Abstract
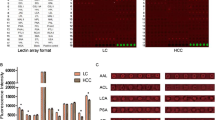
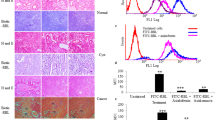
Cephalosporium curvulum lectin (CSL), a lectin from pathogenic fungus has exquisite specificity towards α1–6 linkage of core fucosylated glycans, expressed in hepatocellular and pancreatic cancer. Interaction and effect of CSL and other fucose specific lectins LCA and AOL on HepG2 and PANC-1 cells was investigated. CSL, LCA and AOL exhibited strong binding to PANC-1 cells which could be effectively blocked by competing glycoprotein mucin. Effect of CSL, LCA and AOL on PANC-1 and HepG2 cells was determined by MTT assay and all the three lectins inhibited the cell growth which could be blocked by mucin, cell cycle analysis revealed that CSL increased hypodiploid HepG2 cell population indicating cellular apoptosis. CSL induced apoptosis in HepG2 cells was confirmed by Annexin V/PI assay. CSL induced increase in early apoptotic HepG2 cell population, a time dependent increase in the expression of caspases-3, 9 and cytochrome-c was observed by western blotting suggesting the possible involvement of intrinsic caspase dependent apoptosis. Increase in ROS and decrease in MMP demonstrated involvement of intrinsic caspase dependent apoptosis. Quantification of AFP in HCC patients using CSL lectin-antibody sandwich ELISA, supports diagnostic potential of CSL.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
(Target organ toxicology series) C. Gad Shayne - Toxicology of the gastrointestinal tract-CRC Press (2007).pdf
Rawla, P., Sunkara, T., Gaduputi, V.: Epidemiology of Pancreatic Cancer: Global Trends, Etiology and Risk Factors. World J Oncol. 10, 10–27 (2019). https://doi.org/10.14740/wjon1166
Kobayashi, Y., Tateno, H., Dohra, H., Moriwaki, K., Miyoshi, E., Hirabayashi, J., Kawagishi, H.: A novel Core Fucose-specific Lectin from the mushroom Pholiota squarrosa. J. Biol. Chem. 287, 33973–33982 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M111.327692
Bray, F., Ferlay, J., Soerjomataram, I., Siegel, R.L., Torre, L.A., Jemal, A.: Global cancer statistics 2018: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 68(6), 394–424 (2018). https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21492
Miyoshi, E., Moriwaki, K., Nakagawa, T.: Biological function of Fucosylation in Cancer biology. J. Biochem. 143, 725–729 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1093/jb/mvn011
Miyoshi, E., Nakano, M.: Fucosylated haptoglobin is a novel marker for pancreatic cancer: detailed analyses of oligosaccharide structures. Proteomics. 8, 3257–3262 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200800046
Dingjan, T., Spendlove, I., Durrant, L.G., Scott, A.M., Yuriev, E., Ramsland, P.A.: Structural biology of antibody recognition of carbohydrate epitopes and potential uses for targeted cancer immunotherapies. Mol. Immunol. 67, 75–88 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molimm.2015.02.028
Gorakshakar, A.C., Ghosh, K.: Use of lectins in immunohematology. Asian journal of transfusion science. 10(1), 12–21 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4103/0973-6247.172180
Gupta, G., Surolia, A., Sampathkumar, S.-G.: Lectin microarrays for Glycomic analysis. OMICS: A Journal of Integrative Biology. 14, 419–436 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1089/omi.2009.0150
Li, C., Simeone, D.M., Brenner, D.E., Anderson, M.A., Shedden, K.A., Ruffin, M.T., Lubman, D.M.: Pancreatic Cancer serum detection using a Lectin/Glyco-antibody Array method. J. Proteome Res. 8, 483–492 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1021/pr8007013
De Mejía, E.G., Prisecaru, V.I.: Lectins as bioactive plant proteins: a potential in Cancer treatment. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 45, 425–445 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408390591034445
Abdullaev, F.I., Gonzalez de Mejia, E.: Antitumor effect of plant lectins. Nat. Toxins. 5, 157–163 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1002/19970504NT6
Fu, L., Zhou, C., Yao, S., Yu, J., Liu, B., Bao, J.: Plant lectins: targeting programmed cell death pathways as antitumor agents. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 43, 1442–1449 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocel.2011.07.004
Liu, Z., Luo, Y., Zhou, T.-T., Zhang, W.-Z.: Could plant lectins become promising anti-tumour drugs for causing autophagic cell death? Cell Prolif. (2013). https://doi.org/10.1111/cpr.12054
Miyoshi, E., Moriwaki, K., Terao, N., Tan, C.-C., Terao, M., Nakagawa, T., Matsumoto, H., Shinzaki, S., Kamada, Y.: Fucosylation is a promising target for Cancer diagnosis and therapy. Biomolecules. 2, 34–45 (2012). https://doi.org/10.3390/biom2010034
Ball, D., Rose, E., Alpert, E.: Alpha-Fetoprotein Levels in Normal Adults. The American Journal of the Medical Sciences. 303, 157–159 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1097/00000441-199203000-00004
Li, P.: Elevated serum alpha fetoprotein levels promote pathological progression of hepatocellular carcinoma. WJG. 17, 4563 (2011). https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v17.i41.4563,4571
Aoyagi, Y., Suzuki, Y., Igarashi, K., Saitoh, A., Oguro, M., Yokota, T., Mori, S., Nomoto, M., Isemura, M., Asakura, H.: The usefulness of simultaneous determinations of glucosaminylation and fucosylation indices of alpha-fetoprotein in the differential diagnosis of neoplastic diseases of the liver. Cancer. 67(9), 2390–2394 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1002/1097-0142(19910501)67:9<2390::AID-CNCR2820670928>3.0.CO;2-V
Ido, A.: Highly sensitive lens culinaris agglutinin-reactive α-fetoprotein is useful for early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease. Oncol. Rep. (2011). https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2011.1425
Nagre, N.N., Chachadi, V.B., Eligar, S.M., Shubhada, C., Pujari, R., Shastry, P., Swamy, B.M., Inamdar, S.R.: Purification and Characterization of a Mitogenic Lectin from Cephalosporium , a Pathogenic Fungus Causing Mycotic Keratitis. Biochem. Res. Int. 2010, 1–6 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1155/2010/854656
Inamdar, S.R., Eligar, S.M., Ballal, S., Belur, S., Kalraiya, R.D., Swamy, B.M.: Exquisite specificity of mitogenic lectin from Cephalosporium curvulum to core fucosylated N-glycans. Glycoconj. J. 33, 19–28 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-015-9628-0
Ballal, S., Belur, S., Laha, P., Roy, S., Swamy, B.M., Inamdar, S.R.: Mitogenic lectins from Cephalosporium curvulum (CSL) and Aspergillus oryzae (AOL) mediate host–pathogen interactions leading to mycotic keratitis. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 434, 209–219 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11010-017-3050-9
Goldman, M.: In fluorescent antibody methods, pp. 101–161. Academic Press, New York (1968)
Spiro, R.G., Bhoyroo, V.D.: Structure of the O-glycosidically linked carbohydrate units of fetuin. J. Biol. Chem. 249(18), 5704–5717 (1974)
Matés, J.M., Segura, J.A., Alonso, F.J., Márquez, J.: Oxidative stress in apoptosis and cancer: an update. Arch. Toxicol. 86, 1649–1665 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00204-012-0906-3
Ghazarian, H., Idoni, B., Oppenheimer, S.B.: A glycobiology review: carbohydrates, lectins and implications in cancer therapeutics. Acta Histochem. 113, 236–247 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acthis.2010.02.004
Machado, E., Kandzia, S., Carilho, R., Altevogt, P., Conradt, H.S., Costa, J.: N-glycosylation of total cellular glycoproteins from the human ovarian carcinoma SKOV3 cell line and of recombinantly expressed human erythropoietin. Glycobiology. 21, 376–386 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cwq170
Shimomura, O., Oda, T., Tateno, H., Ozawa, Y., Kimura, S., Sakashita, S., Noguchi, M., Hirabayashi, J., Asashima, M., Ohkohchi, N.: A Novel Therapeutic Strategy for Pancreatic Cancer: Targeting Cell Surface Glycan Using rBC2LC-N Lectin–Drug Conjugate (LDC). Mol Cancer Ther. 17, 183–195 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-17-0232
Abbott, K.L., Nairn, A.V., Hall, E.M., Horton, M.B., McDonald, J.F., Moremen, K.W., Dinulescu, D.M., Pierce, M.: Focused glycomic analysis of the N-linked glycan biosynthetic pathway in ovarian cancer. Proteomics. 8, 3210–3220 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1002/pmic.200800157
Okuyama, S., Nakamura-Tsuruta, S., Tateno, H., Hirabayashi, J., Matsubara, K. and Hori, K., 2009. Strict binding specificity of small-sized lectins from the red alga Hypnea japonica for core (α1-6) fucosylated N-glycans. Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry, pp.0903051362-0903051362
Jagadeesh, N., Belur, S., Hegde, P., Kamalanathan, A.S., Swamy, B.M., Inamdar, S.R.: An L-fucose specific lectin from Aspergillus Niger isolated from mycotic keratitis patient and its interaction with human pancreatic adenocarcinoma PANC-1 cells. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 134, 487–497 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.04.192
Zhu, J., He, J., Liu, Y., Simeone, D.M., Lubman, D.M.: Identification of glycoprotein markers for pancreatic Cancer CD24 + CD44 + stem-like cells using Nano-LC–MS/MS and tissue microarray. J. Proteome Res. 11, 2272–2281 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1021/pr201059g
Eligar, S.M., Pujari, R., Swamy, B.M., Shastry, P., Inamdar, S.R.: Sclerotium rolfsii lectin inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis in human ovarian cancer cell line PA-1. Cell Prolif. 45, 397–403 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2184.2012.00831.x
Inamdar, S.R., Savanur, M.A., Eligar, S.M., Chachadi, V.B., Nagre, N.N., Chen, C., Barclays, M., Ingle, A., Mahajan, P., Borges, A., Shastry, P., Kalraiya, R.D., Swamy, B.M., Rhodes, J.M., Yu, L.-G.: The TF-antigen binding lectin from Sclerotium rolfsii inhibits growth of human colon cancer cells by inducing apoptosis in vitro and suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Glycobiology. 22, 1227–1235 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1093/glycob/cws090
Shimizu, K., Taniichi, T., Satomura, S., Matsuura, S., Taga, H., Taketa, K.: Establishment of assay kits for the determination of microheterogeneities of alpha-fetoprotein using lectin-affinity electrophoresis. Clinica Chimica Acta. 214, 3–12 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(93)90297-H
Matsumura, K., Higashida, K., Hata, Y., Kominami, J., Nakamura-Tsuruta, S., & Hirabayashi, J. (2009). Comparative analysis of oligosaccharide specificities of fucose-specific lectins from Aspergillus oryzae and Aleuria aurantia using frontal affinity chromatography. Analytical biochemistry, 386(2), 217-221.
Acknowledgements
Dr. Shashikala Inamdar acknowledges the support by funding from Department of Science and Technology, India (No.SR/S0/BB-0085/2010/ 2012), UGC for the funding from under UPE (F.No14-4/2012(NS/PE) and The Karnatak Cancer Therapy and Research Institute, Padmashree Dr. R. B. Patil Hospital, Hubli, Karnataka for providing serum samples, Shivakumar Belur acknowledges UGC for RGNFSC.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Belur, S., Jagadeesh, N., Swamy, B.M. et al. A core fucose specific lectin from Cephalosporium curvulum induces cellular apoptosis in hepatocellular and pancreatic cancer cells and effective in detecting AFP. Glycoconj J 37, 435–444 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-020-09921-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-020-09921-3