Abstract
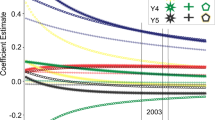
Based on multi-factor orthogonally designed field experimental plots, the correlations among yield components as well as their direct and indirect effects on the seed yield of Bromus inermis L. cv. ‘Carlton’ were investigated. The seed yield parameters fertile tillers/m2 (Y1), spikelets/fertile tiller (Y2), florets/spikelet (Y3), seed number/spikelet (Y4), seed weight (Y5), and seed yield (Z) were determined by hand in the field for the years 2003–2005. Via ridge regression analysis, a steady algorithmic model of seed yield with its five components was found that could closely estimate the seed yield. The component Y1 had the largest correlation coefficient with Z, followed by Y2. The contributions of the five components to the seed yield in decreasing order are Y1 > Y4 > Y2 > Y5 > Y3. The inter-correlation among the components Y1 to Y5 and Z exhibited significance but Y1 was not correlated with Y3. Therefore, direct selection for large Y1, Y2, and Y4 would be an effective means of selection for high seed yield in the grass.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abreu ME, Munne-Bosch S (2009) Salicylic acid deficiency in NahG transgenic lines and sid2 mutants increases seed yield in the annual plant Arabidopsis thaliana. J Exp Bot 60:1261–1271. doi:10.1093/jxb/ern363
An C, Jenkins JN, Wu J, Guo Y, McCarty JC (2010) Use of fiber and fuzz mutants to detect QTL for yield components, seed, and fiber traits of upland cotton. Euphytica 172:21–34. doi:10.1007/s10681-009-0009-2
Armstron Kc (1973) Chromosome Pairing in hexaploid hybrids from Bromus-Erectus (2n = 28) by Bromus-Inermis (2n=56). Can J Genet Cytol 15:427–436
Barrios C, Armando L, Berone G, Tomas A (2010) Seed yield components and yield per plant in populations of Panicum coloratum L. var. makarikariensis Goossens. Proceedings of 7th international herbage seed conference, Dallas
Bidgoli AM, Akbari GA, Mirhadi MJ, Zand E, Soufizadeh S (2006) Path analysis of the relationships between seed yield and some morphological and phenological traits in safflower (Carthamus tinctorius L.). Euphytica 148:261–268
Bishaw Z, Turner M (2008) Linking participatory plant breeding to the seed supply system. Euphytica 163:31–44. doi:10.1007/s10681-007-9572-6
Bliss FA, Barker LN, Franckow Jd, Hall TC (1973) Genetic and environmental variation of seed yield, yield components, and seed protein quantity and quality of cowpea. Crop Sci 13:656–660
Boelt B, Studer B (2010) Breeding for grass seed yield. fodder crops and amenity grasses. Proceedings of 7th international herbage seed conference, Dallas, pp 161–174. doi:10.1007/978-1-4419-0760-8_7
Canode CL (1980) Grass-seed production in the intermountain Pacific North-west, USA. P D Hebbletheaite ed, London, pp 189–202
Casler MD, Vogel KP, Balasko JA, Berdahl JD, Miller DA, Hansen JL, Fritz JO (2000) Genetic progress from 50 years of smooth bromegrass breeding. Crop Sci 40:13–22
Chatterjee S, Price B (1977) Regression analysis by example. Wiley, Inc, New York
Crook S (2001) Visual foxpro client-server handbook. Redware Research Ltd., Hove
Culvenor RA, Casler MD (1999) Response to divergent selection for ease of particle size reduction of dried leaves of smooth bromegrass (Bromus inermis Leyss) and correlated effects on nutritive value indicators and plant fitness. Euphytica 107:61–70
Das MK, Taliaferro CM (2009) Genetic variability and interrelationships of seed yield and yield components in switchgrass. Euphytica 167:95–105. doi:10.1007/s10681-008-9866-3
Dillemuth FP, Rietschier EA, Cronin JT (2009) Patch dynamics of a native grass in relation to the spread of invasive smooth brome (Bromus inermis). Biol Invasions 11:1381–1391. doi:10.1007/s10530-008-9346-7
Ding X-Q (1986) Agricultural regress design. Jilin Science and Technology Press, Changchun, pp 80–86
El-Nakhlawy FS, Shaheen MA (2009) Response of seed yield, yield components and oil content to the sesame cultivar and nitrogen fertilizer rate diversity. Electron J Environ Agric Food Chem 8:287–293
Fairey DT, Hampton JG (1997) Forage seed production I. CAB International, Madison
Firincioglu HK, Unal S, Erbektas E, Dogruyol L (2010) Relationships between seed yield and yield components in common vetch (Vicia sativa ssp sativa) populations sown in spring and autumn in Central Turkey. Field Crop Res 116:30–37. doi:10.1016/j.fcr.2009.11.005
Gao S, Li Y, Jin H (2005) Application of ridge regression models in economic increasing factors analysis. Stat Decis Making 5:142–144
Golparvar AR, Ghasemi-Pirbalouti A (2009) Correlation and path analysis of seed and oil yield in spring safflower cultivars. Res Crops 10:147–151
Gregory S (1978) Statistical methods and geographer. Longman Inc., London
Hampton JG, Fairey DT (1997) Components of seed yield in grasses and legumes. In: Fairey DT, Hampton JG (eds) Forage seed production. CAB International, Madison
Hampton JG, Fairey DT (1998) Components of seed yield in grasses and legumes. Forage seed production, vol. 1: temperate species. CAB International, Wallingford, pp 45–69
Hedayat AS, Sloane NJA, Stufken J (1999) Orthogonal arrays. Theory and applications. Springer, New York, p 363
Herrmann D, Flajoulot S, Julier B (2010) Sample size for diversity studies in tetraploid alfalfa (Medicago sativa) based on codominantly coded SSR markers. Euphytica 171:441–446. doi:10.1007/s10681-009-0077-3
Hoerl AE, Kennard RW (1970a) Ridge regression: biased estimation for non-orthogonal problem. Technometrics 12:55–67
Hoerl AE, Kennard RW (1970b) Ridge regression: applications to non-orthogonal problems. Technometrics 12:69–82
Hoerl AE, Kenard RW, Kent FB (1975) Ridge regression: some simulations. Communication statistics 4:105–123
Hristov N, Mladenov N, Djuric V, Kondic-Spika A, Marjanovic-Jeromela A, Simic D (2010) Genotype by environment interactions in wheat quality breeding programs in Southeast Europe. Euphytica 174:315–324. doi:10.1007/s10681-009-0100-8
Humphreys MW, Gasior D, Lesniewska-Bocianowska A, Zwierzykowski Z, Rapacz M (2007) Androgenesis as a means of dissecting complex genetic and physiological controls: selecting useful gene combinations for breeding freezing tolerant grasses. Euphytica 158:337–345. doi:10.1007/s10681-006-9240-2
Kalia RK, Rai MK, Kalia S, Singh R, Dhawan AK (2011) Microsatellite markers: an overview of the recent progress in plants. Euphytica 177:309–334. doi:10.1007/s10681-010-0286-9
Landjeva S, Lohwasser U, Boerner A (2010) Genetic mapping within the wheat D genome reveals QTL for germination, seed vigour and longevity, and early seedling growth. Euphytica 171:129–143. doi:10.1007/s10681-009-0016-3
Lattin JM, Carroll JD, Green PE (2003) Analyzing multivariate data. Brooks/Cole, an imprint of Thomson Learning, Duxbury, Pacific Grove, CA
Lawless JF, Wang P (1976) A simulation study of ridge and other regression estimators. Commun Stat Ser A5:307–323
Liu GX, Mao PS, Huang SQ, Sun YC, Han JG (2008a) Effects of soil disturbance, seed rate, nitrogen fertilizer and subsequent cutting treatment on establishment of Bromus inermis seedlings on degraded steppe grassland in China. Grass Forage Sci 63:331–338. doi:10.1111/j.1365-2494.2008.00638.x
Liu GX, Mao PS, Wang YW, Han JG (2008b) Effects of adult neighbour and gap size on seedling emergence and early growth of Bromus inermis Leyss. Ecol Res 23:197–205. doi:10.1007/s11284-007-0364-1
Lopes RR, Franke LB (2009) Path analysis in white clover seed yield components. Revista Brasileira De Zootecnia—Brazilian J Anim Sci 38:1865–1869
Ma C, Han J, Sun J, Zhang Q, Lu G (2004) Effects of nitrogen fertilizer on seed yields and yield components of Zoysia japonica established by seeding and transplant. Agric Sci China 3:553–560
Mahmood T, Rahman MH, Stringam GR, Yeh F, Good A (2005) Molecular markers for yield components in Brassica juncea—do these assist in breeding for high seed yield? Euphytica 144:157–167. doi:10.1007/s10681-005-5339-0
Malla S, Ibrahim AMH, Little R, Kalsbeck S, Glover KD, Ren C (2010) Comparison of shifted multiplicative model, rank correlation, and biplot analysis for clustering winter wheat production environments. Euphytica 174:357–370. doi:10.1007/s10681-010-0130-2
Marquardt DW, Snee RD (1975) Ridge regression in practices. Am Stat 29:3–14
Meints PD, Chastain TG, Young WC, Banowetz GM, Garbacik CJ (2001) Stubble management effects on three creeping red fescue cultivars grown for seed production. Agron J 93:1276–1281
Mohammadi R (2006) Study of genetic variation in Bromus inermis Leyss populations. Iran J Rangelands Forests Plant Breed Genet Res 14:138–147
Nagy G, Lazanyi J, Kovacs P (2009) Weather characteristic impacts on bromegrass (Bromus inermis Leyss) development. Cereal Res Commun 37:169–172
Nakamura T, Ishikawa M (2006) Transformation of suspension cultures of bromegrass (Bromus inermis) by Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 84:293–299. doi:10.1007/s11240-005-9037-3
Newell GJ, Lee B (1981) Ridge regression: an alternative to multiple linear regression for highly correlated data [in food technology]. J Food Sci (USA) 46:968–969
Ofori I (1996) Correlation and path-coefficient analysis of components of seed yield in bambara groundnut (Vigna subterranea). Euphytica 91:103–107
Otfinowski R, Kenkel NC, Catling PM (2007) The biology of Canadian weeds. 134. Bromus inermis Leyss. Can J Plant Sci 87:183–198
Otfinowski R, Kenkel NC, RCv Acker (2008) Reconciling seed dispersal and seed bank observations to predict smooth brome (Bromus inermis) invasions of a Northern Prairie. Invasive Plant Sci Manage 1:279–286. doi:10.1614/ipsm-08-066.1
Ozturk O, Ada R (2009) Correlation and path coefficient analysis of yield and quality components of some sunflower (Helianthus annuus L.) cultivars. Asian J Chem 21:1400–1412
Prohens J (2009) Modern variety breeding for present and future needs introduction. Euphytica 170:1–3. doi:10.1007/s10681-009-0021-6
Rashidi M, Zand B, Abbassi S (2009) Response of seed yield and seed yield components of alfalfa (Medicago sativa) to different seeding rates. Am-Eurasian J Agric Environ Sci 5:786–790
SAS-Institute-Inc (1988) SAS/STAT user’s guide. SAS Institute Inc., North Carolina
Schwabe R (1996) Optimum designs for multi-factor models. Springer, New York
Sleper DA, Drolsom PN, Jorgense Na (1973) Breeding for improved dry-matter digestibility in smooth bromegrass (Bromus-Inermis Leyss). Crop Sci 13:556–558
Sodavadiya PR, Pithia MS, Savaliya JJ, Pansuriya AG, Korat VP (2009) Studies on characters association and path analysis for seed yield and its components in pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan (L.) Millsp.). Legume Res 32:203–205
Soil-Survey-Staff. (1996) Keys to soil taxonomy (7th ed.). Natural Resources Conservation Service, Washington, DC
Sun T (2004) Effects of fertilizer application on seed yield formation and seed physiological and biochemical characters during the seed development of grasses. In grassland science. China Agricultrural University, Beijing
Sun T, Han J, Zhao S, Yue W (2005) Effects of fertilizer application on seed yield and yield components of Psathyrostachys juncea. Grassland China 27:16–21
Taghizadeh R, Jafari A, Choukan R, Asghari A (2008) Evaluation for seed yield and seed components among accessions of crested wheatgrass (Agropyron desertorum and Agropyron crustatum). Multifunctional grasslands in a changing world, vol. II: XXI International Grassland Congress and VIII International Rangeland Congress, Hohhot, China. 29 June–5 July 2008, p 361
Tamura K, Kawakami A, Sanada Y, Tase K, Komatsu, Yoshida M (2009) Cloning and functional analysis of a fructosyltransferase cDNA for synthesis of highly polymerized levans in timothy (Phleum pratense L.). J Exp Bot 60:893–905. doi:10.1093/jxb/ern337
Ulea E, Lipsa FD, Irimia N, Balan GM (2009) Investigations on the influence of fertilization and of Onobrychis viciifolia Scop. and Bromus inermis Leiss. mixture on soil microflora. Cercetari Agronomice Moldova 42:47–54
Van Betl, Backes G, de Vriend H, Ostergard H (2010) The role of molecular markers and marker assisted selection in breeding for organic agriculture. Euphytica 175:51–64. doi:10.1007/s10681-010-0169-0
Wang XR (1996) Modern fertilizer experimental deign. Agricultural Press of China, Beijing
Wang Q, Li Q, Cui J, Wang Y, Bai R, Dong Z (2001) Path analysis of seed yield and main agronomic traits in Caragana korshinskii K. Grassland China 23:35–37
Wang Q, Zhou H, Han J, Zhong Y, Liu F (2005) Analysis on a model for water and fertilizer coupling effects on Psathyrostachys juncea seed yield. Acta Prataculturae Sinica 14:41–49
Wang ZF, Wang JF, Wang FH, Bao YM, Wu YY, Zhang HS (2010) Segregation analysis of rice seed germination under cold stress using major gene plus polygene mixed inheritance model. Seed Sci Technol 38:104–113
Wang Q, Zhang T, Cui J, Wang X, Zhou H, Han J, Gislum R (2011) Path and ridge regression analysis of seed yield and seed yield components of Russian Wildrye (Psathyrostachys juncea Nevski) under field conditions. PLoS ONE 6(4):e18245. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0018245
Weidel W, Pajor F, Laczo E, Poti P (2008) The effect of extreme soil conditions on yield and utilization of Medicago sativa, Medicago sativa Varia and Bromus inermis in Harskut. Cereal Res Commun 36:275–278
Wu YQ, Taliaferro CM, Martin DL, Anderson JA, Anderson MP (2008) Correlation analyses of seed yield and its components in bermudagrass. Multifunctional grasslands in a changing world, vol II: XXI International Grassland Congress and VIII International Rangeland Congress, Hohhot, China, 29 June-5 July 2008:562
Yan XY, Li JN, Fu FY, Jin MY, Chen L, Liu LZ (2009) Co-location of seed oil content, seed hull content and seed coat color QTL in three different environments in Brassica napus L. Euphytica 170:355–364. doi:10.1007/s10681-009-0006-5
Yandell BS (1997) Practical data analysis for designed experiments. Chapman & Hall, London
Yang H, Huang Z, Baskin CC, Baskin JM, Cao Z, Zhu X, Dong M (2009) Responses of caryopsis germination, early seedling growth and ramet clonal growth of Bromus inermis to soil salinity. Plant Soil 316:265–275. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9778-y
Zhang Y, Wang J (2007) Physiological characteristics of leaf photosynthesis under mixture sowing of lucerne and Bromus inermis and single sowing. Pratacultural Sci 24:17–21
Acknowledgments
The National Science & Technology Pillar Program of China (2011BAD17B05), The National Basic Research and Development Programme (973 project, 2007CB106805) and 948 Research Project (No. 202099) funded this study. We are grateful for the skilful technical assistance of Mr. Zhang Bing, Miss Yan Xuehua, Miss Han Juhoung, Mr. Zhang Xijun, Mr. Wang Shouguo, and Mr. Zhang Guoqi, who are animal husbandry engineers at the Daye Institute of Forage & Grass Products in Jiuquan, at the Gansu Branch of Chengdu Daye International Interest Co. Ltd.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, Q., Cui, J., Wang, X. et al. Algorithmic models of seed yield and its components in smooth bromegrass (Bromus inermis L.) via large sample size under field conditions. Euphytica 185, 363–375 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0541-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-011-0541-8