Abstract
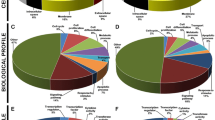
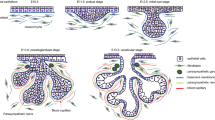
Sjögren’s syndrome or radiotherapy for head and neck cancer leads to the irreversible hypofunction of salivary gland (SG). The stem/progenitor cell-based regenerative strategy has been proven to be the most promising approach to repair the function of SG. The molecular mechanisms that regulate SG morphogenesis, especially during lumen formation, provide valuable hints for establishment of such regenerative strategies. It has been demonstrated that numerous growth factors particularly belonging to SHH, BMP, and FGF signaling pathway are involved in the regulation of lumen formation and have shown protective effects on the SG from irradiation in mouse models. However, it remains elusive whether the expression pattern and function of these signaling molecules are conserved in humans. In this study, we examined the expression patterns of the molecules critical for SHH, BMP, and FGF signaling cascades from the canalicular stage to the terminal bud stage, the key stages for lumen formation, in human SG and compared them with the expression data observed in mice. Our results manifested that genes involved in SHH signaling pathway showed identical expression patterns, while genes involved in BMP as well as FGF pathway exhibited similar but distinct expression patterns in humans to those in the mouse. We concluded that the expression patterns of genes involved in SHH, BMP, and FGF pathways in the development of human SG exhibit high similarity to that in the development of mouse SG during lumen formation, suggesting that the molecular mechanism regulating the morphogenesis of SG during lumen formation may be conserved in mice and humans. Our results will have an implication in the future establishment of stem-cell based approaches for the repair of SG function.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ach T, Schwarz-Furlan S, Ach S, Agaimy A, Gerken M, Rohrmeier C, Zenk J, Iro H, Brockhoff G, Ettl T (2016) Genomic aberrations of MDM2, MDM4, FGFR1 and FGFR3 are associated with poor outcome in patients with salivary gland cancer. J Oral Pathol Med 45:500–509
Aoto K, Nishimura T, Eto K, Motoyama J (2002) Mouse GLI3 regulates Fgf8 expression and apoptosis in the developing neural tube, face, and limb bud. Dev Biol 251:320–332
Borghese E (1950) The development in vitro of the submandibular and sublingual glands of Mus musculus. J Anat 84:287
Gazzerro E, Canalis E (2006) Bone morphogenetic proteins and their antagonists. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 7:51–65
Gresik EW, Koyama N, Hayashi T, Kashimata M (2009) Branching morphogenesis in the fetal mouse submandibular gland is codependent on growth factors and extracellular matrix. J Med Invest 56:228–233
Haara O, Fujimori S, Schmidt-Ullrich R, Hartmann C, Thesleff I, Mikkola ML (2011) Ectodysplasin and Wnt pathways are required for salivary gland branching morphogenesis. Development 138:2681–2691
Hashizume A, Hieda Y (2006) Hedgehog peptide promotes cell polarization and lumen formation in developing mouse submandibular gland. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 339:996–1000
Heikinheimo KA, Laine MA, Ritvos OV, Voutilainen RJ, Hogan BL, Leivo IV (1999) Bone morphogenetic protein-6 is a marker of serous acinar cell differentiation in normal and neoplastic human salivary gland. Cancer Res 59:5815–5821
Hoffman MP, Kidder BL, Steinberg ZL, Lakhani S, Ho S, Kleinman HK, Larsen M (2002) Gene expression profiles of mouse submandibular gland development: FGFR1 regulates branching morphogenesis in vitro through BMP-and FGF-dependent mechanisms. Development 129:5767–5778
Hu X, Zhang S, Chen G, Lin C, Huang Z, Chen Y, Zhang Y (2013) Expression of SHH signaling molecules in the developing human primary dentition. BMC Dev Biol 13:11
Hu X, Xu S, Lin C, Zhang L, Chen Y, Zhang Y (2014) Precise chronology of differentiation of developing human primary dentition. Histochem Cell Biol 141:221–227
Iber D, Menshykau D (2013) The control of branching morphogenesis. Open Biol 3:130088
Jaskoll T, Zhou YM, Chai Y, Makarenkova HP, Collinson JM, West JD, Hajihosseini MK, Lee J, Melnick M (2002) Embryonic submandibular gland morphogenesis: stage-specific protein localization of FGFs, BMPs, Pax6 and Pax9 in normal mice and abnormal SMG phenotypes in FgfR2-IIIc(+/Delta), BMP7(-/-) and Pax6(-/-) mice. Cells Tissues Organs 170:83–98
Jaskoll T, Leo T, Witcher D, Ormestad M, Astorga J, Bringas P Jr, Carlsson P, Melnick M (2004a) Sonic hedgehog signaling plays an essential role during embryonic salivary gland epithelial branching morphogenesis. Dev Dyn 229:722–732
Jaskoll T, Witcher D, Toreno L, Bringas P, Moon AM, Melnick M (2004b) FGF8 dose-dependent regulation of embryonic submandibular salivary gland morphogenesis. Dev Biol 268:457–469
Knosp WM, Knox SM, Hoffman MP (2012) Salivary gland organogenesis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev 1:69–82
Konings AW, Coppes RP, Vissink A (2005) On the mechanism of salivary gland radiosensitivity. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 62:1187–1194
Larsen M, Yamada KM, Musselmann K (2010) Systems analysis of salivary gland development and disease. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Syst Biol Med 2:670–682
Liu F, Wang S (2014) Molecular cues for development and regeneration of salivary glands. Histol Histopathol 29:305–312
Lombaert IM, Abrams SR, Li L, Eswarakumar VP, Sethi AJ, Witt RL, Hoffman MP (2013) Combined KIT and FGFR2b signaling regulates epithelial progenitor expansion during organogenesis. Stem Cell Rep 1:604–619
Mattingly A, Finley JK, Knox SM (2015) Salivary gland development and disease. Wiley Interdiscip Rev 4:573–590
Miyazono K, Kamiya Y, Morikawa M (2010) Bone morphogenetic protein receptors and signal transduction. J Biochem 147:35–51
Patel VN, Hoffman MP (2014) Salivary gland development: a template for regeneration. Semin Cell Dev Biol 25–26:52–60
Patel VN, Rebustini IT, Hoffman MP (2006) Salivary gland branching morphogenesis. Differentiation 74:349–364
Riva A, Tandler B, Riva FT (1988) Ultrastructural observations on human sublingual gland. Am J Anat 181:385–392
Ruiz i Altaba A (1999) Gli proteins encode context-dependent positive and negative functions: implications for development and disease. Development 126:3205–3216
Shackleford JM, Klapper C (1962) Structure and carbohydrate histochemistry of mammalian salivary glands. Am J Anat 111:25–47
Sieber C, Kopf J, Hiepen C, Knaus P (2009) Recent advances in BMP receptor signaling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 20:343–355
Teshima TH, Ianez RC, Coutinho-Camillo CM, Tucker AS, Lourenco SV (2016) Apoptosis-associated protein expression in human salivary gland morphogenesis. Arch Oral Biol 69:71–81
Tucker AS (2007) Salivary gland development. Semin Cell Dev Biol 18:237–244
Yin H, Cabrera-Perez J, Lai Z, Michael D, Weller M, Swaim WD, Liu X, Catalan MA, Rocha EM, Ismail N, Afione S, Rana NA, Di Pasquale G, Alevizos I, Ambudkar I, Illei GG, Chiorini JA (2013) Association of bone morphogenetic protein 6 with exocrine gland dysfunction in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome and in mice. Arthritis Rheum 65:3228–3238
Zouvelou V, Luder HU, Mitsiadis TA, Graf D (2009) Deletion of BMP7 affects the development of bones, teeth, and other ectodermal appendages of the orofacial complex. J Exp Zool B Mol Dev Evol 312B:361–374
Acknowledgements
The study is financially supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China (81870739) and the project of College of Life Sciences, Fujian Normal University (FZSKG2018012).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Guan, Z., Dong, B., Huang, C. et al. Expression patterns of genes critical for SHH, BMP, and FGF pathways during the lumen formation of human salivary glands. J Mol Hist 50, 217–227 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-019-09819-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-019-09819-x