Abstract
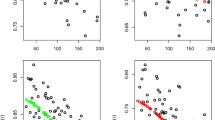
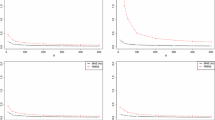
Parsimonious extreme value copula models with O(d) parameters for d observed variables of extrema are presented. These models utilize the dependence characteristics, including factor and tree structures, assumed on the underlying variables that give rise to the data of extremes. For factor structures, a class of parametric models is obtained by taking the extreme value limit of factor copulas with non-zero tail dependence. An alternative model suitable for both factor and tree structures imposes constraints on the parametric Hüsler-Reiss copula to get representations in terms of O(d) other parameters. Dependence properties are discussed. As the full density is often intractable, the method of composite (pairwise) likelihood is used for model inference. Procedures to improve the stability of bivariate density evaluation are also developed. The proposed models are applied to two data examples — one for annual extreme river flows and one for bimonthly extremes of daily stock returns.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aas, K., Czado, C., Frigessi, A., Bakken, H.: Pair-copula constructions of multiple dependence. Insurance: Math. Econ. 44, 182–198 (2009)
Bedford, T., Cooke, R.M.: Probability density decomposition for conditionally dependent random variables modeled by vines. Ann. Math. Artif. Intell. 32, 245–268 (2001)
Bedford, T., Cooke, R.M.: Vines — a new graphical model for dependent random variables. Ann. Stat. 30, 1031–1068 (2002)
Besag, J.: Spatial interaction and the statistical analysis of lattice systems. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 36, 192–236 (1974)
Brechmann, E.C., Czado, C., Aas, K.: Truncated regular vines in high dimensions with application to financial data. Can. J. Stat. 40, 68–85 (2012)
Burr, I.W.: Cumulative frequency functions. Ann. Math. Stat. 13, 215–232 (1942)
Canadian Heritage Rivers System: Fraser River. http://chrs.ca/the-rivers/fraser/. Accessed on August 14, 2016 (2016)
Carlson, M.: A Brief History of the 1987 Stock Market Crash with a Discussion of the Federal Reserve Response. Finance and Economics Discussion Series, Federal Reserve Board of Governors (2007)
Clayton, D.G.: A model for association in bivariate life tables and its application in epidemiological studies of familial tendency in chronic disease incidence. Biometrika 65, 141–151 (1978)
Coles, S.: An Introduction to Statistical Modeling of Extreme Values. Springer, London (2001)
Cook, R.D., Johnson, M.E.: A family of distributions for modelling non-elliptically symmetric multivariate data. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 43, 210–218 (1981)
Cox, D.R., Reid, N.: A note on pseudolikelihood constructed from marginal densities. Biometrika 91, 729–737 (2004)
Dagum, C.: A model of income distribution and the conditions of existence of moments of finite order Proceedings of the 40th Session of the International Statistical Institute, vol. 46, pp 199–205 (1975)
Davison, A.C., Padoan, S.A., Ribatet, M.: Statistical modeling of spatial extremes. Stat. Sci. 27, 161–186 (2012)
Demarta, S., McNeil, A.J.: The t copula and related copulas. Int. Stat. Rev. 73, 111–129 (2005)
Drees, H., Huang, X.: Best attainable rates of convergence for estimators of the stable tail dependence function. J. Multivar. Anal. 64, 25–46 (1998)
Galambos, J.: Order statistics of samples from multivariate distributions. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 70, 674–680 (1975)
Galambos, J. The Asymptotic Theory of Extreme Order Statistics: , 2nd edn. Krieger Publishing Co., Malabar (1987)
Gao, X., Song, P.X.K.: Composite likelihood Bayesian information criteria for model selection in high-dimensional data. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 105, 1531–1540 (2010)
Genton, M.G., Ma, Y., Sang, H.: On the likelihood function of Gaussian max-stable processes. Biometrika 98, 481–488 (2011)
Godambe, V.P.: An optimum property of regular maximum likelihood estimation. Ann. Math. Stat. 31, 1208–1211 (1960)
Gumbel, E.J.: Distributions des valeurs extrêmes en plusieurs dimensions. Publ. de l’Institut de Statistique de l’Université, de Paris 9, 171–173 (1960)
Huang, X.: Statistics of bivariate extremes. PhD thesis, Erasmus University Rotterdam, Tinbergen Institute Research Series 22 (1992)
Huser, R., Davison, A.C.: Composite likelihood estimation for the Brown-Resnick process. Biometrika 100, 511–518 (2013)
Hüsler, J., Reiss, R.D.: Maxima of normal random vectors: Between independence and complete dependence. Stat. Probab. Lett. 7, 283–286 (1989)
Joe, H.: Parametric families of multivariate distributions with given margins. J. Multivar. Anal. 46, 262–282 (1993)
Joe, H.: Dependence Modeling with Copulas. Chapman & Hall, Boca Raton (2014)
Joe, H., Li, H., Nikoloulopoulos, A.K.: Tail dependence functions and vine copulas. J. Multivar. Anal. 101, 252–270 (2010)
Krupskii, P., Joe, H.: Factor copula models for multivariate data. J. Multivar. Anal. 120, 85–101 (2013)
Lindsay, B.G.: Composite likelihood methods. Contemp. Math. 80, 221–239 (1988)
Mardia, K.V.: Multivariate Pareto distributions. Ann. Math. Stat. 33, 1008–1015 (1962)
Nikoloulopoulos, A.K., Joe, H., Li, H.: Extreme value properties of multivariate t copulas. Extremes 12, 129–148 (2009)
Padoan, S.A.: Multivariate extreme models based on underlying skew-t and skew-normal distributions. J. Multivar. Anal. 102, 977–991 (2011)
Padoan, S.A., Ribatet, M., Sisson, S.A.: Likelihood-based inference for max-stable processes. J. Am. Stat. Assoc. 105, 263–277 (2010)
Pickands, J.: Multivariate extreme value distributions Proceedings 43rd Session International Statistical Institute, vol. 2, pp 859–878 (1981)
Ribatet, M.: Spatial extremes: Max-stable processes at work. J de la Socié,té Franċaise de Statistique 154, 156–177 (2013)
Schmidt, R., Stadtmüller, U.: Non-parametric estimation of tail dependence. Scand. J. Stat. 33, 307–335 (2006)
Singh, S.K., Maddala, G.S.: A function for size distribution of incomes. Econometrica 44, 963–970 (1976)
Sklar, A.: Fonctions de répartition à n dimensions et leurs marges. Publications de l’Institut de Statistique de l’Université, de Paris 8, 229–231 (1959)
Smith, R.L.: Max-stable Processes and Spatial Extremes. Unpublished Manuscript (1990)
Smith, R.L.: Measuring risk with extreme value theory. In: Dempster, M.A.H. (ed.) Risk Management: Value at Risk and Beyond, pp 224–246. Cambridge University Press (2002)
Stroud, A., Secrest, D.: Gaussian Quadrature Formulas Prentice-Hall. Englewood Cliffs, NJ (1966)
Takahasi, K.: Note on the multivariate Burr’s distribution. Ann. Inst. Stat. Math. 17, 257–260 (1965)
Tsay, R.S. Analysis of Financial Time Series: , 3rd edn. Wiley, Hoboken (2010)
Varin, C., Vidoni, P.: A note on composite likelihood inference and model selection. Biometrika 92, 519–528 (2005)
Varin, C., Reid, N., Firth, D.: An overview of composite likelihood methods. Stat. Sin. 21, 5–42 (2011)
Zhao, Y., Joe, H.: Composite likelihood estimation in multivariate data analysis. Can. J. Stat. 33, 335–356 (2005)
Acknowledgements
This research has been supported by UBC’s Four Year Doctoral Fellowship and NSERC Discovery Grant 8698. We would like to thank the associate editor and the anonymous referees for their helpful comments, which improved the presentation of the paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, D., Joe, H. Multivariate extreme value copulas with factor and tree dependence structures. Extremes 21, 147–176 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10687-017-0298-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10687-017-0298-0
Keywords
- Extreme value limit
- Gaussian quadrature
- Hüsler-Reiss distribution
- Parsimonious dependence
- Vine graphical model