Abstract
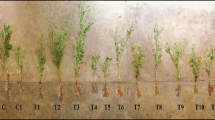
Phytoextraction assisted by plant growth regulators (PGRs) is gaining popularity in phytoremediation applications. A pot experiment was conducted to compare the effects of foliar applications of 11 PGRs, including Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), Indole-3-butyric acid (IBA), diethyl aminoethyl hexanoate (DA-6), 6-Benzylaminopurine (6-BA), 1-naphthylacetic acid (NAA), Abscisic acid (ABA), 2,4-Dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D), Ethrel (ETH), Brassinolide (BR), Gibberellin (GA3), and Compound sodium nitrophenolate (CSN) on plant development, chlorophyll content, antioxidant enzyme activities, Cd phytoextraction capacity and micro-distribution of Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. grown in Cd contaminated soil. The effect on biomass yield was dependent on the PGRs type, with IBA being the most efficient. The addition of PGRs increased Cd extraction efficiency, with their effect decreasing in the order: IAA > DA-6 > IBA > 2,4-D > 6-BA > NAA > BR > CSN > ETH > GA3 > ABA. Application of PGRs increased Cd concentrations in leaves and stems but reduction was found in roots (except for 2,4-D). Exogenous PGRs increased the activities of stress ameliorating enzymes (SOD and CAT) and led to a reduction in MDA (malondialdehyde) concentration. In leaves, scanning electron microscope-Energy dispersive spectrometer (SEM–EDS) confirmed that application of IBA or DA-6 further fixed more Cd in upper and lower epidermal cells, which might relate to more Cd migration from roots to shoots in Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. These findings suggest that the treatment with IBA or DA-6 appears to be optimal for enhancing the phytoextraction efficiency of Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. in Cd contaminated soil.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aderholt M, Vogelien DL, Koether M, Greipsson S (2017) Phytoextraction of contaminated urban soils by Panicum virgatum L. enhanced with application of a plant growth regulator (BAP) and citric acid. Chemosphere 175:85–96
Ahmad B, Jaleel H, Sadiq Y, Khan MM, Shabbir A (2018) Response of exogenous salicylic acid on cadmium induced photosynthetic damage, antioxidant metabolism and essential oil production in peppermint. Plant Growth Regul 86(2):273–286
Allison LE (1976) Organic carbon. In: Black CA (ed) Methods of soil analysis: part 2. chemical and microbiological properties. American Society of Agronomy, Madison, pp 1367–1378
Alloway BJ (1995) Heavy metals in soils, 2nd edn. Blackie Academic and Professional, London
Asgher M, Khan MIR, Anjum NA, Khan NA (2015) Minimising toxicity of cadmium in plants—role of plant growth regulators. Protoplasma 252:399–413
Bali S, Kaur P, Kohli SK, Ohri P, Thukral AK, Bhardwaj R, Wijaya L, Alyemeni MN, Ahmad P (2018) Jasmonic acid induced changes in physio-biochemical attributes and ascorbate-glutathione pathway in Lycopersicon esculentum under lead stress at different growth stages. Sci Total Environ 645:1344–1360
Barbafieri M, Tassi E (2011) Brassinosteroids for phytoremediation application. In: Hayat ES, Ahmad A (eds) Brassinosteroids: a class of plant hormone. Springer, Berlin, pp 403–437
Bulak P, Walkiewicz A, Brzezińska M (2014) Plant growth regulators-assisted phytoextraction. Biol Plant 58:1–8
Caregnato FF, Koller CE, MacFarlane GR, Moreira JCF (2008) The glutathione antioxidant system as a biomarker suite for the assessment of heavy metal exposure and effect in the grey mangrove, Avicennia marina (Forsk) Vierh. Mar Pollut Bull 56:1119–1127
Chaney RL, Malik M, Li YM, Brown SL, Brewer EP, Angle JS, Baker AJ (1997) Phytoremediation of soil metals. Curr Opin Biotechnol 8:279–284
Chen B, Luo S, Wu YJ, Ye JY, Wang Q, Xu XM, Pan FS, Khan KY, Feng Y, Yang XE (2017) The effects of the endophytic bacterium pseudomonas fluorescens sasm05 and IAA on the plant growth and cadmium uptake of Sedum alfredii Hance. Front Microbiol 8:2538
Chen L, Wang D, Long C, Cui ZX (2019) Effect of plant growth regulations on phytoremediation of uranium and cadmium contaminated soil by Zebrina pendula schnizl. Fresenius Environ Bull 28(2A):1434–1442
Faessler E, Evangelou MW, Robinson BH, Schulin R (2010) Effects of indole-3-acetic acid (IAA) on sunflower growth and heavy metal uptake in combination with ethylene diamine disuccinic acid (EDDS). Chemosphere 80(8):901–907
Fuentes HD, Khoo CS, Pe T, Muir S, Khan AG (2000) Phytoremediation of a contaminated mine site using plant growth regulators to increase heavy metal uptake. In: Proceedings of the 5th international conference on clean technologies for the mining industry, pp 427–435
George EF, Hall MA, Klerk GJD (2008) Plant growth regulators I: introduction; auxins, their analogues and inhibitors. Plant propagation by tissue culture. Springer, Dordrecht, pp 175–204
Ghosh M, Singh SP (2005) A comparative study of cadmium phytoextraction by accumulator and weed species. Environ Pollut 133(2):365–371
Guan MY, Zhang HH, Pan W, Jin CW, Lin XY (2018) Sulfide alleviates cadmium toxicity in Arabidopsis plants by altering the chemical form and the subcellular distribution of cadmium. Sci Total Environ 627:663–670
Hadi F, Bano A, Fuller MP (2010) The improved phytoextraction of lead (Pb) and the growth of maize (Zea mays L.): the role of plant growth regulators (GA3 and IAA) and EDTA alone and in combinations. Chemosphere 80(4):457–462
He S, Wu Q, He Z (2014) Synergetic effects of DA-6/GA3 with EDTA on plant growth, extraction and detoxification of Cd by Lolium perenne. Chemosphere 117:132–138
He SJ, Hu YJ, Wang HB, Wang HJ, Li QC (2017) Effects of indole-3-acetic acid on arsenic uptake ad antioxidative enzymes in Pteris cretica var. nervosa and Pteris ensiformis. Int J Phytoremed 19(3):231–238
He SY, Guo HH, He ZL, Wang L (2019) Effects of a new-type cleaning agent and a plant growth regulator on phytoextraction of cadmium from a contaminated soil. Pedosphere 29(2):161–169
Hu PJ, Qiu RL, Senthilkumar P, Jiang D, Chen ZW, Tang YT, Liu JF (2009) Tolerance, accumulation and distribution of zinc and cadmium in hyperaccumulator potentilla griffithii. Environ Exp Bot 66(2):317–325
Kumar PB, Dushenkov V, Motto H, Raskin I (1995) Phytoextraction-the use of plants to remove heavy-metals from soils. Environ Sci Technol 29(5):1232–1238
Kupper H, Zhao FJ, McGrath SP (1999) Cellular compartmentation of zinc in leaves of the hyperaccumulator Thlaspi caerulescens. Plant Physiol 119(1):305–311
Kupper H, Lombi E, Zhao FJ, McGrath SP (2000) Cellular compartmentation of cadmium and zinc in relation to other elements in the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri. Planta 212(1):75–84
Li NY, Fu QL, Zhuang P, Zou B, Guo B, Li ZA (2012a) Effect of fertilizers on Cd uptake of Amaranthus hypochondriacus, a high biomass, fast growing and easily cultivated potential Cd hyperaccumulator. Int J Phytorem 14(2):162–173
Li JT, Baker AJM, Ye ZH, Wang HB, Shu WS (2012b) Phytoextraction of Cd-contaminated soils: current status and future challenges. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 42(20):2113–2152
Li ZY, Ma ZW, Kuijp TJVD, Yuan Z, Huang L (2014) A review of soil heavy metal pollution from mines in China: pollution and health risk assessment. Sci Total Environ 468:843–853
Li ZW, Zhang RS, Zhang HM (2018) Effects of plant growth regulators (DA-6 and 6-BA) and EDDS chelator on phytoextraction and detoxification of cadmium by Amaranthus hybridus Linn. Int J Phytorem 20(11):1121–1128
Liphadzi MS, Kirkham MB, Paulsen GM (2006) Auxin-enhanced root growth for phytoremediation of sewage-sludge amended soil. Environ Technol 27(6):695–704
Liu W, Shu WS, Lan CY (2004) Viola baoshanensis, a plant that hyperaccumulates cadmium. Chin Sci Bull 49(1):29–32
Liu L, Ma QQ, Lin LJ, Tang Y, Wang J, Lv XL, Liao MA, Xia H, Chen SX, Li JH, Wang X, Lai YS, Liang D (2017) Effects of exogenous abscisic acid on cadmium accumulation in two ecotypes of hyperaccumulator Bidens pilosa. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 36(6):1643–1649
Long C, Wang D, Chen L, Jiang WJ, Xiang MW (2017) Effect of four kinds of phytohormones on U and Cd accumulation in Helianthus annuus. Chin J Environ Eng 11(5):3251–3256 (in Chinese)
López ML, Peralta-Videa JR, Benitez T, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2005) Enhancement of lead uptake by alfalfa (Medicago sativa) using EDTA and a plant growth promotor. Chemosphere 61(4):595–598
Lu HP, Li ZA, Wu JT, Shen Y, Li YW, Zou B, Tao YT, Zhuang P (2017) Influences of calcium silicate on chemical forms and subcellular distribution of cadmium in Amaranthus hypochondriacus L. Sci Rep 7:40583
MAPRC (Ministry of Agriculture of the People’s Republic of China) (2017) Determination of chlorophyll content in fruits, vegetables and derived products—Spectrophotometry method (NY/T 3082-2017). MAPRC, Beijing (in Chinese)
Meng H, Hua S, Shamsi IH, Jilani G, Li Y, Jiang L (2009) Cadmium-induced stress on the seed germination and seedling growth of Brassica napus L., and its alleviation through exogenous plant growth regulators. Plant Growth Regul 58(1):47–59
Okem A, Kulkarni MG, Staden JV (2015) Enhancing phytoremediation potential of Pennisetum clandestinum Hochst in cadmium-contaminated coil using smoke-water and smoke-isolated karrikinolide. Int J Phytorem 17(11):1046–1052
Padmavathiamma PK, Li LY (2007) Phytoremediation technology: hyper-accumulation metals in plants. Water Air Soil Pollut 184(1–4):105–126
Piotrowska-Niczyporuk A, Bajguz A, Zambrzycka E, Godlewska-Zylkiewicz B (2012) Phytohormones as regulators of heavy metal biosorption and toxicity in green alga Chlorella vulgaris (Chlorophyceae). Plant Physiol Biochem 52(1):52–65
Ramakrishna B, Rao SSR (2012) 24-Epibrassinolide alleviated zinc induced oxidative stress in radish (Rap-hanus sativus L.) seedlings by enhancing anti-oxidative system. Plant Growth Regul 68:249–259
Sarret G, Saumitou-Laprade P, Bert V, Proux O, Hazemann JL, Traverse A, Marcus MA, Manceau A (2002) Forms of zinc accumulated in the hyperaccumulator Arabidopsis halleri. Plant Physiol 130(4):1815–1826
Sattar MA, Paasivirta J (1980) Fate of chlorophenoxyacetic acids in acid soil. Chemosphere 9:745
Shahzad B, Tanveera M, Zhao C, Rehman A, Cheema SA, Sharma A, Song H, Rehman SU, Dong ZR (2018) Role of 24-epibrassinolide (EBL) in mediating heavy metal and pesticide induced oxidative stress in plants: a review. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 147:935–944
Sharma I, Pati PK, Bhardwaj R (2011) Effect of 2,4-epibrassinolide on oxidative stress markers induced by nickel-ion in Raphanus sativus L. Acta Physiol Plant 33(5):1723–1735
Shi WG, Liu WZ, Yu WJ, Zhang YH, Ding S, Li H, Mark T, Kraigher H, Luo ZB (2019) Abscisic acid enhances lead translocation from the roots to the leaves and alleviates its toxicity in Populus × canescens. J Hazard Mater 362:275–285
Singh S, Prasad SM (2015) IAA alleviates Cd toxicity on growth, photosynthesis and oxidative damages in eggplant seedlings. Plant Growth Regul 77(1):87–98
Singh S, Singh A, Bashri G, Prasad SM (2016) Impact of Cd stress on cellular functioning and its amelioration by phytohormones: an overview on regulatory network. Plant Growth Regul 80(3):253–263
Tack FMG, Meers E (2010) Assisted phytoextraction: helping plants to help us. Elements 6(6):383–388
Tanaka Y, Sano T, Tamaoki M, Nakajima N, Kondo N, Hasezawa S (2005) Ethylene inhibits abscisic acid-induced stomatal closure in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 138(4):2337–2343
Tassi E, Pouget J, Petruzzelli G, Barbafieri M (2008) The effects of exogenous plant growth regulators in the phytoextraction of heavy metals. Chemosphere 71(1):66–73
Verma A, Malik CP, Gupta VK (2011) In Vitro effects of brassinosteroids on the growth and antioxidant enzyme activities in groundnut. ISRN Agron 2012:8
Wang J, Chen J, Pan K (2013) Effect of exogenous abscisic acid on the level of antioxidants in Atractylodes macrocephala Koidz under lead stress. Environ Sci Pollut Res 20(3):1441–1449
Wei SH, Zhou QX, Wang X, Zhang KS, Guo GL, Ma LQY (2005) A newly-discovered Cd-hyperaccumulator Solanum nigrum L. Chin Sci Bull 50(1):33–38
Wojick M, D’Haen VJ, Tukiendorf A (2005) Cadmium tolerance in Thlaspi caerulescens II: localization of cadmium in Thlaspi caerulescens. Environ Exp Bot 53(2):163–171
Yu CL (2011) Study on the plant growth regulator enhancing remediation efficiency of Solanum nigrum L. on contaminated soil by cadmium. Harbin University of Science and Technology (in Chinese)
Zhang L, Liang XG, Shen S, Yin H, Zhou LL, Gao Z, Lv XY, Zhou SL (2018) Increasing the abscisic acid level in maize grains induces precocious maturation by accelerating grain filling and dehydration. Plant Growth Regul 86(1):65–79
Zhao L, Xiong J, Li LP, Zhu C (2009) Low concentration of exogenous abscisic acid increases lead tolerance in rice seedlings. Biol Plant 53(4):728
Zhao FJ, Ma Y, Zhu YG, Tang Z, McGrath SP (2015) Soil contamination in China: current status and mitigation strategies. Environ Sci Technol 49(2):750–759
Zhuang P, Yang QW, Wang HB, Shu WS (2007) Phytoextraction of heavy metals by eight plant species in the field. Water Air Soil Pollut 184:235–242
Acknowledgements
This research was financially supported by the National Key Technologies R&D Program of China (2015BAD05B05), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31670513), the Science and Technology Program of Guangdong, China (2018B030324003 and 2016A020221023), National Key R&D Program of China (2016YFD0800704), Special Program for Key Basic Research and Cultivation Project of Guangdong, China (2015A030308015), Program of Bureau of Science and Information Technology of Guangzhou Municipality (201903010022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
PZ and ZL designed the study; SS, XZ and XC carried out the experiments; YF and YL contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; SS analyzed the data and wrote the manuscript; and MM and CL contributed to language modification.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sun, S., Zhou, X., Cui, X. et al. Exogenous plant growth regulators improved phytoextraction efficiency by Amaranths hypochondriacus L. in cadmium contaminated soil. Plant Growth Regul 90, 29–40 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-019-00548-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-019-00548-5