Abstract
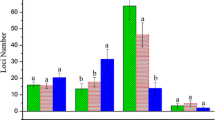
In order to explore the molecular mechanism of salt tolerance and heterosis in cotton, a methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism method based on capillary electrophoresis was used to analyze DNA methylation level in a cotton hybrid CCRI 29 and its two parents. The major results and conclusions are as follows: Firstly, salt tolerance test showed that CCRI 29 had higher salt-tolerance level than its both parents. The global DNA methylation level in CCRI 29 under salt treatment significantly increased, whereas the two parents did not change significantly between salt treatment and control. All kinds of variation of DNA methylation happened in cotton under salt treatment, and hypermethylation happened at a significantly higher rate than that of hypomethylation in CCRI 29 but not in its two parents. The results suggested that the increase of global DNA methylation level in cotton genome and also different methylation types played an important role in tolerance to salt treatment in cotton. Secondly, both hypomethylation and hypermethylation happened to different genes and some genes maintained the same methylation level after salt stress, which meant that complex gene expression alterations occurred when responding to salt stress in cotton, indicating the complicated characteristics of roles that specific genes played in salt tolerance. Thirdly, although most cytosine methylation sites in hybrid CCRI 29 shared the same status as that of at least one of the parents, the site number of hypomethylation is significantly higher than that of hypermethylation in CCRI 29 compared to parents under both control and salt stress, indicating that demethylation could be the mechanism to explain heterosis in cotton hybrid.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aina R, Sgorbati S, Santagostino A, Labra A, Ghiani A, Citterio S (2004) Specific hypomethylation of DNA is induced by heavy metals in white clover and industrial hemp. Physiol Plant 121:472–480
Bilichak A, Ilnystkyy Y, Hollunder J, Kovalchuk I (2012) The progeny of Arabidopsis thaliana plants exposed to salt exhibit changes in DNA methylation, histone modifications and gene expression. PLoS One 7(1):e30515
Bonasio B, Tu S, Reinberg D (2010) Molecular signals of epigenetic states. Science 330:612–616
Bruce AB (1910) The Mendelian theory of heredity and the augmentation of vigor. Science 32:627–662
Chen M, Lv S, Meng Y (2010) Epigenetic performers in plants. Dev Growth Differ 52:555–566
Choi CS, Sano H (2007) Abiotic-stress induces demethylation and transcriptional activation of a gene encoding a glycerophosphodiesterase-like protein in tobacco plants. Mol Genet Genomics 277:589–600
Davik J, Koehler G, From B, Torp T, Rohloff J, Eidem P, Wilson RC, Sønsteby A, Randall SK, Alsheikh M (2013) Dehydrin, alcohol dehydrogenase, and central metabolite levels are associated with cold tolerance in diploid strawberry (Fragaria spp.). Planta 237:265–277
Dyachenko OV, Zakharchenko NS, Shevchuk TV, Bohnert HJ, Cushman JC, Buryanov YI (2006) Effect of hypermethylation of CCWGG sequences in DNA of Mesembryanthemum crystallinum plants on their adaptation to salt stress. Biochemistry (Moscow) 71(4):461–465
East EM (1936) Heterosis. Genetics 21:375–397
Grativol C, Hemerly AS, Ferreira PCG (2012) Genetic and epigenetic regulation of stress responses in natural plant populations. BBA-Gene Regul Mech 1819:176–185
Groszmann M, Greaves IK, Albert N, Fujimoto R, Helliwell CA, Dennis ES, Peacock WJ (2011) Epigenetics in plants-vernalisation and hybrid vigour. BBA-Gene Regul Mech 1809:427–437
Guo WZ, Zhang TZ, Sheng XL, John Y, Kohel RJ (2003) Development of SCAR marker linked to a major QTL for high fiber strength and its molecular marker assisted selection in Upland cotton. Crop Sci 6:2252–2256
He GM, He H, Deng XW (2013) Epigenetic variations in plant hybrids and their potential roles in heterosis. J Genet Genomics 40:205–210
James AB, Hong Y, Sivanandan C, Daniel V, Reiner A (2010) Heterosis. Plant Cell 22:2105–2112
Jiang YR, Lv YJ, Zhu SJ (2006) Advance in studies of the mechanism of salt tolerance and controlling of salt damage in Upland cotton. Cotton Sci 18(4):248–254
Joel AJ, Zhang Q (2001) Direction of methylation and its effect on heterosis in rice. In: Book of Abstracts of 8th National Rice Biotechnology Network Meeting, Aurangabad, pp 231–237
Jones DF (1917) Dominance of linked factors as a means of accounting for heterosis. Genetics 2:466–479
Khan UQ (2002) Study of heterosis in fiber quality traits of Upland cotton. Asian J Plant Sci 1:593–595
Kimatu JN, Diarso M, Song CD, Agboola RS, Pang JS, Qi X, Liu B (2011) DNA cytosine methylation alterations associated with aluminium toxicity and low pH in Sorghum bicolor. Afr J Agric Res 6:4579–4593
Kovarik A, Koukalova B, Bezdek M, Opatrny Z (1997) Hypermethylation of tobacco heterochromatic loci in response to osmotic stress. Theor Appl Genet 95:301–306
Labra M, Grassi F, Imazio S, Fabio TD, Citterio S, Sgorbati S, Agradi E (2004) Genetic and DNA-methylation changes induced by potassium dichromate in Brassica napus L. Chemosphere 54(8):1049–1058
Li XL, Lin ZX, Nie YC, Guo XP, Zhang XL (2009) MSAP analysis of epigenetic changes in cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) under salt stress. Acta Agro Sin 35(4):588–596
Lindlöf A, Bräutigam M, Chawade A, Olsson B, Olsson O (2007) Identification of cold-induced genes in cereal crops and Arabidopsis through comparative analysis of multiple EST sets. In: Hochreiter S, Wagner R (eds) Bioinformatics research and development—first international conference BIRD ‘07, LNBI, vol 4414. Springer, Berlin, pp 48–65
Liu B, Wendel JF (2003) Epigenetic phenomena and the evolution of plant allopolyploids. Mol Phylogenet Evol 29(3):365–379
Lukens LN, Zhan SH (2007) The plant genome’s methylation status and response to stress, implications for plant improvement. Curr Opin Plant Biol 10:317–322
Mahajan S, Tuteja N (2005) Cold, salinity and drought stresses: an overview. Arch Biochem Biophys 444:139–158
Mastan SG, Rathore MS, Bhatt VD, Yadav P, Chikara J (2012) Assessment of changes in DNA methylation by methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism in Jatropha curcas L. subjected to salinity stress. Gene 508:125–129
McClelland M, Nelson M, Raschke E (1994) Effect of site-specific modification on restriction endonucleases and DNA modification methyltransferases. Nucleic Acids Res 22:3640–3659
Morgan SH, Maity PJ, Geilfus CM, Lindberg S, Mühling KH (2014) Leaf ion homeostasis and plasma membrane H+-ATPase activity in Vicia faba change after extra calcium and potassium supply under salinity. Plant Physiol Bioch 82:244–253
Paterson AH, Brubaker CL, Wendel JF (1993) A rapid method for extraction of cotton (Gossypium spp.) genomic DNA suitable for RFLP or PCR analysis. Plant Mol Biol Rep 11(2):122–127
Sairam RK, Dharmar K, Chinnusamy V, Meena RC (2009) Waterlogging-induced increase in sugar mobilization, fermentation, and related gene expression in the roots of mungbean (Vigna radiata). J Plant Physiol 166:602–616
Sakthivel K, Girishkumar K, Ramkumar G, Shenoy VV, Kajjidoni ST, Salimath PM (2010) Alterations in inheritance pattern and level of cytosine DNA methylation, and their relationship with heterosis in rice. Euphytica 175:303–314
Shan XH, Wang XY, Yang G, Wu Y, Su SZ, Li SP, Liu HK, Yuan YP (2013) Analysis of the DNA methylation of Maize (Zea mays L.) in response to cold stress based on methylation-sensitive amplified polymorphisms. J Plant Biol 56:32–38
Shen H, He H, Li J, Chen W, Wang X, Guo L, Peng Z, He G, Zhong S, Qi Y, Terzaghi W, Deng XW (2012) Genome-wide analysis of DNA methylation and gene expression changes in two Arabidopsis ecotypes and their reciprocal hybrids. Plant Cell 24(3):875–892
Shull GH (1908) The composition of a field of maize. Ann Breed Assoc Rep 4:296–301
Sun YG, Wang B, Jin SH, Qu XX, Li YJ, Hou BK (2013) Ectopic expression of Arabidopsis glycosyltransferase UGT85A5 enhances salt stress tolerance in Tobacco. PLoS One 8(3):e59924
Tan MP (2010) Analysis of DNA methylation of maize in response to osmotic and salt stress based on methylation-sensitive amplified polymorphism. Plant Physiol Bioch 48:21–26
Tsaftaris AS, Kafka M (1997) Mechanisms of heterosis in crop plants. J Crop Prod 1(1):95–111
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Fijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: a new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucleic Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Wang WS, Pan YJ, Zhao XQ, Dwivedi D, Zhu LH, Ali J, Fu BY, Li ZK (2011a) Drought-induced site-specific DNA methylation and its association with drought tolerance in rice (Oryza sativa L.). J Exp Bot 62:1951–1960
Wang WS, Zhao XQ, Pan YJ, Zhu LH, Fu BY, Li ZK (2011b) DNA methylation changes detected by methylation-sensitive amplified polymorphism in two contrasting rice genotypes under salt stress. J Genet Genomics 38:419–424
Xing CZ, Zhao YL, Yu SX, Guo LP, Zhang XL, Wang HL (2006) Relationship between leaves gene differential expression in full opening flower stages of hybrids & their parents and heterosis in pest-resistant cotton. Acta Genet Sin 33:948–956
Xiong LZ, Xu CG, Saghai Maroof MA, Zhang QF (1999) Patterns of cytosine methylation pattern in an elite rice hybrid and its parental lines detected by a methylation-sensitive amplification polymorphism technique. Mol Gen Genet 261(3):439–446
Xiong WS, Li XR, Fu DH, Mei JQ, Li QF, Lu GY, Qian LW, Fu Y, Disi JO, Li JN, Qian W (2013) DNA Methylation alterations at 5′-CCGG Sites in the Interspecific and Intraspecific Hybridizations Derived from Brassica rapa and B. napus. PLoS One 8(6):e65946
Xu ML, Li XQ, Korban SS (2000) AFLP-based detection of DNA methylation. Plant Mol Biol Rep 18:361–368
Yamauchi T, Watanabe K, Fukazawa A, Mori H, Abe F, Kawaguchi K, Oyanagi A, Nakazono M (2014) Ethylene and reactive oxygen species are involved in root aerenchyma formation and adaptation of wheat seedlings to oxygen-deficient conditions. J Exp Bot 65(1):261–273
Yang JL, Liu LW, Gong YQ, Huang DQ, Wang F, He LL (2007) Analysis of genomic DNA methylation level in radish under cadmium stress by methylationsensitive amplified polymorphism technique. J Plant Physiol Mol Biol 33(3):219–226
Yu SB, Li JX, Tan YF, GaoYJ Li XH, Zhang QF, Saghai Maroof MA (1997) Importance of epistasis as the genetic basis of heterosis in an elite rice hybrid. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94:9226–9231
Zemach A, McDaniel IE, Silva P, Zilberman D (2010) Genome-wide evolutionary analysis of eukaryotic DNA methylation. Science 328(5980):916–919
Zhang MS, Yan HY, Zhao N, Lin XY, Pang JS, Xu KZ, Liu LX, Liu B (2007) Endosperm-specific hypomethylation, and meiotic inheritance and variation of DNA methylation level and pattern in sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) interstrain hybrids. Theor Appl Genet 115:195–207
Zhang LN, Ye WW, Wang JJ, Fan BX, Wang DL (2010) Genetic diversity analysis of salinity related germplasm in cotton. Biodivers Sci 18(2):142–149
Zhao XX, Chai Y, Liu B (2007) Epigenetic inheritance and variation of DNA methylation level and pattern in maize intra-specific hybrids. Plant Sci 172:930–938
Zhao YL, Yu SX, Xing CZ, Fan SL, Song MZ (2008) Analysis of DNA methylation in cotton hybrids and their parents. Mol Biol 42:169–178
Zhao YL, Yu SX, Xing CZ, Fan SL, Song MZ, Ye WW (2009) Differential gene expression between hybrids and their parents during the four crucial stages of cotton growth and development. Agric Sci China 8(2):144–153
Zhao YL, Yu SX, Ye WW, Wang HM, Wang JJ, Fand BX (2010) Study on DNA cytosine methylation of cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) genome and its implication for salt tolerance. Agric Sci China 9(6):783–791
Zhu JK (2001) Plant salt tolerance. Trends Plant Sci 6(2):66–71
Zhu XX, Ainijiang Zhang YM, Guo WZ, Zhang TZ (2011) Relationships between differential gene expression and heterosis in cotton hybrids developed from the foundation parent CRI-12 and its pedigree-derived lines. Plant Sci 180:221–227
Acknowledgments
Research supported by the Natural Science Foundation of Jiangsu Province of China (BK20131204), the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31000729), Key Research and Development Project of Jiangsu Province (Modern Agriculture, BE2015353), Autonomous Innovation Project of Jiangsu Agricultural Science & Technology [CX(15)1005], the State Key Laboratory of Cotton Biology Open Fund (CB2015A09), Qing Lan Project of Colleges and Universities in Jiangsu Province, Scientific Research and Innovation Projects for Graduate Students in Jiangsu Province (YKC15071).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, B., Zhang, M., Fu, R. et al. Epigenetic mechanisms of salt tolerance and heterosis in Upland cotton (Gossypium hirsutum L.) revealed by methylation-sensitive amplified polymorphism analysis. Euphytica 208, 477–491 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1586-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-015-1586-x