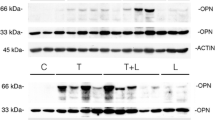
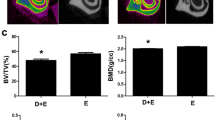
Abstract
p53 is known to advance the cell arrest and cell senescence in human tumors. In this study, we displayed that osteogenic ability of p53-knockout (p53−/−) mice was significantly increased in the tooth extraction socket compared with wild-type (WT) counterparts. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BM-MSCs) from mandibular were collected and exhibited with elevated proliferation potential and colony-forming units compared with the control, as well as stronger mineral deposits and osteogenic markers. Besides, the bone mass and bone parameter in p53−/− mice were markedly enhanced compared with the counterpart after extractions by micro-CT. Masson’s trichrome staining and immunohistochemistry also revealed that new bone filling and osterix/osteocalcin (Osx/OCN)-immunopositive staining in p53−/− mice were remarkably increased at each time point. Furthermore, consistent with the enhanced osteogenic markers, the angiogenic marker of blood vessels (alpha smooth muscle actin, α-SMA) was significantly elevated in p53−/− mice in contrast to WT mice. Importantly, we found that the osteoclast numbers exhibited an increased trend in p53−/− mice compared with WT mice during socket healing. Collectively, our result suggest that p53 deficiency could promote the osteogenesis and angiogenesis in the tooth extraction socket and might lend possibility for p53-based therapeutic approaches in acceleration of extraction bone healing.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araujo MG, Silva CO, Misawa M, Sukekava F (2015) Alveolar socket healing: what can we learn? Periodontol 2000 68(1):122–134. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12082
Araujo MG, Silva CO, Souza AB, Sukekava F (2019) Socket healing with and without immediate implant placement. Periodontol 2000 79(1):168–177. https://doi.org/10.1111/prd.12252
Artigas N, Gamez B, Cubillos-Rojas M, Sanchez-de Diego C, Valer JA, Pons G, Ventura F (2017) P53 inhibits sp7/osterix activity in the transcriptional program of osteoblast differentiation. Cell Death Differ 24(12):2022–2031. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.113
Aubrey BJ, Kelly GL, Janic A, Herold MJ, Strasser A (2018) How does p53 induce apoptosis and how does this relate to p53-mediated tumour suppression? Cell Death Differ 25(1):104–113. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.169
Boonyagul S, Banlunara W, Sangvanich P, Thunyakitpisal P (2014) Effect of acemannan, an extracted polysaccharide from aloe vera, on bmscs proliferation, differentiation, extracellular matrix synthesis, mineralization, and bone formation in a tooth extraction model. Odontology 102(2):310–317. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10266-012-0101-2
Buser D, Martin W, Belser UC (2004) Optimizing esthetics for implant restorations in the anterior maxilla: anatomic and surgical considerations. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implant 19:43–61
Chandar N, Donehower L, Lanciloti N (2000) Reduction in p53 gene dosage diminishes differentiation capacity of osteoblasts. Anticancer Res 20(4):2553–2559
Chen H, Kolman K, Lanciloti N, Nerney M, Hays E, Robson C, Chandar N (2012) P53 and mdm2 are involved in the regulation of osteocalcin gene expression. Exp Cell Res 318(8):867–876. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.02.022
Choi S, Chen M, Cryns VL, Anderson RA (2019) A nuclear phosphoinositide kinase complex regulates p53. Nat Cell Biol.https://doi.org/10.1038/s41556-019-0297-2
De Kok IJ, Drapeau SJ, Young R, Cooper LF (2005) Evaluation of mesenchymal stem cells following implantation in alveolar sockets: A canine safety study. Int J Oral Maxillofac Implant 20(4):511–518
Giaccia AJ, Kastan MB (1998) The complexity of p53 modulation: emerging patterns from divergent signals. Genes Dev 12(19):2973–2983
Ito Y, Teitelbaum SL, Zou W, Zheng Y, Johnson JF, Chappel J, Zhao H (2010) Cdc42 regulates bone modeling and remodeling in mice by modulating rankl/m-csf signaling and osteoclast polarization. J Clin Investig 120(6):1981–1993. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI39650
Jain A, Singh M, Ganapathy KP, Ramola V, Passi D, Jain K (2016) Evaluation of two socket healing procedures with and without mesenchymal stem cells: a comparative study. Natl J Maxillofac Surg 7(2):159–165. https://doi.org/10.4103/0975-5950.201366
Jha N, Choi EH, Kaushik NK, Ryu JJ (2017) Types of devices used in ridge split procedure for alveolar bone expansion: a systematic review. PLoS ONE 12(7):e0180342. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0180342
Jiang F, Yang X, Meng X, Zhou Z, Chen N (2018) Effect of cbx7 deficiency on the socket healing after tooth extractions. J Bone Miner Metab.https://doi.org/10.1007/s00774-018-0958-4
Kennedy A, Ng CT, Biniecka M, Saber T, Taylor C, O’Sullivan J, Fearon U (2010) Angiogenesis and blood vessel stability in inflammatory arthritis. Arthritis Rheumat 62(3):711–721. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27287
Kusumbe AP, Ramasamy SK, Adams RH (2014) Coupling of angiogenesis and osteogenesis by a specific vessel subtype in bone. Nature 507(7492):323–328. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13145
Li L, Mao Y, Zhao L, Li L, Wu J, Zhao M, Jiang P (2019) P53 regulation of ammonia metabolism through urea cycle controls polyamine biosynthesis. Nature 567(7747):253–256. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41586-019-0996-7
Liang Y, Yin C, Lu XI, Jiang H, Jin F (2019) Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells protect lungs from smoke inhalation injury by differentiating into alveolar epithelial cells via notch signaling. J Biosci 44(1):2
Martino MM, Maruyama K, Kuhn GA, Satoh T, Takeuchi O, Muller R, Akira S (2016) Inhibition of il-1r1/myd88 signalling promotes mesenchymal stem cell-driven tissue regeneration. Nat Commun 7:11051. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms11051
McConnell AM, Yao C, Yeckes AR, Wang Y, Selvaggio AS, Tang J, Stripp BR (2016) P53 regulates progenitor cell quiescence and differentiation in the airway. Cell Rep 17(9):2173–2182. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2016.11.007
Mu S, Tee BC, Emam H, Zhou Y, Sun Z (2018) Culture-expanded mesenchymal stem cell sheets enhance extraction-site alveolar bone growth: an animal study. J Periodontal Res 53(4):514–524. https://doi.org/10.1111/jre.12541
Nakajima R, Ono M, Hara ES, Oida Y, Shinkawa S, Pham HT, Kuboki T (2014) Mesenchymal stem/progenitor cell isolation from tooth extraction sockets. J Dent Res 93(11):1133–1140. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034514549377
Nguyen DTT, Richter D, Michel G, Mitschka S, Kolanus W, Cuevas E, Wulczyn FG (2017) The ubiquitin ligase lin41/trim71 targets p53 to antagonize cell death and differentiation pathways during stem cell differentiation. Cell Death Differ 24(6):1063–1078. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2017.54
Olivier M, Hollstein M, Hainaut P (2010) Tp53 mutations in human cancers: origins, consequences, and clinical use. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2(1):a001008. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a001008
Ramasamy SK, Kusumbe AP, Wang L, Adams RH (2014) Endothelial notch activity promotes angiogenesis and osteogenesis in bone. Nature 507(7492):376–380. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature13146
Reagan MR, Mishima Y, Glavey SV, Zhang Y, Manier S, Lu ZN, Ghobrial IM (2014) Investigating osteogenic differentiation in multiple myeloma using a novel 3d bone marrow niche model. Blood 124(22):3250–3259. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2014-02-558007
Rittling SR, Matsumoto HN, McKee MD, Nanci A, An XR, Novick KE, Denhardt DT (1998) Mice lacking osteopontin show normal development and bone structure but display altered osteoclast formation in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 13(7):1101–1111. https://doi.org/10.1359/jbmr.1998.13.7.1101
Ross CL, Ang DC, Almeida-Porada G (2019) Targeting mesenchymal stromal cells/pericytes (mscs) with pulsed electromagnetic field (pemf) has the potential to treat rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol 10:266. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2019.00266
Schwartz KA, Lanciloti NJ, Moore MK, Campione AL, Chandar N (1999) P53 transactivity during in vitro osteoblast differentiation in a rat osteosarcoma cell line. Mol Carcinog 25(2):132–138
Serino G, Biancu S, Iezzi G, Piattelli A (2003) Ridge preservation following tooth extraction using a polylactide and polyglycolide sponge as space filler: a clinical and histological study in humans. Clin Oral Implants Res 14(5):651–658
Srivastava S, Weitzmann MN, Cenci S, Ross FP, Adler S, Pacifici R (1999) Estrogen decreases tnf gene expression by blocking jnk activity and the resulting production of c-jun and jund. J Clin Investig 104(4):503–513. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI7094
Talib WH, Al Kury LT (2018) Parthenolide inhibits tumor-promoting effects of nicotine in lung cancer by inducing p53-dependent apoptosis and inhibiting vegf expression. Biomed Pharmacother 107:1488–1495. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2018.08.139
Throndson RR, Sexton SB (2002) Grafting mandibular third molar extraction sites: a comparison of bioactive glass to a nongrafted site. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 94(4):413–419
Trombelli L, Farina R, Marzola A, Bozzi L, Liljenberg B, Lindhe J (2008) Modeling and remodeling of human extraction sockets. J Clin Periodontol 35(7):630–639. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1600-051X.2008.01246.x
Valente LJ, Gray DH, Michalak EM, Pinon-Hofbauer J, Egle A, Scott CL, Strasser A (2013) P53 efficiently suppresses tumor development in the complete absence of its cell-cycle inhibitory and proapoptotic effectors p21, puma, and noxa. Cell Rep 3(5):1339–1345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2013.04.012
Wang X, Kua HY, Hu Y, Guo K, Zeng Q, Wu Q, Li B (2006) P53 functions as a negative regulator of osteoblastogenesis, osteoblast-dependent osteoclastogenesis, and bone remodeling. J Cell Biol 172(1):115–125. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.200507106
Wang F, Zhou Y, Zhou J, Xu M, Zheng W, Huang W, Zou D (2018) Comparison of intraoral bone regeneration with iliac and alveolar bmscs. J Dent Res 97(11):1229–1235. https://doi.org/10.1177/0022034518772283
Wienken M, Dickmanns A, Nemajerova A, Kramer D, Najafova Z, Weiss M, Dobbelstein M (2016) Mdm2 associates with polycomb repressor complex 2 and enhances stemness-promoting chromatin modifications independent of p53. Mol Cell 61(1):68–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2015.12.008
Xu R, Fu Z, Liu X, Xiao T, Zhang P, Du Y, Jiang H (2016) Transplantation of osteoporotic bone marrow stromal cells rejuvenated by the overexpression of satb2 prevents alveolar bone loss in ovariectomized rats. Exp Gerontol 84:71–79. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.exger.2016.09.001
Yi B, Shen Y, Tang H, Wang X, Li B, Zhang Y (2019) Stiffness of aligned fibers regulates the phenotypic expression of vascular smooth muscle cells. Acs Appl Mater Interfaces 11(7):6867–6880. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsami.9b00293
Yu YF, Zhang Y, Shen N, Zhang RY, Lu XQ (2014) Effect of vegf, p53 and telomerase on angiogenesis of gastric carcinoma tissue. Asian Pac J Trop Med 7(4):293–296. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1995-7645(14)60041-9
Zhou Z, Yin Y, Jiang F, Niu Y, Wan S, Chen N, Shen M (2016) Cbx7 deficiency plays a positive role in dentin and alveolar bone development. J Mol Histol 47(4):401–411. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-016-9682-3
Zlotorynski E (2016) Cancer biology: the dark side of p21. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 17(8):461. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrm.2016.90
Acknowledgements
Research was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81730066), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81670966) and the Project of Invigorating College through Science and Education.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yang, X., Zhou, Z., Mao, Z. et al. Role of p53 deficiency in socket healing after tooth extractions. J Mol Hist 51, 55–65 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09856-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-020-09856-x