Abstract
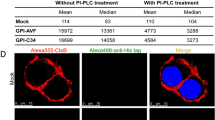
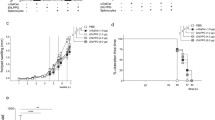
Previously, it was shown that the cell-membrane-expressed glycosphingolipid, globotriaosylceramide (Gb3/Pk/CD77), protects against HIV-1 infection and may be a newly described natural resistance factor against HIV infection. We have now investigated the potential of a novel, water soluble, non-toxic and completely synthetic analogue of Gb3/Pk (FSL-Gb3) to inhibit HIV-1 infection in vitro. A uniquely designed analogue, FSL-Gb3, of the natural Gb3/Pk molecule was synthesized. HIV-1IIIB (X4 virus) and HIV-1Ba-L (R5 virus) infection of PHA/interleukin-2-activated, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and Jurkat T cells in vitro was assessed, as well as infection of U87.CD4.CCR5 by various clinical R5 tropic viruses after treatment with FSL-Gb3. We monitored Gb3, CD4 and CXCR4 expression by fluorescent antibody cell sorting and viral replication by p24gag ELISA. Total cellular Gb3 was examined by glycosphingolipid extraction and thin layer chromatography. In vivo toxicity was monitored in mice by histological assessment of vital organs and lymphoid tissue. FSL-Gb3 blocked X4 and R5 of both lab and clinical viral strains in activated PBMCs or the U87.CD4.CCR5 cell line with a 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) of approximately 200–250 μM. FACS and TLC overlay showed that FSL-Gb3 can insert itself into cellular plasma membranes and that cellular membrane-absorbed FSL-Gb3 is able to inhibit subsequent HIV-1 infection. There was no effect of FSL-Gb3 on cell surface levels of CD4 or CXCR4. Thus, FSL-Gb3 can inhibit HIV-1 by two mechanisms: direct inhibition of virus and inhibition of viral entry. Infusion of FSL-Gb3 into laboratory mice at doses well in excess of theoretical therapeutic doses was tolerated with no untoward reactions. Our results demonstrate the potential utility of using a completely synthetic, water soluble globotriaosylceramide analogue, FSL-Gb3, having low toxicity, for possible future use as a novel therapeutic approach for the systemic treatment of HIV/AIDS.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moulds, J.M., Moulds, J.J.: Blood group associations with parasites, bacteria, and viruses. Transfus. Med. Rev. 14, 302–311 (2000)
Spitalnik, P.F., Spitalnik, S.L.: The P blood group system: biochemical, serological, and clinical aspects. Transfus. Med. Rev. 9, 110–122 (1995)
Schwartz-Albiez, R., Dorken, B., Moller, P., Brodin, N.T., Monner, D.A., Kniep, B.: Neutral glycosphingolipids of the globo-series characterize activation stages corresponding to germinal center B cells. Int. Immunol. 2, 929–936 (1990)
Lund, N., Olsson, M.L., Ramkumar, S., Sakac, D., Yahalom, V., Levene, C., Hellberg, A., Ma, X.Z., Binnington, B., Jung, D., Lingwood, C.A., Branch, D.R.: The human Pk histo-blood group antigen provides protection against HIV-1 infection. Blood 13, 4989–4991 (2009)
Fantini, J., Hammache, D., Piéroni, G., Yahi, N.: Role of glycosphingolipid microdomains in CD4-dependent HIV-1 fusion. Glycoconj. J. 17, 199–204 (2000)
Manes, S., Lacalle, R.A., Gomez-Mouton, C., del Real, G., Mira, E., Martinez-A, C.: Membrane raft microdomains in chemokine receptor function. Semin. Immunol. 13, 147–157 (2001)
Liao, Z., Cimakasky, L.M., Hampton, R., Nguyen, D.H., Hildreth, J.E.: Lipid rafts and HIV pathogenesis: host membrane cholesterol is required for infection by HIV type 1. AIDS Res. Hum. Retroviruses 11, 1009–1019 (2001)
Fantini, J., Hammache, D., Delezay, O., Pieroni, G., Tamalet, C., Yahi, N.: Sulfatide inhibits HIV-1 entry into CD4 super(−)/CXCR4 super(+) cells. Virology 246, 211–220 (1998)
Hammache, D., Piéroni, G., Yahi, N., Delézay, O., Koch, N., Lafont, H., Tamalet, C., Fantini, J.: Specific interaction of HIV-1 and HIV-2 surface envelope glycoproteins with monolayers of galactosylceramide and ganglioside GM3. J. Biol. Chem. 273, 7967–7971 (1998)
Mahfoud, R., Garmy, N., Maresca, M., Yahi, N., Puigserver, A., Fantini, J.: Identification of a common sphingolipid-binding domain in alzheimer, prion, and HIV-1 proteins. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 11292–11296 (2002)
Mylvaganam, M., Lingwood, C.A.: Adamantyl globotriaosyl ceramide: a monovalent soluble mimic which inhibits verotoxin binding to its glycolipid receptor. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 257, 391–394 (1999)
Lund, N., Branch, D.R., Mylvaganam, M., Chark, D., Ma, X.Z., Sakac, D., Binnington, B., Fantini, J., Puri, A., Blumenthal, R., Lingwood, C.A.: A novel soluble mimic of the glycolipid, globotriaosyl ceramide inhibts HIV infection. AIDS 20, 333–343 (2006)
Lund, N., Branch, D.R., Sakac, D., Lingwood, C.A., Siatskas, C., Robinson, C.J., Brady, R.O., Medin, J.A.: Lack of susceptibility of cells from patients with fabry disease to productive infection with R5 human immunodeficiency virus. AIDS 19, 1543–1546 (2005)
Furukawa, K., Iwamura, K., Uchikawa, M., Sojka, B.N., Wiels, J., Okajima, T., Urano, T., Furukawa, K.: Molecular basis for the p phenotype: identification of distinct and multiple mutations in the alpha 1, 4-galactosyltransferase gene in swedish and japanese individuals. J. Biol. Chem. 275, 37752–37756 (2000)
Steffensen, R., Carlier, K., Wiels, J., Levery, S.B., Stroud, M., Cedergren, B., Nilsson-Sojka, B., Bennett, E.P., Jersild, C., Clausen, H.: Cloning and expression of the histo-blood group pk UDP-galactose: Ga1beta-4G1cbeta1-cer alpha1, 4-galactosyltransferase: molecular genetic basis of the p phenotype. J. Biol. Chem. 272, 16723–16729 (2000)
Hellberg, A., Steffensen, R., Yahalom, V., Sojka, B.N., Heier, H.E., Levene, C., Poole, J., Olsson, M.L.: Additional molecular bases of the clinically important p blood group phenotype. Transfusion 43, 899–907 (2003)
Hellberg, A., Ringressi, A., Yahalom, V., Safwenberg, J., Reid, M.E., Olsson, M.L.: Genetic heterogeneity at the glycosyltransferase loci underlying the GLOB blood group system and collection. Br. J. Haematol. 125, 528–536 (2004)
Hellberg, A., Poole, J., Olsson, M.L.: Molecular basis of the globoside-deficient P(k) blood group phenotype. identification of four inactivating mutations in the UDP-N-acetylgalactosamine: globotriaosylceramide 3-beta-N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase gene. J. Biol. Chem. 277, 29455–29459 (2002)
Ramkumar, S., Sakac, D., Binnington, B., Branch, D.R., Lingwood, C.A.: Induction of HIV-1 resistance: cell susceptibility to infection is an inverse function of globotriaosyl ceramide levels. Glycobiology 19, 76–82 (2009)
Frame, T., Carroll, T., Korchagina, E., Bovin, N., Henry, S.: Synthetic glycolipid modification of red blood cell membranes. Transfusion 47, 876–882 (2007)
Yousefi, S., Ma, X.Z., Singla, R., Zhou, Y.C., Sakac, D., Bali, M., Liu, Y., Sahai, B.M., Branch, D.R.: HIV-1 infection is facilitated in T cells by decreasing p56lck protein tyrosine kinase activity. Clin. Exp. Immunol. 133, 78–90 (2003)
Nutikka, A., Binnington, B., Lingwood, C.A.: Methods for the identification of host receptors for shiga toxin. In: Philpott, D., Ebel, F. (eds.) E. coli: Shiga toxin methods and protocols, pp. 197–208. Humana Press, Totowa (2003)
Boyd, B., Magnusson, G., Zhiuyan, Z., Lingwood, C.A.: Lipid modulation of glycolipid receptor function: availability of gal(alpha 1–4)gal disaccharide for verotoxin binding in natural and synthetic glycolipids. Eur. J. Biochem. 223, 873–878 (1994)
Delezay, O., Hammache, D., Fantini, J., Yahi, N.: SPC3, a V3 loop-derived synthetic peptide inhibitor of HIV-1 infection, binds to cell surface glycosphingolipids. Biochemistry 35, 15663–15671 (1996)
Xiao, L., Owen, S.M., Goldman, I., Lal, A.A., dejong, J.J., Goudsmit, J., Lal, R.B.: CCR5 coreceptor usage of non-syncytium-inducing primary HIV-1 is independent of phylogenetically distinct global HIV-1 isolates: delineation of consensus motif in the V3 domain that predicts CCR5 usage. Virology 240, 83–92 (1998)
Brown, B.K., Darden, J.M., Tovanabutra, S., Oblander, T., Frost, J., Sanders-Buell, E., de Souza, M.S., Birx, D.L., McCutchan, F.E., Polonis, V.R.: Biologic and genetic characterization of a panel of 60 human immunodeficiency virus type 1 isolates, representing clades A, B, C, D, CRF01 AE and CRF02 AG, for the development and assessment of candidate vaccines. J. Virol. 79, 6089–60101 (2005)
Acknowledgments
This work was funded by the Canadian Blood Services through a graduate fellowship award to Amanda Harrison and operating grants from the Canadian Institutes for Health Research (CIHR), the Ontario HIV Treatment Network (OHTN), and the Canadian Association for HIV Research (CANFAR). Stephen Henry is a founder and shareholder in KODE Biotech Ltd. There are no other author conflicts of interest or financial interest in this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Harrison, A.L., Olsson, M.L., Jones, R.B. et al. A synthetic globotriaosylceramide analogue inhibits HIV-1 infection in vitro by two mechanisms. Glycoconj J 27, 515–524 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-010-9297-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10719-010-9297-y