Abstract
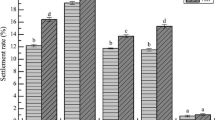
The effects of different diatom species and types of substrates in combination with 0.45 μM GABA on the metamorphosis of Haliotis asinina larvae were tested. Diatom slurry elicited the best metamorphic response followed by Amphora sp., Amphora + Nitzschia and Nitzschia cf. frustulum in that order. With regards to substrate types, roughened plexiglass seemed to be the most preferred while fibrocement the least preferred surface. Overall, diatom slurry grown on plexiglass surface promoted the greatest number of metamorphosed H. asinina postlarvae. For economic considerations and practical reasons, chemical inducers like gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), should be used singly or separately from other settlement-inducing cues, such as the “substrate-diatom” complex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
L. A. Barlow (1990) ArticleTitleElectrophysiological and behavioral responses of larvae of the red abalone (Haliotis rufescens) to settlement-inducing substances Bulletin of Marine Science 46(2): IssueID2 537–554
P. J. Bryan P.-Y. Qian (1998) ArticleTitleInduction of larval settlement and metamorphosis in the abalone, Haliotis diversicolor (Reeve) Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 223(1): IssueID1 39–51 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0022-0981(97)00156-1
W. M. Darley B. E. Volcani (1969) ArticleTitleRole of silicon in diatom metabolism. A silicon requirement for DNA synthesis in the diatom Cylindrotheca fusiformis Experimental Cell Research 58 334–342 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0014-4827(69)90514-X Occurrence Handle5404077
S. Daume A. Krsinich S. Farrell M. Gervis (2000) ArticleTitleSettlement, early growth and survival of Haliotis rubra in response to different algal species Journal of Applied Phycology 12 479–488 Occurrence Handle10.1023/A:1008110828581
W. G. Gallardo S. A. Buen (2003) ArticleTitleEvaluation of mucus, Navicula and mixed diatoms as larval settlement inducers for the tropical abalone, Haliotis asinina Aquaculture 221 357–364 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0044-8486(03)00121-2
R. S. J. Gapasin B. B. Polohan (2004) ArticleTitleInduction of larval settlement and metamorphosis in the donkey-ear abalone, Haliotis asinina by chemical cues Hydrobiologia 51 IssueID3 99–17
C. D. Garland S. L. Cooke J. F. Grant T. A. McMeekin (1985) ArticleTitleIngestion of the bacteria and the cuticle of the crustose (non-articulated) coralline algae by post-larval and juvenile abalone (Haliotis rubra Leach) from Tasmanian waters Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 91 137–149 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-0981(85)90226-6
R. R. L. Guillard (1978) Counting slides A. Sournia (Eds) Phytoplankton manual: Monographs on oceanographic methodology 6 UNESCO Paris 182–189
M. G. Hadfield (1977) Chemical interactions in larval settling of a marine gastropod D. J. Faulkner W. H. Fenical (Eds) Marine Natural Products Chemistry Plenum Press New York 403–413
M. G. Hadfield (1978) Metamorphosis in marine molluscan larvae: an analysis of stimulus and response F. S. Chia M. E. Rice (Eds) Settlement and metamorphosis of marine invertebrate larvae Elsevier New York 165–175
M. G. Hadfield C. C. Unabia C. M. Smith T. M. Michael (1994) Settlement preferences of the ubiquitous fouler Hydroides elegans M. F. Thompson R. Nagabhushanam R. Sarojini M. Fingerman (Eds) Recent developments in biofouling control Oxford and IBH Publishing Co New Delhi 67–74
K. O. Hahn (1989) Handbook of culture of abalone and other marine gastropods CRC Press, Inc., Boca Raton Florida, USA, 348
H. F. Kaspar D. O. Mountfort (1995) ArticleTitleMicrobial production and degradation of gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) in the abalone larval settlement habitat FEMS Mirobiology Ecology 17 205–212 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0168-6496(95)00025-6
T. Kawamura (1996) The role of benthic diatoms in the early life stages of the Japanese abalone (Haliotis discus hannai) Y. Watanabe Y. Yamashita Y. Oozeki (Eds) Survival Strategies in Early Life Stages of Marine Resources A.A. Balkema Rotterdam 355–367
T. Kawamura S. Kikuchi (1992) ArticleTitleEffects of benthic diatoms on settlement and metamorphosis of abalone larvae (in Japanese with English abstract) Suisanzoshoku 40 403–409
T. Kawamura R. D. Roberts C. M. Nicholson (1998) ArticleTitleFactors affecting the food value of diatom strains for post-larval abalone Haliotis iris Aquaculture 160 81–88 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0044-8486(97)00223-8
T. Kawamura H. Takami (1995) ArticleTitleAnalysis of feeding and growth rate of newly metamorphosed abalone Haliotis discus hannai fed on four species of benthic diatom Fisheries Science 61 357–358
S. Manivasaham R. Selvaraj A. Purushothaman A. Subramanian (1989) ArticleTitleAntibacterial activity of Nitzschia obtusa Current Science 58 IssueID2 83–85
I. Matthews P. A. Cook (1995) ArticleTitleDiatom diet of abalone post-larvae (Haliotis midae) and the effect of pre-grazing the diatom overstorey Marine and Freshwater Research 46 IssueID3 545–548
D. E. Morse H. Duncan N. Hooker A. Morse (1979) ArticleTitleGamma-aminobutyric acid, a neurotransmitter, induces planktonic abalone larvae to settle and begin metamorphosis Science 204 407–410
A. N. C. Morse D. E. Morse (1984) ArticleTitleRecruitment and metamorphosis of Haliotis larvae induced by molecules uniquely available at the surfaces of the crustose red algae Journal of Experimental Marine Biology and Ecology 75 191–215 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0022-0981(84)90166-7
G. A. Moss (1999) ArticleTitleFactors affecting settlement and early post-settlement survival of the New Zealand abalone Haliotis australis New Zealand Journal of Marine and Freshwater Research 33 271–278
M. Naviner J. P. Berge P. Durand H. le Bris (1999) ArticleTitleAntibacterial activity of the marine diatom Skeletonema costatum against aquaculture pathogens Aquaculture 174 IssueID1/2 15–24 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0044-8486(98)00513-4
J. R. Pavlik (1992) ArticleTitleChemical ecology of the settlement of benthic marine invertebrates Oceanography and Marine Biology Review 30 273–335
R. D. Roberts C. M. Nicholson (1997) ArticleTitleVariable response from abalone larvae (Haliotis iris, H. virginea) to a range of settlement cues Molluscan Research 18 131–141
SAS Institute. 1988. SAS/STAT TM User’s Guide, Release 6.03 Edition. SAS Institute, Cary, North Carolina, USA, 1028 pp
S. Sawatpeera E. S. Upatham M. Kruatrachue V. Ingsrisawang T. Singhagraiwan Y. P. Chitramvong K. Parkpoomkamol (1998) ArticleTitleDetermination of gut contents of Thai abalone Haliotis asinina Linnaeus Journal of Shellfish Research 17 IssueID3 765–769
R. Searcy-Bernal A. E. Salas-Garza R. A. Flores-Aguilar P. R. Hinojosa-Rivera (1992) ArticleTitleSimultaneous comparison of methods for settlement and metamorphosis induction in the red abalone, Haliotis rufescens Aquaculture 105 241–250 Occurrence Handle10.1016/0044-8486(92)90090-8
R. Searcy-Bernal C. Anguiano-Beltran (1998) ArticleTitleOptimizing the concentration of gamma-amnobutyric acid (GABA) for inducing larval metamorphosis in the red abalone, Haliotis rufescens (Mollusca:Gastropoda) Journal of the World Aquaculture Society 29 IssueID4 463–470
H. Suzuki T. Ioriya T. Seki Y. Aruga (1987) ArticleTitleChanges of algal community on the plastic plates used for rearing the abalone Haliotis discus hannai Nippon Suisan Gakkaishi 53 IssueID12 2163–2167
H. Takami T. Kawamura Y. Yamashita (1997a) ArticleTitleContribution of diatoms as food sources for post-larval abalone Haliotis discus hannai on a crustose coralline algae Molluscan Research 18 143–151
H. Takami T. Kawamura Y. Yamashita (1997b) ArticleTitleSurvival and growth rates of post-larval abalone Haliotis discus hannai fed conspecific trail mucus and/or benthic diatom Coconeis scutellum var. parva Aquaculture 152 129–138 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0044-8486(96)01524-4
C. S. Walter R. Mahesh (2000) ArticleTitleAntibacterial and antifungal activities of some marine diatoms in culture Indian Journal of Marine Science 29 IssueID3 238–242
S. A. Woodin (1991) ArticleTitleRecruitment of infauna: positive or negative cues? American Zoology 31 797–807
Yanagihashi, S., M. Takao & K. Ohiwa, 1986. On seed production of abalone in Aichi Prefectural Sea-Farming Center. Seed production system of abalone Haliotis discus discus in Aichi Prefectural Sea-Farming Center, 2–44.
R. Yanase (1982) ArticleTitleA few observations on the settlement of abalone larvae Izu Branch News 206 2–4
Y. Yang B.- L. Wu (1995) ArticleTitleInduction of larval settlement and metamorphosis of Haliotis discus hannai Ino (Gastropoda, Mollusca) Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology 13 IssueID1 71–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gapasin, R.S., Polohan, B.B. Response of the Tropical Abalone, Haliotis asinina, Larvae on Combinations of Attachment Cues. Hydrobiologia 548, 301–306 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-0754-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10750-005-0754-8