Abstract
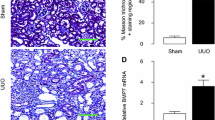
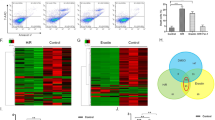
Renal ischemia–reperfusion (IR) injury is a common issue in urological surgery, and the renal tubules, particularly the proximal tubules, are extremely vulnerable to IR injury. In this work, we detected the differently expressed genes (DEGs) between normal rabbit kidneys and IR kidneys by RNA-sequencing, then identified that matrix metalloproteinase–7 (MMP7) played an important role in the progress of IR injury. Indeed, A time-dependent promotion of renal injury was detected in rabbit model, as demonstrated by the increased levels of MMP2/7/9, and the decreased of tight junction protein–1 (TJP1). Furtherly, similar results were confirmed in human renal proximal tubule epithelial (HK-2) cells model. Notably, downregulation of MMP7 affected the activity of MMP2/9 by suppressing expression of cleaved-MMP2/9 not the pro-MMP2/9 protein, which directly alleviated the degradation of TJP1 in HK-2 model. On the contrary, MMP7 had not been affected by inhibiting MMP2/9. In addition, coimmunoprecipitation assay showed that knockdown MMP7 restrained the interaction between MMP2/9 and TJP1. Collectively, this study suggested that MMP7 could serve as early biomarkers for renal tubular injury, and revealed that MMP7 could destroy the integrity of tubular epithelium through degrading TJP1 by activating MMP2/9.









Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Some or all data, models, or code generated or used during the study are available from the corresponding author by request.
References
Baker OJ (2016) Current trends in salivary gland tight junctions. Tissue Barriers 4(3):e1162348. https://doi.org/10.1080/21688370.2016.1162348
Berzal S, González-Guerrero C, Rayego-Mateos S, Ucero Á, Ocaña-Salceda C, Egido J, Ortiz A, Ruiz-Ortega M, Ramos AM (2015) TNF-related weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) regulates junctional proteins in tubular epithelial cells via canonical NF-ΚB pathway and ERK activation. J Cell Physiol 230(7):1580–1593. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.24905
Dunsmore SE, Saarialho-Kere UK, Roby JD, Wilson CL, Matrisian LM, Welgus HG, Parks WC (1998) Matrilysin expression and function in airway epithelium. J Clin Investig 102(7):1321–1331. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI1516
Fang F, Luo W, Yang M, Yang P, Yang X (2019) Urinary matrix metalloproteinase-7 and prediction of AKI progression post cardiac surgery. Dis Mark 2019:9217571. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/9217571
Farquhar MG, Palade GE (1963) Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J Cell Biol 17(5):375–412. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.17.2.375
Fu H, Zhou D, Zhu H, Liao J, Lin L, Hong X, Hou FF, Liu Y (2019) Matrix metalloproteinase-7 protects against acute kidney injury by priming renal tubules for survival and regeneration. Kidney Int 95(5):1167–1180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2018.11.043
Furuse M, Tsukita S (2006) Claudins in occluding junctions of humans and flies. Trends in Cell Biol 16(4):181–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tcb.2006.02.006
Gewin LS (2018) Renal tubule repair: is Wnt/β-catenin a friend or foe? Genes 9(2):58. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes9020058
Goligorsky MS, Lieberthal W, Racusen L, Simon EE (1993) Integrin receptors in renal tubular epithelium: new insights into pathophysiology of acute renal failure. Am J Physiol 264(1 Pt 2):F1–8. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajprenal.1993.264.1.F1
Ho J, Rush DN, Krokhin O, Antonovici M, Gao A, Bestland J, Wiebe C et al (2016) Elevated urinary matrix metalloproteinase-7 detects underlying renal allograft inflammation and injury. Transplantation 100(3):648–654. https://doi.org/10.1097/TP.0000000000000867
Ke B, Fan C, Yang L, Fang X (2017) Matrix metalloproteinases-7 and kidney fibrosis. Front Physiol 8:21. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2017.00021
Kwon O, Nelson WJ, Sibley R, Huie P, Scandling JD, Dafoe D, Alfrey E, Myers BD (1998) Backleak, tight junctions, and cell- cell adhesion in postischemic injury to the renal allograft. J Clin Investig 101(10):2054–2064. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI772
Manole E, Ceafalan LC, Oproiu AM, Popa-Wagner A, Popescu BO (2015) Claudin-1 and occludin expression in demyelinating peripheral neuropathies. Rom J Morphol Embryol 56(3):1097–1102
McGuire JK, Li Q, Parks WC (2003) Matrilysin (matrix metalloproteinase-7) mediates E-cadherin ectodomain shedding in injured lung epithelium. Am J Pathol 162(6):1831–1843. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64318-0
Parks WC, Wilson CL, López-Boado YS (2004) Matrix metalloproteinases as modulators of inflammation and innate immunity. Nat Rev Immunol 4(8):617–629. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri1418
Ponticelli C (2014) Ischaemia-reperfusion injury: a major protagonist in kidney transplantation. Nephrol Dialy Transplant 29(6):1134–1140. https://doi.org/10.1093/ndt/gft488
Prozialeck WC, Edwards JR (2007) Cell adhesion molecules in chemically-induced renal injury. Pharmacol Ther 114(1):74–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pharmthera.2007.01.001
Racusen LC, Solez K (1991) Ideas in pathology. Exfoliation of renal tubular cells. Mod Pathol 4(3):368–370
Saat TC, van den Akker EK, Ijzermans JN, Dor FJ, de Bruin RW (2016) Improving the outcome of kidney transplantation by ameliorating renal ischemia reperfusion injury: lost in translation? J Transl Med 14(1):20. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-016-0767-2
Shirahata T, Nakamura H, Nakajima T, Nakamura M, Chubachi S, Yoshida S, Tsuduki K et al (2018) Plasma SE-cadherin and the plasma SE-cadherin/SVE-cadherin ratio are potential biomarkers for chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Biomarkers 23(5):414–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/1354750X.2018.1434682
Smith SF, Hosgood SA, Nicholson ML (2019) Ischemia-reperfusion injury in renal transplantation: 3 key signaling pathways in tubular epithelial cells. Kidney Int 95(1):50–56. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.kint.2018.10.009
Tamura Y, Watanabe F, Nakatani T, Yasui K, Fuji M, Komurasaki T, Tsuzuki H et al (1998) Highly selective and orally active inhibitors of type IV collagenase (MMP-9 and MMP-2): N-sulfonylamino acid derivatives. J Med Chem 41(4):640–649. https://doi.org/10.1021/jm9707582
Tan RJ, Li Y, Rush BM, Cerqueira DM, Zhou D, Fu H, Ho J, Stolz DB, Liu Y (2019) Tubular injury triggers podocyte dysfunction by β-catenin–driven release of MMP-7. JCI Insight 4(24):e122399. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.122399
Tirapelli LF, Barione DF, Trazzi BFM, Tirapelli DPC, Novas PC, Silva CS, Martinez M et al (2009) Comparison of two models for evaluation histopathology of experimental renal ischemia. Transpl Proc 41(10):4083–4087. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.transproceed.2009.09.061
Wang D, Dai C, Li Y, Liu Y (2011) Canonical Wnt/β-catenin signaling mediates transforming growth factor-Β1-driven podocyte injury and proteinuria. Kidney Int 80(11):1159–1169. https://doi.org/10.1038/ki.2011.255
Wang X, Miao Y, Ni J, Wang Y, Qian T, Yu J, Liu Q, Wang P, Yi S (2018) Peripheral nerve injury induces dynamic changes of tight junction components. Front Physiol 9:1519. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01519
Wu J, Zhao D, Wu S, Wang D (2015) Ang-(1–7) exerts protective role in blood-brain barrier damage by the balance of TIMP-1/MMP-9. Eur J Pharmacol 748:30–36. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.12.007
Yang X, Chen C, Teng S, Fu X, Zha Y, Liu H, Wang L et al (2017) Urinary matrix metalloproteinase-7 predicts severe AKI and poor outcomes after cardiac surgery. J Am Soc Nephrol: JASN 28(11):3373–3382. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2017020142
Yang X, Ou J, Zhang H, Xu X, Zhu L, Li Q, Li J, Xie D, Sun J, Zha Y, Li Y (2019) Urinary matrix metalloproteinase 7 and prediction of IgA nephropathy progression’. Am J Kidney Dis. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2019.07.018
Yu AS, Alan SL (2015) Claudins and the kidney’. J Am Soc Nephrol 26(1):11–19. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2014030284
Zhang S, An Q, Wang T, Gao S, Zhou G (2018) Autophagy- and MMP-2/9-mediated reduction and redistribution of ZO-1 contribute to hyperglycemia-increased blood-brain barrier permeability during early reperfusion in stroke. Neuroscience 377:126–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2018.02.035
Zhong Z, Hu Q, Fu Z, Wang R, Xiong Y, Zhang Y, Liu Z, Wang Y, Ye Q (2016) Increased expression of aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 reduces renal cell apoptosis during ischemia/reperfusion injury after hypothermic machine perfusion. Artif Organs 40(6):596–603. https://doi.org/10.1111/aor.12607
Zhou D, Tian Y, Sun L, Zhou L, Xiao L, Tan RJ, Tian J, Fu H, Hou FF, Liu Y (2017) Matrix metalloproteinase-7 is a urinary biomarker and pathogenic mediator of kidney fibrosis’. J Am Soc Nephrol: JASN 28(2):598–611. https://doi.org/10.1681/ASN.2016030354
Zhou X, Zang X, Guan Y, Tolbert T, Zhao TC, Bayliss G, Zhuang S (2018) Targeting enhancer of zeste homolog 2 protects against acute kidney injury. Cell Death Dise 9(11):1067. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41419-018-1012-0
Funding
This work was supported by the Medical Science Advancement Program (Clinical Medicine) of Wuhan University [Grant Numbers: TFLC2018003], National Science Foundation for Young Scientists of China [Grant Numbers: 81700657], and National Postdoctoral Program for Innovative Talents [Grant Numbers: BX201700177].
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HQC designed and carried out the research, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript. LJN, LWJ, CYW and CB helped to carry out the experiments and contributed ideas. LZZ, XY and WYF provided guidance and revised the manuscript. YQF and ZZB designed the experiments, provided overall guidance, and helped to write the manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board/Ethics Committee of Zhongnan Hospital of Wuhan University. All animal experiments were carried out in accordance with Experimental Animal Management Ordinance (National Science and Technology Committee of China) and the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hu, Q., Lan, J., Liang, W. et al. MMP7 damages the integrity of the renal tubule epithelium by activating MMP2/9 during ischemia–reperfusion injury. J Mol Hist 51, 685–700 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09914-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09914-4