Abstract
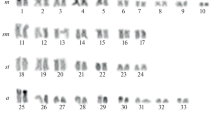
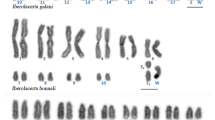
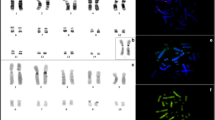
Classical and molecular cytogenetic (18S rDNA, telomeric sequence, and LINE-1 retrotransposon probes) studies were carried out to contribute to an understanding of the organization of repeated DNA elements in the Amazon River dolphin (boto, Inia geoffrensis). Twenty-seven specimens were examined, each presenting 2n = 44 chromosomes, the karyotype formula 12m + 14sm + 6st + 10t + XX/XY, and fundamental number (FN) = 74. C-positive heterochromatin was observed in terminal and interstitial positions, with the occurrence of polymorphism. Interstitial telomeric sequences were not observed. The nucleolar organizer region (NOR) was located at a single site on a smallest autosomal pair. LINE-1 was preferentially distributed in the euchromatin regions, with the greatest accumulation on the X chromosome. Although the karyotype structure in cetaceans is considered to be conserved, the boto karyotype demonstrated significant variations in its formula, heterochromatin distribution, and the location of the NOR compared to other cetacean species. These results contribute to knowledge of the chromosome organization in boto and to a better understanding of karyoevolution in cetaceans.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acosta MJ, Marchal JA, Fernández-Espartero CH, Bullejos M, Sánchez A (2008) Retroelements (LINEs and SINEs) in vole genomes: Differential distribution in the constitutive heterochromatin. Chromosome Res 16:949–959. doi:10.1007/s10577-008-1253-3
Árnason U (1974) Comparative chromosome studies in Cetacea. Hereditas 77:1–36. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1974.tb01351.x
Árnason U (1980) C-and G-banded karyotypes of three delphinids: Stenella clymene, Lagenorhynchys albirostris and Phocoena phocoena. Hereditas 92:179–187. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1980.tb01693.x
Árnason U (1981a) Localization of NORs in cetacean karyotypes. Hereditas 95:269–275. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1981.tb01417.x
Árnason U (1981b) Banding studies on the gray and sperm whale karyotypes. Hereditas 95:277–281. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1981.tb01418.x
Árnason U (2006) Order Cetartiodactyla: Cetacea. In: O’Brien SJ, Menninger JC, Nash WG (eds) Atlas of mammalian chromosomes. Hoboken Wiley-Liss, Danvers, pp 541–546
Árnason U, Benirschke K (1973) Karyotypes and idiograms of sperm and pygmy sperm whales. Hereditas 75:7–73. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1973.tb01143.x
Árnason U, Purdom IF, Jones KW (1978) Conservation and chromosomal localization of DNA satellites in balenopterid whales. Chromosoma 66:141–159. doi:10.1007/BF00295136
Bernard C, Allshire RC (2002) Centromeres become unstuck without heterochromatin. Trends Cell Biol 12:419–424. doi:10.1016/S0962-8924(02)02344-9
Best RC, da Silva VMF (1993) Inia geoffrensis. Mammalian Species 426:1–8
Bielec PE, Riggs PK, Womack JE, Busbee DL (1997) A high resolution GBG-banded karyotype of the Atlantic bottlenose dolphin, Tursiops truncatus: generation of an ideogram, and NOR localization by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Cytogenet Cell Genetic 78:6–11. doi:10.1159/000134615
Bielec PE, Gallagher DS, Womack JE, Busbee DL (1998) Homologies between human and dolphin chromosomes detected by heterologous chromosome painting. Cytogenet Cell Genetic 81:18–26. doi:10.1159/000015002
Boyle AL, Ballard SG, Ward DC (1990) Differential distribution of long and short interspersed element sequences in the mouse genome: chromosome karyotyping by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:7757–7761. doi:10.1073/pnas.87.19.7757
Cabral-de-Mello DC, Moura RC, Martins C (2010) Chromosomal mapping of repetitive DNAs in the beetle Dichotomius geminatus provides the first evidence for an association of 5S rRNA and histone H3 genes in insects, and repetitive DNA similarity between the B chromosome and A complement. Heredity 104:393–400. doi:10.1038/hdy.2009.12
Cassens I, Vicario S, Waddell VG, Balchowsky H, Belle DV et al (2000) Independent adaptation to riverine habitats allowed survival of ancient cetacean lineages. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:11343–11347. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.21.11343
Castiglia R, Garagna S, Merico V, Oguge N, Corti M (2006) Cytogenetics of a new cytotype of African Mus (subgenus Nannomys) minutoides (Rodentia, Muridae) from Kenya: C- and G- banding and distribution of (TTAGGG)n telomeric sequences. Chromosome Res 14:587–594. doi:10.1007/s10577-006-1054-5
Charlesworth B, Sniedowski P, Stephan W (1994) The evolutionary dynamics of repetitive DNA in eukaryotes. Nature 371:215–220. doi:10.1038/371215a0
Chow JC, Ciaudo C, Fazzari MJ, Mise N, Servant N et al (2010) LINE-1 Activity in facultative heterochromatin formation during X chromosome Inactivation. Cell 141:956–969. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.04.042
CRES (Center for Reproduction of Endangered Species) (2006) Tursiops truncates. In: O’Brien SJ, Menninger JC, Nash WG (eds) Atlas of mammalian chromosomes. Hoboken Wiley-Liss, Danvers, p 552
Duffield DA, Spence MA, Paquin C (1978) Evaluation of metaphase association patterns for acrocentric chromosomes in the order Cetacea. Cytologia 43:541–549
Duffield DA, Chamberin-Lea J, Sweenwy JC, Odell DK, Asper ED et al (1991) Use of corneal cell culture for R-Band chromosome studies on stranded cetaceans. NOAA Tech Rep NMFS 98:91–100
Esnault C, Maestre J, Heidmann T (2000) Human LINE retrotransposons generate processed pseudogenes. Nature 24:363–367. doi:10.1038/74184
Fitch DHA, Bailey WJ, Tagle DA, Goodman M, Sieut L et al (1991) Duplication of the y-globin gene mediated by L1 long interspersed repetitive elements in an early ancestor of simian primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:7396–7400
Graham T, Boissinot S (2005) The genomic distribution of L1 elements: the role of insertion bias and natural selection. J Biomed Biotechnol 2006:1–5. doi:10.1155/JBB/2006/75327
Gross MC, Schneider CH, Valente GT, Martins C, Feldberg E (2010) Variability of 18S rDNA locus among Symphysodon fishes: chromosomal rearrangements. J Fish Biol 76:1117–1127. doi:10.1111/j.1095-8649.2010.02550.x
Hashimoto DT, Porto-Foresti F (2010) Chromosome polymorphism of heterochromatin and nucleolar regions in two populations of the fish Astyanax bockmanni (Teleostei: Characiformes) Neotrop Ichthyol 8(4):861–866 http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/S1679-62252010000400016
Heinzelmann L, Telles PCC, Danilewicz D, Chies JAB, Andrades-Miranda J (2008) The karyotype of franciscana dolphin (Pontoporia blainvillei). J Hered 100:119–122. doi:10.1093/jhered/esn064
Howell WM, Black DA (1980) Controlled silver-staining of nucleolus organizer regions with a protective colloidal developer: a 1-step method. Experientia 36:1014–1015. doi:10.1007/BF01953855
Hsu TC, Benirschke K (1977) An Atlas of mammalian chromosomes. Springer, New York
Hsu TC, Spirito SE, Pardue ML (1975) Distribution of 18S + 28S ribosomal genes in mammalian genomes. Chromosoma 53:25–36. doi:10.1007/BF00329388
Huang X, Hu J, Hu X, Zhang C et al (2007) Cytogenetic characterization of the bay scallop, Argopecten irradians irradians, by multiple staining techniques and fluorescence in situ hybridization. Genes Genet Syst 82(3):257–263
Ijdo JW, Wells RA, Baldini A, Reeders ST (1991) Improved telomere detection using a telomere repeat probe (TTAGGG)n generated by PCR. Nucleic Acids Res 19:4780
Imai HT (1991) Mutability of constitutive heterochromatin (C-bands) during eukaryotic chromosomal evolution and their cytological meaning. Jpn J Genet 66:635–661
IUCN (2012) IUCN (International Union for Conservation of Nature) red list of threatened species. Version 2012.1. www.iucnredlist.org. Accessed 20 August 2012
Jarrell GH (1979) Karyotype of the bowhead whale (Balaena mysticetus). J Mammal 60:607–610
Kapitonov VV, Holmquist GP, Jurka J (1998) L1 repeat is a basic unit of heterochromatin satellites in Cetaceans. Mol Biol Evol 15:611–612 cgi/content/short/15/5/611
Kulemzina AI, Trifonoy VA, Perlman PL, Rubtsova NV, Volobuey V et al (2009) Cross-species chromosome painting in Cetartiodactyla: reconstructing the karyotype evolution in key phylogenetic lineages. Chromosome Res 17:419–436. doi:10.1007/s10577-009-9032-3
Kulu DD, Veomett I, Sparkes RS (1971) Cytogenetic comparison of four species of cetaceans. J Mammal 52:828–832
Lee SH, Cho SY, Shannon MF, Fan J, Ragasamy D (2010) The impact of CpG island on defining transcriptional activation of the mouse L1 retrotransposable elements. PLoS ONE 5(6):e11353. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011353
Levan A, Fredga K, Sandberg A (1964) Nomenclature for centromeric position on chromosomes. Hereditas 52:201–220. doi:10.1111/j.1601-5223.1964.tb01953.x
Long EO, Dawid IB (1980) Repeated genes in eukaryotes. Ann Rev Biochem 49:727–764. doi:10.1146/annurev.bi.49.070180.003455
Lyon MF (2000) LINE-1 elements and X chromosome inactivation: a function for “junk” DNA? Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 97:6248–6249. doi:10.1073/pnas.97.12.6248
Martins C, Cabral-de-Mello DC, Targino GV, Mazzuchelli J, Oliveira SG (2011) Cytogenetic mapping and contribution to the knowledge of animal genomes. In: Urbano KV (ed) Advances in genetics research, vol 4. Nova Science Publisher, New York, pp 1–82
McEachern MJ, Krauskopf A, Blackburn EH (2000) Telomeres and their control. Annu Rev Genet 34:331–358
McGowen MR, Spaulding M, Gatesy J (2009) Divergence date estimation and a comprehensive molecular tree of extant cetaceans. Mol Phylogenet Evol 53:891–906. doi:10.1016/j.ympev.2009.08.018
McStay B, Grummt I (2008) The epigenetics of rRNA genes: from molecular to chromosome biology. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 24:131–157. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.24.110707.175259
Minrong C, Hanqin L, Zhimei G (1996) The karyotype and the C-band patterns of the Baiji dolphin, Lipotes vexillifer. Acta Hydrobiol Sin 20:138–143. doi:CNKI:SUN:SSWX.0.1996-02-006
Moorhead PS, Nowell PC, Mellinan WJ, Battips DM, Hungerford DA (1960) Chromosome preparations of leukocytes cultured from human peripheral blood. Exp Cell Res 20:613–616. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(60)90138-5
Nguyen TT, Aniskin VM, Gerbault-Seureau M et al (2008) Phylogenetic position of the saola (Pseudoryx nghetinhensis) inferred from cytogenetic analysis of eleven species of Bovidae. Cytogenet Genome Res 122:41–54. doi:10.1159/000151315
Nigumann P, Redik K, Mätlik K, Speek M (2002) Many human genes are transcribed from the antisense promoter of L1 retrotransposon. Genomics 79(5):628–634. doi:10.1006/geno.2002.6758
Pause KC, Bonde RK, Mcguire PM, Zori RT, Gray BA (2006) G-Banded karyotype and ideogram for the North Atlantic Right Whale (Eubalaena glacialis). J Hered 97:303–306. doi:10.1093/jhered/esj033
Pikaard CS (2000) The epigenetics of nucleolar dominance. Trends Genet 16:495–500. doi:10.1146/annurev.cellbio.24.110707.175259
Pinkel D, Straume T, Gray JW (1986) Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:2934–2938. doi:10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934
Rebuzzini P, Castiglia R, Negardze SG, Mitsainas G, Munclinger P (2009) Quantitative variation of LINE-1 sequences in five species and three subspecies of the subgenus Mus and in five Robertsonian races of Mus musculus domesticus. Chromosome Res 17:65–76. doi:10.1007/s10577-008-9004-z
Rice DW (1998) Marine mammals of the world systematics and distribution. Special publication no. 4 of The society for marine mammalogy. Allan Press, Lawrence
Rubes J, Musilova P, Kopecna O, Kubickova S et al (2012) Comparative molecular cytogenetics in Cetartiodactyla. Cytogenet Genome Res. doi:10.1159/000338932
Sambrook J, Russell DW (2001) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor
Seabright M (1971) A rapid banding technique for human chromosomes. Lancet 11:971–972. doi:10.1016/S0140-6736(71)90287-X
Segal Y, Peissel B, Renieri A, Marchi M, Ballabio A et al (1999) LINE-1 elements at the sites of molecular rearrangements in Alport Syndrome-Diffuse Leiomyomatosis. Am J Hum Genet 64:62–69. doi:10.1086/302213
Sumner AT (1972) A simple technique for demonstrating centromeric heterochromatin. Exp Cell Res 75:304–306. doi:10.1016/0014-4827(72)90558-7
Tarpley RJ, Jarrel GH, George JC, Cubbage J, Stott GG (1995) Male pseudohermaphroditism in the Bowhead Whale, Balaena mysticetus. J Mammal 76:1267–1275
Vianna JA, Bonde RK, Caballero S, Giraldo JP, Lima RP et al (2006) Phylogeography, phylogeny and hybridization in trichechid sirenians: implications for manatee conservation. Mol Ecol 15:433–447. doi:10.1111/j.1365-294X.2005.02771.x
Watanabe H, Tateno H, Kusaksabe H, Matsuoka T, Kamiguchi Y et al (2007) Fertibility and chromosomal integrity of frozen-thawed Bryde’s whale (Baleonoptera edeni) spermatozoa intracytoplasmically injected into mouse oocytes. Zygote 15:9–14. doi:10.1017/S0967199406003923
Waters PD, Dobigny ATP, Robison TJ (2004) LINE-1 distribution in Afrotheria and Xenarthra: implications for understanding the evolution of LINE-1 in eutherian genomes. Chromosoma 113:137–144. doi:10.1007/s00412-004-0301-9
Widegren B, Árnason U, Akusjarvi G (1985) Characteristics of a conserved 1,579 bp highy repetitive component in the killer whale, Orcinus orca. Mol Biol Evol 2:411–419
Wise JP, Wise SS, Kraus S, Shaffiey F, Grau M et al (2008) Hexavalent chromium is cytotoxic and genotoxic to the North Atlantic right whale (Eubalaena glacialis) lung and testes fibroblasts. Mutat Res 650:30–38. doi:10.1016/j.mrgentox.2007.09.00
Zurita F, Jimenez R, Guardia RD, Burgos M (1999) The relative rDNA content of a NOR determines its level of expression and its probability of becoming active. A sequential silver staining and in situ hybridization study. Chromosome Res 7:563–570. doi:10.1023/A:100929771397
Acknowledgments
The authors thank C.H. Schneider, M.C. Gross, M.L. Terencio and N.D.M. Carvalho for laboratory assistance, suggestions and N.A.S. Carmo for help with field work. This study was part of Projeto Boto, a cooperative agreement between the National Amazon Research Institute–INPA/MCT and the Mamirauá Sustainable Development Institute–MSDI–OS/MCT. The work was made possible by support from the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Level Personnel (CAPES) through a scholarship awarded to HLB; Center for Studies of Adaptation to Environmental Changes in the Amazon (ADAPTA): The State of Amazonas Research Foundation (FAPEAM), National Council for Scientific and Technological Development (CNPq) of the Brazilian Government 573976/2008-2; National Amazon Research Institute (INPA–PPI-PRJ 12.16), Projeto Boto; and Petrobras Ambiental (PRJ 12.86).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bonifácio, H.L., da Silva, V.M.F., Martin, A.R. et al. Molecular cytogenetic characterization of the Amazon River dolphin Inia geoffrensis . Genetica 140, 307–315 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-012-9680-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10709-012-9680-7