in common prostome freshwater ciliates: the effect of food and temperature Aquatic Microbial Ecology 26 167–179
M. Zeller R. Melero B. Santer (2004) ArticleTitleDiapause in the calanoid freshwater copepod Eudiaptomus gracilis Journal of Plankton Research 26 1–10 Occurrence Handle10.1093/plankt/fbh128
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santer, B., Hansen, AM. Diapause of Cyclops vicinus (Uljanin) in Lake Søbygård: Indication of a Risk-spreading Strategy. Hydrobiologia 560, 217–226 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1067-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-1067-7