Abstract
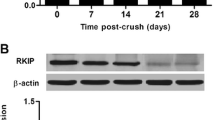
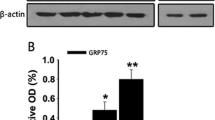
GTP-binding protein Gem, a member protein of the Ras superfamily, can regulate actin cytoskeleton reorganization mediated by Rho-associated coiled-coil-containing protein kinase (ROCK). One attractive activity of the ROCK is playing a potential role in physiological and pathological process in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs) apoptosis. However, the function of Gem in retina is still with limited understanding. To investigate whether Gem is involved in optic nerve injury, we performed an optic nerve crush (ONC) model in adult rats. Western blot analysis indicated that Gem was significantly increased in the retina at the 3rd day after ONC. Meanwhile, double-immunofluorescent staining showed that Gem expression was mainly up-regulated in ganglion cell layer and co-localized with NeuN (a marker of RGCs). Additionally, the co-localizations of Gem/active-caspase-3 and Gem/TUNEL-positive cells were detected in RGCs. Furthermore, the expression of active-caspase-3 and TUNEL-positive cells was parallel with that of Gem. Finally, expression pattern of ROCK family (only ROCK2 but not ROCK1) was increased in the differentiated process, which was collected with the expression of GEM and active-caspase-3. Based on the present results, it is suggested that Gem might play a crucial role in RGCs apoptosis after ONC, which might be involved in ROCK pathway.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bermel C, Tonges L, Planchamp V, Gillardon F, Weishaupt JH, Dietz GP, Bahr M, Lingor P (2009) Combined inhibition of Cdk5 and ROCK additively increase cell survival, but not the regenerative response in regenerating retinal ganglion cells. Mol Cell Neurosci 42:427–437
Bien A, Seidenbecher CI, Bockers TM, Sabel BA, Kreutz MR (1999) Apoptotic versus necrotic characteristics of retinal ganglion cell death after partial optic nerve injury. J Neurotrauma 16:153–163
Cohen L, Mohr R, Chen YY et al (1994) Transcriptional activation of a ras-like gene (kir) by oncogenic tyrosine kinases. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 91:12448–12452
Diekmann H, Fischer D (2013) Glaucoma and optic nerve repair. Cell Tissue Res 353:327–337
Frisca F, Crombie DE, Dottori M, Goldshmit Y, Pebay A (2013) Rho/ROCK pathway is essential to the expansion, differentiation, and morphological rearrangements of human neural stem/progenitor cells induced by lysophosphatidic acid. J Lipid Res 54:1192–1206
Hatzoglou A, Ader I, Splingard A, Flanders J, Saade E, Leroy I, Traver S, Aresta S, de Gunzburg J (2007) Gem associates with Ezrin and acts via the Rho-GAP protein Gmip to down-regulate the Rho pathway. Mol Biol Cell 18:1242–1252
Herskowitz JH, Feng Y, Mattheyses AL et al (2013) Pharmacologic inhibition of ROCK2 suppresses amyloid-beta production in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J Neurosci 33:19086–19098
Huang TL, Huang SP, Chang CH, Lin KH, Sheu MM, Tsai RK (2014) Factors influencing the retrograde labeling of retinal ganglion cells with fluorogold in an animal optic nerve crush model. Ophthalmic Res 51:173–178
Inan S, Buyukafsar K (2008) Antiepileptic effects of two Rho-kinase inhibitors, Y-27632 and fasudil, in mice. Br J Pharmacol 155:44–51
Kerman M, Kanter M, Coskun KK, Erboga M, Gurel A (2012) Neuroprotective effects of caffeic acid phenethyl ester on experimental traumatic brain injury in rats. J Mol Histol 43:49–57
Kermer P, Klocker N, Labes M, Bahr M (1998) Inhibition of CPP32-like proteases rescues axotomized retinal ganglion cells from secondary cell death in vivo. J Neurosci 18:4656–4662
Koch JC, Tonges L, Barski E, Michel U, Bahr M, Lingor P (2014) ROCK2 is a major regulator of axonal degeneration, neuronal death and axonal regeneration in the CNS. Cell Death Dis 5:e1225
Lingor P, Teusch N, Schwarz K, Mueller R, Mack H, Bahr M, Mueller BK (2007) Inhibition of Rho kinase (ROCK) increases neurite outgrowth on chondroitin sulphate proteoglycan in vitro and axonal regeneration in the adult optic nerve in vivo. J Neurochem 103:181–189
Lingor P, Tonges L, Pieper N, Bermel C, Barski E, Planchamp V, Bahr M (2008) ROCK inhibition and CNTF interact on intrinsic signalling pathways and differentially regulate survival and regeneration in retinal ganglion cells. Brain 131:250–263
Lossi L, Tamagno I, Merighi A (2004) Molecular morphology of neuronal apoptosis: analysis of caspase 3 activation during postnatal development of mouse cerebellar cortex. J Mol Histol 35:621–629
Maguire J, Santoro T, Jensen P, Siebenlist U, Yewdell J, Kelly K (1994) Gem: an induced, immediate early protein belonging to the Ras family. Science 265:241–244
Osborne NN, Wood JP, Chidlow G, Bae JH, Melena J, Nash MS (1999) Ganglion cell death in glaucoma: what do we really know? Br J Ophthalmol 83:980–986
Pernet V, Joly S, Jordi N, Dalkara D, Guzik-Kornacka A, Flannery JG, Schwab ME (2013) Misguidance and modulation of axonal regeneration by Stat3 and Rho/ROCK signaling in the transparent optic nerve. Cell Death Dis 4:e734
Pettmann B, Henderson CE (1998) Neuronal cell death. Neuron 20:633–647
Pineda AA, Minohara M, Kawamura N, Matsushita T, Yamasaki R, Sun X, Piao H, Shimokawa H, Kira J (2011) Preventive and therapeutic effects of the selective Rho-kinase inhibitor fasudil on experimental autoimmune neuritis. J Neurol Sci 306:115–120
Quigley HA (1993) Open-angle glaucoma. N Engl J Med 328:1097–1106
Raff MC, Barres BA, Burne JF, Coles HS, Ishizaki Y, Jacobson MD (1993) Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system. Science 262:695–700
Reynet C, Kahn CR (1993) Rad: a member of the Ras family overexpressed in muscle of type II diabetic humans. Science 262:1441–1444
Sang A, Xu Y, Jin N et al (2013) Involvement of transcription initiation factor IIB in the light-induced death of rat retinal ganglion cells in vivo. J Mol Histol 44:11–18
Satoh S, Toshima Y, Ikegaki I, Iwasaki M, Asano T (2007) Wide therapeutic time window for fasudil neuroprotection against ischemia-induced delayed neuronal death in gerbils. Brain Res 1128:175–180
Sun H, Li L, Zhou F et al (2013) The member of high temperature requirement family HtrA2 participates in neuronal apoptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage in adult rats. J Mol Histol 44:369–379
Tonges L, Frank T, Tatenhorst L, Saal KA, Koch JC, Szego EM, Bahr M, Weishaupt JH, Lingor P (2012) Inhibition of rho kinase enhances survival of dopaminergic neurons and attenuates axonal loss in a mouse model of Parkinson’s disease. Brain 135:3355–3370
Vesterinen HM, Currie GL, Carter S, Mee S, Watzlawick R, Egan KJ, Macleod MR, Sena ES (2013) Systematic review and stratified meta-analysis of the efficacy of RhoA and Rho kinase inhibitors in animal models of ischaemic stroke. Syst Rev 2:33
Villar-Cheda B, Dominguez-Meijide A, Joglar B, Rodriguez-Perez AI, Guerra MJ, Labandeira-Garcia JL (2012) Involvement of microglial RhoA/Rho-kinase pathway activation in the dopaminergic neuron death. Role of angiotensin via angiotensin type 1 receptors. Neurobiol Dis 47:268–279
Wang Y, Cheng X, Zhou Z, Wu H, Long L, Gu X, Xu G (2013) Increased expression of Gem after rat sciatic nerve injury. J Mol Histol 44:27–36
Wen H, Cao J, Yu X et al (2013) Spatiotemporal patterns of Gem expression after rat spinal cord injury. Brain Res 1516:11–19
Wen X, Wang L, Liu Z, Liu Y, Hu J (2014) Intracranial injection of PEG-PEI/ROCK II-siRNA improves cognitive impairment in a mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Neurosci. doi:10.3109/00207454.2013.877014
Wu J, Li J, Hu H, Liu P, Fang Y, Wu D (2012) Rho-kinase inhibitor, fasudil, prevents neuronal apoptosis via the Akt activation and PTEN inactivation in the ischemic penumbra of rat brain. Cell Mol Neurobiol 32:1187–1197
Yoshimi E, Yamamoto H, Furuichi Y, Shimizu Y, Takeshita N (2010) Sustained analgesic effect of the Rho kinase inhibitor AS1892802 in rat models of chronic pain. J Pharmacol Sci 114:119–122
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Natural Science Foundation of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (No. 2012GXNSFAA276039) and Science Fund Project of People’s Hospital of Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region (No. qn2014-1).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Fan Xu, Hui Huang and Yu Wu have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xu, F., Huang, H., Wu, Y. et al. Upregulation of Gem relates to retinal ganglion cells apoptosis after optic nerve crush in adult rats. J Mol Hist 45, 565–571 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-014-9579-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-014-9579-y