Abstract
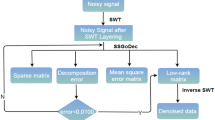
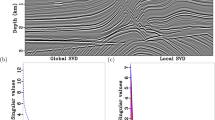
Rank-reduction methods are effective for separating random noise from the useful seismic signal based on the truncated singular value decomposition (TSVD). However, the results that the TSVD operator provides are still a mixture of noise and signal subspaces. This problem can be solved using the damped rank-reduction method by damping the singular values of noise-contaminated signals. When the seismic data include highly linear or curved events, the rank should be large enough to preserve the details of the useful signal. However, the damped rank-reduction operator becomes less powerful when using a large rank parameter. Hence, the denoised data contain significant remaining noise. More recently, the optimally damped rank-reduction method has been proposed to solve the extra noise problem as the rank value increases. The optimally damped rank-reduction operator works well for a moderately large rank, but becomes ineffective for a very large rank. We introduce an adaptive damped rank-reduction algorithm to attenuate the residual noise for a very large rank parameter. To elaborate on the proposed algorithm, we first construct a gain matrix by only using the input rank parameter, which we introduce directly into the adaptive singular-value weighting formula to make it more stable as the rank parameter becomes too large. Then, we derive a damping operator based on the improved optimal weighting operator to attenuate the residual noise. The proposed method, which can be regarded as an improved version of the optimally damped rank-reduction method, is insensitive to the input parameter. Examples of synthetic and real three-dimensional seismic data show the denoising improvement using the proposed method.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Datasets and source codes associated with this research will be made available online (www.ahay.org) as a reproducible paper.
References
Aharchaou M, Anderson J, Hughes S, Bingham J (2017) Singular-spectrum analysis via optimal shrinkage of singular values, in SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2017. Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 4950–4954
Bai M, Huang G, Wang H, Chen Y (2020) Seismic signal enhancement based on the low-rank methods. Geophys Prospect 68:2783–2807
Beylkin G (1987) Discrete radon transform. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 35:162–172
Bracewell RN, Bracewell RN (1986) The fourier transform and its applications. McGraw-Hill New York, 31999
Cadzow JA (1988) Signal enhancement - a composite property mapping algorithm. IEEE Trans Acoust Speech Signal Process 1:49–62
Cavalcante Q, Porsani MJ (2022) Low-rank seismic data reconstruction and denoising by cur matrix decompositions. Geophys Prospect 70:362–376
Chen W, Song H, Chuai X (2019) Fully automatic random noise attenuation using empirical wavelet transform. J Seismic Explor 28:147–162
Chen Y, Bai M, Guan Z, Zhang Q, Zhang M, Wang H (2020) Five-dimensional seismic data reconstruction using the optimally damped rank-reduction method. Geophys J Int 222(1):1824–1845
Chen Y, Fomel S (2015) Random noise attenuation using local signal-and-noise orthogonalization. Geophysics 80:WD1–WD9
Chen Y, Huang W, Zhang D, Chen W (2016) An open-source matlab code package for improved rank-reduction 3D seismic data denoising and reconstruction. Comput Geosci 95:59–66
Chen Y, Zhang D, Jin Z, Chen X, Zu S, Huang W, Gan S (2016) Simultaneous denoising and reconstruction of 5-D seismic data via damped rank-reduction method. Geophys J Int 206:1695–1717
Donoho DL (1995) De-noising by soft-thresholding. IEEE Trans Inform Theory 41:613–627
Feng J, Liu X, Li X, Xu W, Liu B (2021) Low-rank tensor minimization method for seismic denoising based on variational mode decomposition. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 19:1–5
Fomel S, Liu Y (2010) Seislet transform and seislet frame. Geophysics 75:V25–V38
Gilles J (2013) Empirical wavelet transform. IEEE Trans Signal Process 61:3999–4010
Goudarzi A, Riahi MA (2012) Seismic coherent and random noise attenuation using the undecimated discrete wavelet transform method with wdga technique. J Geophys Eng 9:619–631
Huang W, Wang R, Chen Y, Li H, Gan S (2016) Damped multichannel singular spectrum analysis for 3D random noise attenuation. Geophysics 81:V261–V270
Kabir MN, Verschuur D (1995) Restoration of missing offsets by parabolic radon transform. Geophys Prospect 43:347–368
Kazemi N, Bongajum E, Sacchi MD (2016) Surface-consistent sparse multichannel blind deconvolution of seismic signals. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 54:3200–3207
Kreimer N, Sacchi MD (2013) Nuclear norm minimization and tensor completion in exploration seismology. In: 2013 IEEE international conference on acoustics, speech and signal processing, IEEE, 4275–4279
Li J, Fan W, Li Y, Qian Z (2020) Low-frequency noise suppression in desert seismic data based on an improved weighted nuclear norm minimization algorithm. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 17:1993–1997
Li J, Wang D, Ji S, Li Y, Qian Z (2017) Seismic noise suppression using weighted nuclear norm minimization method. J Appl Geophys 146:214–220
Li S, Liu B, Ren Y, Chen Y, Yang S, Wang Y, Jiang P (2020) Deep learning inversion of seismic data. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 58(3):2135–2149
Liu G, Chen X (2013) Noncausal f-x-y regularized nonstationary prediction filtering for random noise attenuation on 3d seismic data. J Appl Geophys 93:60–66
Liu G, Chen X, Du J, Wu K (2012) Random noise attenuation using f-x regularized nonstationary autoregression. Geophysics 77:V61–V69
Mousavi SM, Langston CA, Horton SP (2016) Automatic microseismic denoising and onset detection using the synchrosqueezed continuous wavelet transform. Geophysics 81:V341–V355
Nadakuditi RR (2014) Optshrink: an algorithm for improved low-rank signal matrix denoising by optimal, data-driven singular value shrinkage. IEEE Trans Informa Theory 60:3002–3018
Neelamani R, Baumstein AI, Gillard DG, Hadidi MT, Soroka WL (2008) Coherent and random noise attenuation using the curvelet transform. Lead Edge 27:240–248
Oboué YASI, Chen Y (2021) Enhanced low-rank matrix estimation for simultaneous denoising and reconstruction of 5d seismic data. Geophysics 86:V459–V470
Oropeza V, Sacchi M (2011) Simultaneous seismic data denoising and reconstruction via multichannel singular spectrum analysis. Geophysics 76:V25–V32
Shao D, Han L, Li T, Li Y, Lin H, Dong X (2019) Low-rank approximation based variational mode decomposition for desert seismic noise attention. In: 81st EAGE Conference and Exhibition 2019, European Association of Geoscientists & Engineers, 1–5
Siahsar MAN, Gholtashi S, Torshizi EO, Chen W, Chen Y (2017) Simultaneous denoising and interpolation of 3-d seismic data via damped data-driven optimal singular value shrinkage. IEEE Geosci Remote Sens Lett 14:1086–1090
Trickett S (2008a) F-xy cadzow noise suppression. In: SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2008: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 2586–2590
Trickett S (2008b) F-xy Cadzow noise suppression. In: CSPG CSEG CWLS Convention, 303–306
Trickett S (2015) Preserving signal: Automatic rank determination for noise suppression. In: SEG Technical Program Expanded Abstracts 2015: Society of Exploration Geophysicists, 4703–4707
Wang C, Zhu Z, Gu H (2020) Low-rank seismic denoising with optimal rank selection for hankel matrices. Geophys Prospect 68:892–909
Wang H, Liu X, Chen Y (2020) Separation and imaging of seismic diffractions using a localized rank-reduction method with adaptively selected ranks. Geophysics 85(6):V497–V506
Xue Y, Man M, Zu S, Chang F, Chen Y (2017) Amplitude-preserving iterative deblending of simultaneous source seismic data using high-order radon transform. J Appl Geophys 139:79–90
Yang Y, Ma J, Osher S (2013) Seismic data reconstruction via matrix completion. Inverse Probl Imaging 7(4):1379
Zhai M-Y (2014) Seismic data denoising based on the fractional fourier transformation. J Appl Geophys 109:62–70
Zhang D, Zhou Y, Chen H, Chen W, Zu S, Chen Y (2017) Hybrid rank-sparsity constraint model for simultaneous reconstruction and denoising of 3d seismic data. Geophysics 82:V351–V367
Zhang M, Liu Y, Zhang H, Chen Y (2020) Incoherent noise suppression of seismic data based on robust low-rank approximation. IEEE Trans Geosci Remote Sens 58:8874–8887
Zhou Y, Zhang S (2017) Robust noise attenuation based on nuclear norm minimization and a trace prediction strategy. J Appl Geophys 147:52–67
Zu S, Zhou H, Wu R, Jiang M, Chen Y (2019) Dictionary learning based on dip patch selection training for random noise attenuation. Geophysics 84:V169–V183
Funding
Funding was provided by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant Number 41804140).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Oboué, Y.A.S.I., Chen, W., Saad, O.M. et al. Adaptive Damped Rank-Reduction Method for Random Noise Attenuation of Three-Dimensional Seismic Data. Surv Geophys 44, 847–875 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-022-09756-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-022-09756-7