Abstract
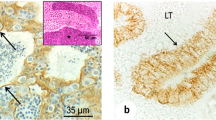
In the last few decades, several growth factors were identified in the testis of various mammalian species. Growth factors are shown to promote cell proliferation, regulate tissue differentiation, and modulate organogenesis. In the present investigation we have studied the localization of EGF and EGFR in the adult bovine testis by means of immunohistochemical method. Our results demonstrated that EGF and EGFR were localized solely to the bovine testicular germ cells (spermatogonia, spermatocytes, and round spermatids). In contrast, the somatic testicular cells (i.e., Sertoli, Leydig, and myofibroblast cells) exhibited no staining affinity. EGF and EGFR were additionally detected in the epithelial lining of straight tubules and rete testis. Interestingly, the distribution of EGF and EGFR in the germ cells was mainly dependent upon the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium since their localization appeared to be preponderant during the spermatogonia proliferation and during the meiotic and spermiogenic processes. In conclusion, such findings may suggest that EGF and EGFR are important paracrine and/or autocrine regulators of spermatogenesis in bovine.
Access this article
We’re sorry, something doesn't seem to be working properly.
Please try refreshing the page. If that doesn't work, please contact support so we can address the problem.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abd-Elmaksoud A, Sinowatz F (2005) Expression and localization of growth factors and their receptors in the mammalian testis. Review/Part I. Anat Histol Embryol 34(5):319–334
Anklesaria P, Teixido J, Laiho M et al (1990) Cell–cell adhesion mediated by binding of membrane-anchored transforming growth factor alpha to epidermal growth factor receptors promotes cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 87(9):3289–3293
Ascoli M (1981) Regulation of gonadotropin receptors and gonadotropin responses in a clonal strain of Leydig tumor cells by epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem 256(1):179–183
Bartlett JM, Spiteri-Grech J, Nieschlag E (1990) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor I and stage-specific levels of epidermal growth factor in stage synchronized rat testes. Endocrinology 127(2):747–758
Carpenter G, Cohen S (1990) Epidermal growth factor. J Biol Chem 265(14):7709–7712
Caussanel V, Tabone E, Mauduit C et al (1996) Cellular distribution of EGF, TGFalpha and their receptor during postnatal development and spermatogenesis of the boar testis. Mol Cell Endocrinol 123(1):61–69
Cupp AS, Skinner MK (2001) Expression, action, and regulation of transforming growth factor alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor during embryonic and perinatal rat testis development. J Androl 22(6):1019–1029
Fisher DA, Lakshmanan J (1990) Metabolism and effects of epidermal growth factor and related growth factors in mammals. Endocr Rev 11(3):418–442
Foresta C, Caretto A, Varotto A et al (1991) Epidermal growth factor receptors (EGFR) localization in human testis. Arch Androl 27(1):17–24
Foresta C, Varotto A (1994) Immunocytochemical localization of epidermal growth factor receptors in human testis from infertile subjects. Fertil Steril 61(5):941–948
Gnessi L, Fabbri A, Spera G (1997) Gonadal peptides as mediators of development and functional control of the testis: an integrated system with hormones and local environment. Endocr Rev 18:541–609
Hsu SM, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Huleihel M, Lunenfeld E (2004) Regulation of spermatogenesis by paracrine/autocrine testicular factors. Asian J Androl 6:259–268
Kaloglu C, Bulut HE, Onarlioglu B (2000) Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) immunolocalization in the male rat reproductive tract during pre- and postnatal periods. Turk J Vet Anim Sci 24:501–509
Leblond CP, Clermont Y (1952) Definition of the stages of the cycle of the seminiferous epithelium in the rat. Ann NY Acad Sci 55:548–573
Levine E, Cupp AS, Miyashiro L et al (2000) Role of transforming growth factor-alpha and the epidermal growth factor receptor in embryonic rat testis development. Biol Reprod 62(3):477–490
Liu A, Flores C, Kinkead T et al (1994) Effects of sialoadenectomy and epidermal growth factor on testicular function of sexually mature male mice. J Urol 152(2 Pt 1):554–561
Massague J, Cheifetz S, Boyd FT et al (1990) TGF-beta receptors and TGF-beta binding proteoglycans: recent progress in identifying their functional properties. Ann NY Acad Sci 593:59–72
Moore A, Morris ID (1993) Paracrine effects via the epidermal growth factor receptor in the rodent testis may be mediated by non-Leydig interstitial cells. J Endocrinol 136(3):439–446
Mullaney BP, Skinner MK (1992) Transforming growth factor-alpha and epidermal growth factor receptor gene expression and action during pubertal development of the seminiferous tubule. Mol Endocrinol 6(12):2103–2113
Nakazumi H, Sasano H, Maehara I et al (1996) Transforming growth factor-alpha, epidermal growth factor, and epidermal growth factor receptor in human testis obtained from biopsy and castration: immunohistochemical study. Tohoku J Exp Med 178(4):381–388
Niederberger CS, Shubhada S, Kim SJ et al (1993) Paracrine factors and the regulation of spermatogenesis. World J Urol 11(2):120–128
O”Rand MG, Romerell LG (1977) Appearance of the cell surface auto-and isoantigens during spermatogenesis in the rabbit. Dev Biol 55:347–358
Onyango DW, Wango EO, Otiang’a-Owiti GE et al (2000) Morphological characterization of the seminiferous cycle in the goat (Capra hircus): a histological and ultrastructural study. Anat Anz 182:235–241
Ortavant R (1958) Study of spermatogonial generations in the ram. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil 148:1958–1961
Prigent SA, Lemoine NR (1992) The type 1 (EGFR-related) family of growth factor receptors and their ligands. Prog Growth Factor Res 4(1):1–24
Radhakrishnan B, Oke BO, Papadopoulos V et al (1992) Characterization of epidermal growth factor in mouse testis. Endocrinology 131(6):3091–3099
Radhakrishnan B, Suarez-Quian CA (1992) Characterization of epidermal growth factor receptor in testis, epididymis and vas deferens of non-human primates. J Reprod Fertil 96(1):13–23
Russe I, Sinowatz F (1991) Lehrbuch der Embryologie der Haustiere. Verlag Paul Parey, Berlin und Hamburg
Sharpe RM (1994) Regulation of spermatogenesis. In Knobil E, Neill JD (eds) The physiology of reproduction, 2nd edn. Raven Press, New York. pp 1363–1434
Sordoillet C, Chauvin MA, de Peretti E et al (1991) Epidermal growth factor directly stimulates steroidogenesis in primary cultures of porcine Leydig cells: actions and sites of action. Endocrinology 128(4):2160–2168
Stubbs SC, Hargreave TB, Habib FK (1990) Localization and characterization of epidermal growth factor receptors on human testicular tissue by biochemical and immunohistochemical techniques. J Endocrinol 125(3):485–492
Suarez-Quian CA, Dai MZ, Onoda M et al (1989) Epidermal growth factor receptor localization in the rat and monkey testes. Biol Reprod 41(5):921–932
Suarez-Quian CA, Niklinski W (1990) Immunocytochemical localization of the epidermal growth factor receptor in mouse testis. Biol Reprod 43(6):1087–1097
Suarez-Quian CA, Oke BO, Radhakrishnan B (1994) Relationship between submandibular gland epidermal growth factor and spermatogenesis in C3H mice. Tissue Cell 26(3):285–298
Syed V, Khan SA, Nieschlag E (1991) Epidermal growth factor stimulates testosterone production of human Leydig cells in vitro. J Endocrinol Invest 14(2):93–97
Tsutsumi O, Kurachi H, Oka T (1986) A physiological role of epidermal growth factor in male reproductive function. Science 233(4767):975–977
Uguralp S, Bay Karabulut A, Mizrak B et al (2004) The effect of sustained and local administration of epidermal growth factor on improving bilateral testicular tissue after torsion. Urol Res 32(5):323–331
Verhoeven G, Cailleau J (1986) Stimulatory effects of epidermal growth factor on steroidogenesis in Leydig cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol 47(1–2):99–106
Wahab-Wahlgren A, Martinelle N, Holst M et al (2003) EGF stimulates rat spermatogonial DNA synthesis in seminiferous tubule segments in vitro. Mol Cell Endocrinol 201(1–2):39–46
Wong RW, Kwan RW, Mak PH et al (2000) Overexpression of epidermal growth factor induced hypospermatogenesis in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 275(24):18297–18301
Wrobel KH, Pawar HS (1992) Quantitative morphology of the testicular tubular epithelium in the water buffalo (Bubalus bubalis). Andrologia 24:63–68
Wrobel KH, Reichold J, Schimmel M (1995) Quantitative morphology of the ovine seminiferous epithelium. Anat Anz 177:19–32
Wrobel KH, Schimmel M (1989) Morphology of the bovine Sertoli cell during the spermatogenetic cycle. Cell Tissue Res 257:93–103
Wu HH, Kawamata H, Kawai K et al (1993) Immunohistochemical localization of epidermal growth factor and transforming growth factor alpha in the male rat accessory sex organs. J Urol 150:990–993
Yan YC, Sun YP, Zhang ML (1998) Testis epidermal growth factor and spermatogenesis. Arch Androl 40(2):133–146
Yang GS, Lu RK, Chen ZD (2002) Clinical significance of EGF and EGFR expression changes in cryptorchid boys. Asian J Androl 4(4):255–258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kassab, M., Abd-Elmaksoud, A. & Ali, M.A. Localization of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) and epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in the bovine testis. J Mol Hist 38, 207–214 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-007-9089-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10735-007-9089-2