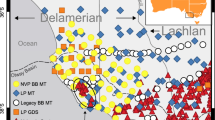
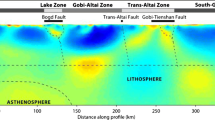
Abstract
Continent–continent collisions are an important tectonic process and have played a fundamental role in the evolution of the modern continents. A combination of geological and geophysical data has provided new constraints on the structure and temporal evolution of these orogens. Magnetotelluric (MT) studies have been an important part of these studies since they can constrain the fluid content and thermal structure which are key parameters for defining the rheology of the crust and upper mantle. MT studies of the Himalaya have defined the geometry of active faults associated with continued plateau growth. Orogen scale MT studies have shown that both the India–Asia collision (Tibetan Plateau and Himalaya) and the Arabia–Eurasia collision (Eastern Anatolia) have developed a low resistivity mid-crustal layer with upper surface at 10–20 km that is likely due to a combination of partial melt and associated aqueous fluids. The properties of this layer are consistent with a strength contrast that permits crustal flow over geological timescales. The upper mantle from the Moho to at least 100 km beneath both Northern Tibet and the Anatolian Plateau is characterized by low resistivity values (10–30 Ωm) indicating the presence of shallow asthenosphere. Future integrated seismic and MT studies of collision zones are needed fully to explore the 3D structures associated with deformation and further constrain geodynamic models.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Airy GB (1855) On the computation of the effect of the attraction of mountain masses, as disturbing the apparent astronomical latitude of stations in geodetic surveys. Phil Trans Royal Soc 145:101–104
Aitchison JC, Ali JR, Davis AM (2007) When and where did India and Asia collide? J Geophys Res 112:B05423. doi:10.1029/2006JB004706
Allmendinger RW, Jordan TE, Kay SM, Isacks BL (1997) The evolution of the Altiplano-Puna Plateau of the Central Andes. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 25:139–174
Allmendinger RW, Reilinger R, Loveless J (2007) Strain and rotation rate from GPS in Tibet, Anatolia and the Altiplano. Tectonics 26:TC3013. doi:10.1029/2006TC002030
Alsdorf D, Nelson D (1999) Tibetan satellite magnetic low: evidence for widespread melt in the Tibetan crust? Geology 27:943–946
Angus DA, Wilson DC, Sandvol E, Ni JF (2006) Lithospheric structure of the Arabian and Eurasian collision zone in Eastern Turkey from S-wave receiver functions. Geophys J Int 166:1335–1346
Archie GE (1942) The electrical resistivity log as an aid in determining some reservoir characteristics. Trans Am Inst Min Metall Pet Eng 146:54–62
Argand E (1924) La tectonique de l’ Asie. Proc 13th Int Geol Congr 7:170–372
Armijo R, Tapponnier P, Mercier JL, Han TL (1986) Quaternary extension in southern Tibet; field observations and tectonic implications. J Geophys Res 91:13803–13872
Arora B, Unsworth MJ, Rawat G (2007) Deep resistivity structure of the Northwest Indian Himalaya and its tectonic implications. Geophys Res Lett 34:L04307. doi:10.1029/2006GL029165
Arzi AA (1978) Critical phenomena in the rheology of partially melted rocks. Tectonophysics 44:173–184
Bai D, Meju M (2003) Deep structure of the Longling-Ruili fault underneath Ruili basin near the eastern Himalayan syntaxis: insights from magnetotelluric imaging. Tectonophysics 364:135–146
Bai D, Meju MA, Liao Z (2001) Magnetotelluric images of deep crustal structure of the Rehai geothermal field near Tengchong, southern China. Geophys J Int 147:677–687
Bai D, Unsworth MJ, Meju MA, Teng J, Kong X, Ma X, Sun J, Wang L, Jiang C, Zhao C, Xiao P, Liu M (2009) Large-scale crustal slip and flow beneath he eastern Tibetan Plateau. (Submitted to Nat Geosci October 2009)
Bayrak M, Nalbant SS (2001) Conductive crust imaged in western Turkey by magnetotellurics. Geophys Res Lett 28:3521–3524
Beaumont C, Jamieson RA, Nguyen MH, Lee B (2001) Himalayan tectonics explained by extrusion of a low-viscosity crustal channel coupled to focused surface denudation. Nature 414:738–742
Bedrosian PA, Unsworth MJ, Wang F (2001) Structure of the Altyn Tagh Fault and Daxue Shan from magnetotelluric surveys: implications for faulting associated with the rise of the Tibetan Plateau. Tectonics 20:474–486
Bendick R, Bilham R, Freymueller J, Larson K, Yin A (2000) Geodetic evidence for a low slip rate in the Altyn Tagh fault system. Nature 404:69
Berdichevsky MD, Borisova VP, Golubtsova NS, Ingerov AI, Konovalov YF, Kulikov AV, Solodilov LN, Chernyavskii GA, Shpak IP (1996) Interpretation of magnetotelluric soundings in the Lesser Caucasus, Izvestiya. Phys Solid Earth 32(4):352–368
Bielinski RA, Park SK, Rybin A, Batalev V, Jun S, Sears S (2003) Lithospheric heterogeneity in the Kyrgyz Tien Shan Imaged by magnetotelluric studies. Geophys Res Lett 30:1806. doi:10.1029/2003gl017455
Boerner DE, Kurtz RD, Craven JA, Ross GM, Jones FW (2000) A synthesis of EM studies in the lithoprobe Alberta Basement Transect: constraints on paleoproterozoic indentation tectonics. Can J Earth Sci 37:1509–1534
Brasse H, Eydam D (2008) Electrical conductivity beneath the Bolivian Orocline and its relation to subduction processes at the South American continental margin. J Geophys Res 113:B07109. doi:10.1029/2007JB005142
Brasse H, Lezaeta P, Rath V, Schwalenberg K, Soyer W, Haak V (2002) The Bolivian Antiplano Conductivity Anomaly. J Geophys Res 107:2096. doi: 10.1029/2001JB000391
Brown LD, Zhao W, Nelson KD, Hauck M, Alsdorf D, Ross A, Cogan M, Clark M, Liu X, Che J (1996) Bright spots, structure and magmatism in southern Tibet from INDEPTH seismic reflection profiling. Science 274:1688–1690
Burgmann R, Dresen G (2008) Rheology of the lower crust and upper mantle: evidence from rock mechanics, geodesy and field observations. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 36:531–567
Caporali A, Aichorn C, Becker M, Fejes I, Gerhatova L, Ghitau D, Grenerczy G, Hefty J, Krauss S, Medak D, Milev G, Mojzes M, Mulic M, Nardo A, Pesec P, Rus T, Simek J, Sledzinski J, Solaric M, Stangl G, Vespe F, Virag G, Vodopivec F, Zablotskyi F (2008) Geokinematics of Central Europe: new insights from the CERGOP-2/environment project. J Geodyn 45:246–256
Chen L, Booker JR, Jones AG, Wu N, Unsworth MJ, Wei W, Tan H (1996) Electrically conductivity crust in Southern Tibet from INDEPTH magnetotelluric surveying. Science 274:1694–1696
Clark MK, Bilham R (2008) Miocene rise of the Shillong Plateau and the beginning of the end for the Eastern Himalaya. Earth Planet Sci Lett 269:337–351
Clark MK, Royden LH (2000) Topographic ooze: building the eastern margin of Tibet by lower crustal flow. Geology 28:703–706
Clark MK, Bush JWM, Royden LH (2005) Dynamic topography produced by lower crustal flow against rheological strength heterogeneities ordering the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys J Int 162:575–590
Coleman M, Hodges K (1995) Evidence for Tibetan Plateau uplift before 14 Myr ago from a new minimum age for east-west extension. Nature 374:49–52
Coney P, Jones DL, Monger J (1980) Cordilleran suspect terranes. Nature 288:329–333
Cook KL, Royden LH (2008) The role of crustal strength variations in shaping orogenic plateaus, with application to Tibet. J Geophys Res 113:B08407. doi:10.1029/2007JB005457
Copley A, McKenzie DP (2007) Models of crustal flow in the India-Asia collision zone. Geophys J Int 169:683–698
Coward M, Dietrich D (1989) Alpine tectonics—an overview. In: Coward MP, Dietrich D, Park RG (eds) Alpine tectonics, Geological Society Special Publication No. 45, pp 1–29
Cowgill E, Gold RD, Chen X, Wang XF, Arrowsmith JR, Southon J (2009) Low quaternary slip rates along the Altyn Tagh fault, northwestern Tibet. Geology 37:647–650
Daignieres M, De Cabissole B, Gallart J, Hirn A, Surifiach E, Torne M (1989) ECORS Pyrenees team, geophysical constraints on the deep structure along the ECORS Pyrenees line. Tectonics 8:1051–1058
Dewey JF, Burke KA (1973) Tibetan, Variscan and Precambrian basement reactivation: products of continental collision. J Geophysics 81:683–692
Dewey JF, Hempton MR, Kidd WSF, Saroglu F, Sengor AMC (1986) Shortening of continental lithosphere: the neotectonics of eastern Anatolia: a young collision zone. In: Coward MP, Ries AC (eds) Collision Tectonics, Geological Society Special Publication, vol. 19, pp 3–36
Eaton DW, Darbyshire F, Evans RL, Grutter H, Jones AG, Yuan X (2009) The elusive lithosphere-astenosphere boundary (LAB) beneath cratons. Lithos 109:1–22
Edmond JM (1992) Himalayan tectonics, weathering processes and the strontium isotope record in marine limestones. Science 258:1594–1597
Edwards MA, Grasemann B (2009) Mediterranean snapshots of accelerated slab retreat: subduction instability in stalled continental collision. In: van Hinsbergen DJJ, Edwards MA, Govers R (eds) Collision and collapse at the Africa-Arabia-Eurasia subduction zone, The Geological Society, London, Special Publication, 311: pp 155–192
Elger K, Oncken O, Glodny J (2005) Plateau-style accumulation of deformation: southern Altiplano. Tectonics 24:TC4020. doi:10.1029/2004TC001675
England P, Molnar P (1997) Active deformation of Asia: from kinematics to dynamics. Science 278:647–650
Francheteau J, Jaupart C, Jie SX, Kang WH, Lee DL, Bai JC, Wei HP, Deng HY (1984) High heat flow in Southern Tibet. Nature 307:32–36
Froidevaux C, Ricard Y (1987) Tectonic evolution of high plateaus. Tectonophysics 134:227–238
Gaillard F, Scaillet B, Pichavant M (2004) Evidence for present-day leucogranite pluton growth in Tibet. Geology 32:801–804
Glover P, Ádám A (2008) Correlation between crustal high conductivity zones and seismic activity and the role of carbon during shear deformation. J Geophys Res 113:B12210. doi:101029/2008JB005804
Glover PWJ, Pous J, Queralt P, Munoz JA, Liesa M, Hole MJ (2000) Integrated two-dimensional lithospheric conductivity modelling in the Pyrenees using field scale and laboratory measurements. Earth Planet Sci Lett 178:59–72
Gok R, Pasyanos ME, Zor E (2007) Lithospheric structure of the continent-continent collision zone: eastern Turkey. Geophys J Int 169:1079–1088
Gokarn SG, Gupta G, Rao CK, Selvaraj C (2002a) Electrical structure across the Indus Tsangpo suture and Shyok suture zones in Northwest Himalaya using magnetotelluric studies. Geophys Res Lett 29:1–4
Gokarn SG, Rao CK, Gupta G (2002b) Crustal structure in the Siwalik Himalayas using magnetotelluric studies. Earth Planets Space 54:19–30
Gokarn SG, Gupta G, Walia D, Sanabam SS, Hazarika N (2008) Deep geoelectric structure over the lower Brahmaputra Valley and Shillong Plateau, NE India using magnetotellurics. Geophys J Int 173:92–104
Harinarayana T, Azeez K, Naganjaneyulu K, Manoj C, Veeraswamy M, Murthy DN, Prabhakar S, Rao E (2004) Magnetotelluric studies in Puga valley geothermal field, NW Himalaya, Jammu and Kashmir, India. J Volcanol Geothermal Res 138(3–4):405–424
Hirn A, Lepine JC, Jobert G, Sapin M, Wittlinger G, Xu Z, Gao E, Wang X, Teng J, Xiong S, Pandey MR, Tatter JM (1984) Crustal structure and variability of the Himalaya border of Tibet. Nature 307:23–25
Hjelt SE, Korja T, Kozlovskaya E, Lahti I, Yliniemi J, BEAR and SVEKALAPKO Seismic Tomography Working Groups (2006) Electrical conductivity and seismic velocity structures of the lithosphere beneath the Fennoscandian Shield, 541–559. In: Gee DG, Stephenson RA (eds) 2006. European lithosphere dynamics. Geological Society, London, Memoirs, 32. The Geological Society of London
Holness MB (1992) Equilibrium dihedral angles in the system quartz-CO2–H2O-NaCl at 800°C and 1–15 k bar: the effects of pressure and fluid composition on the permeability of quartzites. Earth Planet Sci Lett 114:171–184
Holness MB (1993) Temperature and pressure dependence of quartz-aqueous fluid dihedral angles: the control of adsorbed H2O on the permeability of quartzites. Earth Planet Sci Lett 117:363–377
Hyndman RD, Shearer PM (1989) Water in the lower continental crust; modelling magnetotelluric and seismic reflection results. Geophys J R Astron Soc Can 98:343–365
Israil M, Tyagi DK, Gupta PK, Niwas S (2008) Magnetotelluric investigations for imaging electrical structure of Garwhal Himalayan corridor, Uttarakhand, India. J Earth Syst Sci 117:189–200
Jamieson R, Beaumont C (1989) Deformation and metamorphism in convergent orogens: a model for uplift and exhumation of metamorphic terranes. In: Daly JS, Cliff RA, Yardlet BWD (eds) Evolution of metamorphic belts, Special Publication 43, 117–129, Geological Society of London
Jin S, Ye G, Wei WB, Deng M, Unsworth MJ (2006) The electrical structure and fault feature of crust of south-eastern Tibetan Plateau-the result of magnetotelluric prospecting on profile from Xiachayu-Changdu. Earth Sci Front (in Chinese) 13(5):408–415
Johnson MRW (2002) Shortening budgets and the role of continental subduction during the India-Asia collision. Earth Sci Rev 59:101–123
Jones AG (1999) Imaging the continental upper mantle using electromagnetic methods. Lithos 48:57–80
Jones AG, Ledo J, Ferguson IJ (2005) Electromagnetic images of the trans-Hudson orogen: the North American Central Plains anomaly revealed. Can J Earth Sci 42:457–478
Keskin M (2007) Eastern Anatolia: a hot spot in a collision zone without a mantle plume. In: Foulger GR, Jurdy D, (eds) The origins of melting Anomalies: plumes, plates, and planetary processes (P4 book), Geological Society of America Special Paper, 430
Kind R, Yuan X, Saul J, Nelson KD, Sobolev SV, Mechie J, Zhao W, Kosarev G, Ni J, Achauer A, Jiang M (2002) Seismic images of crust and upper mantle beneath Tibet L evidence for Eurasian plate subduction. Science 298:1219–1221
Klemperer SL (2006) Crustal flow in Tibet: geophysical evidence for the physical state of Tibetan lithosphere, and inferred patterns of active flow. In: Law RD, Searle MP, Godin L (eds) Channel flow, ductile extrusion and exhumation in continental collision zones, Geological Society, London, Special Publications, 268: pp 39–70
Kohn MJ (2008) P-T-t data from central Nepal support critical taper and repudiate large-scale channel flow of the greater Himalayan sequence. GSA Bull 120:259–273
Kosarev G, Kind R, Sobelev SV, Yuan X, Hanka W, Oreshin O (1999) Seismic evidence for a detached Indian lithospheric mantle beneath Tibet. Science 283:1306–1309
Ledo J, Ayala C, Pous J, Queralt P, Marcuello A, Munoz JA (2000) New geophysical constraints on the deep structure of the Pyrenees. Geophys Res Lett 27:1037–1040
Leech ML (2008) Does the Karakoram fault interrupt mid-crustal channel flow in the western Himalaya? Earth Planet Sci 276:314–322
Leech ML, Singh S, Jain AK, Klemperer SL, Manickavasagam RM (2005) The onset of India–Asia continental collision: early, steep subduction required by the timing of UHP metamorphism in the western Himalaya. Earth Planet Sci Lett 234:83–97
Lemmonier C, Marquis G, Perrier F, Avouac JP, Chitrakar G, Kafle B, Sapkota S, Gautam U, Tiwari D, Bano M (1999) Electrical structure of the Himalaya of Central Nepal: high conductivity around the mid-crustal ramp along the MHT. Geophys Res Lett 26:3261–3264
Li S, Unsworth MJ, Booker JR, Wei W, Tan H, Jones AG (2003) Partial melt or aqueous fluid in the mid-crust of Southern Tibet? Constraints from INDEPTH magnetotelluric data. Geophys J Int 153:289–304
Losito G, Schnegg PA, Lambelet C, Viti C, Trova A (2001) Microscopic scale conductivity as explanation of magnetotelluric results from the Alps of Western Switzerland. Geophys J Int 147:602–609
Ma XB, Kong XR, Liu HB, Yan YL (2005) The electrical structure of northeastern Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Chinese J Geophys 48(3):689–697
Makovsky Y, Klemperer SL (1999) Measuring the seismic properties of Tibetan bright spots: evidence for free aqueous fluids in the Tibetan middle crust. J Geophys Res 104:10795–10825
Mazzotti S, Hyndman RD (2002) Yakutat collision and strain transfer across the northern Canadian Cordillera. Geology 30:495–498
McKenzie DP (1972) Active tectonics of the Mediterranean region. Geophys J R Astron Soc 30:109–185
Mechie J, Sobolev SV, Ratschbacher L, Babeyko A, Bock G, Jones AG, Nelson KD, Solon K, Brown LD, Zhao W (2004) Precise temperature estimation in the Tibetan crust from seismic detection of the α-β quartz transition. Geology 32:601–604
Meriaux AS, Ryerson FJ, Tapponier P, Van der Woerd J, Finkel RC, Xu X, Xu Z, Caffee MW (2003) Rapid slip along the central Altyn Tagh Fault: morphological evidence from Cherchen He and Sulamu Tagh. J Geophys Res 109:B06401. doi:10.1029/2003JB002558
Meyer B, Tapponnier P, Bourjot L, Metivier F, Gaudemer Y, Peltzer G, Shunmin G, Zhitai C (1998) Crustal thickening in Gansu-Qinghai, lithospheric mantle subduction, and oblique, strike-slip controlled growth of the Tibet Plateau. Geophys J Int 135:1–47
Molnar P, England P, Martinod J (1993) Mantle dynamics, uplift of the Tibetan Plateau and the Indian Monsoon. Rev Geophys 31:357–396
Murphy MA, Yin A, Harrison TM, Durr SB, Chen Z, Ryerson FJ, Kidd WSF, Wang X, Zhou X (1997) Did the Indo-Asian collision alone create the Tibetan Plateau. Geology 25:719–722
Nelson KD, Zhao W, Brown LD, Kuo J, Che J, Liu X, Klemperer SL, Makovsky Y, Meissner R, Mechie J, Kind R, Wenzel F, Ni J, Nabelek J, Chen L, Tan H, Wei W, Jones AG, Booker J, Unsworth MJ, Kidd WSF, Hauck M, Alsdorf D, Ross A, Cogan M, Wu C, Sandvol E, Edwards M (1996) Partially molten middle crust beneath southern Tibet: synthesis of project INDEPTH results. Science 274:1684–1687
Ni J, Barazangi M (1983) High-frequency seismic wave propagation beneath the Indian Shield, Himalayan Arc, Tibetan Plateau and surrounding regions: high uppermost mantle velocities and efficient Sn propagation beneath Tibet. Geophys J R Astr Soc 72:665–689
Park SK, Mackie RL (2000) Resistive (dry?) lower crust in an active orogen, Nanga Parpat, northern Pakistan. Tectonophysics 316:359–380
Patro PK, Harinarayana T (2009) Deep geoelectric structure of the Sikkim Himalayas (NE India) using magnetotelluric studies. Phys Earth Planet 173:171–176
Pearce JA, Bender JF, De Long SE, Kidd WSF, Low PJ, Guner Y, Saroglu F, Yilmaz Y, Moorbath S, Mitchell JG (1990) Genesis of collision volcanism in Eastern Anatolia, Turkey. J Volcanol Geotherm Res 44:189–229
Pham VN, Boyer D, Therme P, Xue C, Li L, Guo Y (1986) Partial melting zones in the crust in Southern Tibet from magnetotelluric results. Nature 319:310–314
Philip H, Cisternas A, Gvishiani A, Gorshkov A (1989) The Caucasus: an actual example of the initial stages of continental collision. Tectonophysics 161:1–21
Pous J, Ledo J, Marcuello A, Dagnieres M (1995) Electrical resistivity model of the crust and upper mantle from a magnetotelluric survey through the central Pyrenees. Geophys J Int 121:750–762
Priestley K, Debayle E, McKenzie D, Pilidou S (2006) Upper mantle structure eastern Asia from multimode surface waveform tomography. J Geophys Res 111:B10304. doi:10.1029/2005JB004082
Quade J, Roe L, DeCelles P, Ojha T (1997) The late Neogene 87Sr/86Sr record of lowland Himalayan rivers. Science 276:1828–1831
Rai SS, Priestley K, Gaur VK, Mitra S, Singh MP, Searle M (2006) Configuration of Indian Moho beneath the NW Himalaya and Ladakh. Geophys Res Lett 33:L15308. doi:10.1029/2006GL026076
Reilinger R, McClusky S, Vernant P, Lawrence S, Ergintav S, Cakmak R, Ozener H, Kadirov F, Guliev I, Stepanyan R, Nadariya M, Hahubia G, Mahmoud S, Sakr K, ArRajehi A, Paradissis D, Al-Aydrus A, Prilepin M, Guseva T, Evren E, Demitrotsa A, Filikov SV, Gomez F, Al-Ghazzi R, Karam G (2006) GPS constraints on continental deformation in the Africa-Arabia-Eurasia continental collision zone and implications for the dynamics of plate interactions. J Geophys Res 111:B05411. doi:10.1029/2005JB004051
Renner J, Evans B, Hirth G (2000) On the rheologically critical melt fraction. Earth Planet Sci Lett 181:585–594
Replumaz A, Tapponnier P (2003) Reconstruction of the deformed collision zone between India and Asia by backward motion of lithospheric blocks. J Geophys Res 108(B6):2285. doi:10.1029/2001JB000661
Roberts JJ, Tyburczy JA (1999) Partial-melt electrical conductivity: influence of melt composition. J Geophys Res 104:7055–7065
Robl J, Stuwe K, Hergarten S, Evans L (2008) Extension during convergence in the Eastern Alps: the influence of strike-slip faults. Geology 36:963–966
Rosenberg CL, Handy MR (2005) Experimental deformation of partially melted granite revisited: implications for the continental crust. J Metamorphic geol 555:1–9
Rotstein Y, Kafka AL (1982) Seismotectonics of the southern boundary of Anatolia, Eastern Mediterranean region: subduction, collision and arc jumping. J Geophys Res 87:7694–7706
Rowley DB, Currie BS (2006) Paleo-altimetry of the late Eocene to Miocene Lunpola Basin, central Tibet. Nature 439:677–681
Royden LH, Burchfiel BC, King RW, Wang E, Chen Z, Shen F, Liu Y (1997) Surface deformation and lower crustal flow in eastern Tibet. Science 276:788–790
Sandvol E, Turkelli N, Barazangi M (2003) The Eastern Turkey seismic experiment: the study of a young continent-continent collision. Geophys Res Lett 30(24):8038. doi:10.1029/2003GL018912
Schmid SM, Pfiffner OA, Froitzheim N, Schonborn G, Kissling E (1996) Geophysical-geological transect and tectonic evolution of the Swiss-Italian Alps. Tectonics 15:1036–1064
Schwalenberg K, Rath V, Haak V (2002) Sensitivity studies applied to a two-dimensional resistivity model from the Central Andes. Geophys J Int 150:673–686
Schwarz G, Kruger D (1997) Resistivity cross section through the southern Central Andes as inferred from magnetotelluric and geomagnetic depth soundings. J Geophys Res 102:11957–11978
Selverstone J (2005) Are the Alps collapsing? Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 33:113–132
Sengor AMC, Kidd WSF (1979) The post-collisional tectonics of the Turkish–Iranian Plateau and a comparison with Tibet. Tectonophysics 55:361–376
Shen ZK, Lü J, Wang M, Bürgmann R (2005) Contemporary crustal deformation around the southeast borderland of the Tibetan Plateau. J Geophys Res 110:B11409. doi:10.1029/2004JB003421
Shin YH, Xu H, Braitenberg C, Fang J, Wang Y (2007) Moho undulations beneath Tibet from GRACE-integrated gravity data. Geophys J Int 170:971–985
Sobolev SV, Babeyko AY (2005) What drives orogeny in the Andes. Geology 33:617–620
Solon K, Jones AG, Nelson KD, Unsworth MJ, Wei W, Tan H, Jin S, Deng M, Booker JR, Li S, Bedrosian PA (2005) Structure of the crust in the vicinity of the Banggong-Nujiang suture central Tibet from INDEPTH magnetotelluric data. J Geophys Res 110:B10102. doi:10.1029/2003JB002405
Spratt JE, Jones AG, Nelson KD, Unsworth MJ, The INDEPTH MT Team (2005) Crustal structure of the India-Asia collision zone, southern Tibet, from INDEPTH MT investigations. Physics Earth Planet Inter 150:227–237
Sun J, Jin G, Bai D, Wang L (2003) Sounding of electrical structure of the crust and upper mantle along the eastern border of Qinghai-Tibet Plateau and its tectonic significance. Sci China 46:243–253
Tapponnier P, Peltzer G, Le Dain AY, Armijo R (1982) Propagating extrusion tectonics in Asia: new insights from simple experiments with plasticine. Geology 10:610–616
Tapponnier P, Xu Z, Roger F, Meyer B, Arnaud N, Wittlinger G, Yang J (2001) Oblique stepwise rise and growth of the Tibetan Plateau. Science 294:1671–1677
Ten Grotenhuis SM, Drury MR, Spiers CJ, Peach CJ (2005) Melt distribution in olivine rocks based on electrical conductivity measurements. J Geophys Res 110:B12201. doi:10.1029/2004JB003462
Thompson SC, Weldon RJ, Rubin CM, Abdrakhmatov K, Molnar P, Berger GW (2002) Late quaternary slip rates across the central Tien Shan, Kyrgyzstan, central Asia. J Geophys Res 107(B9):2203. doi:10.1029/2001JB000596
Tilmann F, Ni J, INDEPTH III Seismic Team (2003) Seismic imaging of the downwelling Indian lithosphere beneath central Tibet. Science 300:1424–1427
Tullis J, Yund R, Farver J (1996) Deformation enhanced fluid distribution in feldspar aggregates and implications for ductile shear zones. Geology 24:63–66
Türkoğlu E, Unsworth M, Çağlar İ, Tuncer V, Avşar Ü (2008) Lithospheric structure of the Arabia–Eurasia collision zone in Eastern Anatolia from magnetotelluric exploration: evidence for widespread weakening by fluids. Geology 36:619–622
Unsworth MJ, Wei W, Jones AG, Li S, Bedrosian PA, Booker JR, Jin S, Deng M (2004) Crustal and upper mantle structure of Northern Tibet imaged with magnetotelluric data. J Geophys Res 109:B02403. doi:10.1029/2002JB002305
Unsworth MJ, Jones AG, Wei W, Marquis G, Gokarn S, Spratt J (2005) Crustal rheology of the Himalaya and Southern Tibet inferred from magnetotelluric data. Nature 438:78–81. doi:10.1038/nature04154
Wang C, Zhao X, Liu Z, Lippert PC, Graham SA, Coe RS, Yi H, Zhu L, Liu S, Li Y (2008) Constraints on the early uplift history of the Tibetan Plateau. Proc Natl Acad Sci 105:4987–4992
Warren CJ, Beaumont C, Jamieson RA (2008a) Deep subduction and rapid exhumation: the role of crustal strength and strain weakening in continental subduction and ultra-high pressure rock exhumation. Tectonics 27:TC6002. doi:10.1029/2008TC002292
Warren CJ, Beaumont C, Jamieson RA (2008b) Modelling tectonic styles and ultra-high pressure (UHP) rock exhumation during the transition from ocean subduction to continental subduction. Earth Planet Sci Lett 267:129–145
Watson EB, Brenan JM (1987) Fluids in the lithosphere, 1. Experimentally-determined wetting characteristics of C02 and H2O fluids and their implications for fluid transport, host-rock physical properties, and fluid inclusion formation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 85:497–515
Wegener A (1912) Die Entstehung der Kontinente. Geologische Rundschau 3:267–292
Wei W, Unsworth MJ, Jones AG, Booker JR, Tan H, Nelson KD, Chen L, Li S, Solon K, Bedrosian PA, Jin S, Deng M, Ledo J, Kay D, Roberts B (2001) Detection of widespread fluids in the Tibetan crust by magnetotelluric studies. Science 292:716–718
Whipple KX (2009) The influence of climate on the tectonic evolution of mountain belts. Nat Geosci 2:97–104
Xu L, Rondenay S, van der Hilst RD (2007) Structure of the crust beneath the southeastern Tibetan Plateau from teleseismic receiver functions. Physics Earth Planet Inter 165:176–193
Yao H, Beghein C, van der Hilst RD (2008) Surface wave array tomography in SE Tibet from ambient seismic noise and two-station analysis—II. Crustal and upper-mantle structure. Geophys J Int 173:205–219
Ye G, Jin S, Wei W, Unsworth MJ (2007) Research of the conductive structure of crust and the upper mantle beneath the South-Central Tibetan Plateau. J China Univ Geosci 18(4):334–343
Yin A, Harrison TM (2000) Geologic evolution of the Himalayan-Tibetan orogen. Annu Rev Earth Planet Sci 28:211–280
Yuan X, Li L, Yin G, Zhu J, Lu G, Feng Y, Lin X, Pham VN, Boyer D, Therme P, Lemouel J (1985) A magnetotelluric study in Luozha-Yangbajing area, (in Chinese). Acta Geol Sinica 1:25–31
Zeitler PK, Meltzer AS, Koons PO, Craw D, Hallet B, Chamberlain CP, Kidd WSF, Park SK, Seeber L, Bishop M, Shroder J (2001) Erosion, himalayan geodynamics, and the geomorphology of metamorphism. GSA Today January 4–10
Zhang S, Wei S, Wang J (1996) Magnetotelluric sounding in the Qiangtang basin of Xizang (Tibet). J China Univ Geosci 21:198–202
Zhang PZ, Shen Z, Wang M, Gan W, Burgmann R, Molnar P, Wang Q, Niu Z, Sun J, Wu J, Hanrong S, Xinzhao Y (2004) Continuous deformation of the Tibetan Plateau from global positioning system data. Geology 32:809–812
Zhao W, Nelson KD, INDEPTH Team (1993) Deep seismic reflection evidence for continental underthrusting beneath southern Tibet. Nature 366:557–559
Zhao G, Chen X, Wang L, Wang J, Tang J, Wan Z, Zhang J, Zhan Y, Xiao Q (2008) Evidence of crustal channel flow in the eastern margin of Tibetan Plateau from MT measurements. Chinese Sci Bull 53:1887–1893
Zor E, Gürbüz C, Türkelli N, Sandvol E, Seber D, Barazangi M (2003) The crustal structure of the East Anatolian Plateau from receiver functions. Geophys Res Lett 30:8044
Acknowledgments
This manuscript has benefited greatly from reviews by Henri Brasse, Ted Bertrand, Mike Edwards and two anonymous reviewers. I thank the editors Toivo Korja and Zhao Guoze for their insightful comments and patience. Dennis Rippe, Ersan Turkoglu and Henri Brasse contributed figures. Finally I thank the many people who have sent me reprints, MT data and models from their studies. This is a rapidly advancing field and I am already aware of new MT studies following the 2008 Sichuan earthquake that have not been included in this review.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Unsworth, M. Magnetotelluric Studies of Active Continent–Continent Collisions. Surv Geophys 31, 137–161 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-009-9086-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10712-009-9086-y