Abstract
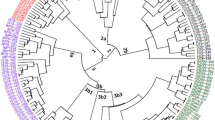
Fifteen alfalfa populations consisting of six public cultivars and nine historically recognized sources of alfalfa germplasm in North American cultivars were examined using sequence related amplified polymorphisms (SRAPs). Three bulk DNA samples from each population were evaluated with fourteen different SRAP primer pairs. This resulted in 249 different amplicons, of which over 90% were polymorphic. A dendrogram from the analysis suggests that the public cultivars are quite diverse from all the historical sources of germplasm. The highest mean genetic similarity among the nine original sources of Medicago germplasm was 0.85 between PI 536535 (Peruvian) and 536536 (Indian), while the lowest (0.47) was between PI 560333 (M. falcata) and 536539 (African). The highest mean genetic similarity among the nine original sources of Medicago germplasm and the public alfalfa cultivars was 0.78 between PI 536532 (Ladak) and Vernal, while the lowest (0.59) was between PI 536539 (African) and Oneida. Relationships based on SRAP analysis appear to generally concur with expected relationships based on fall dormancy. This report demonstrates that SRAPs are a promising marker system for detecting polymorphisms in alfalfa.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PI:
-
U.S. National Plant Germplasm System Plant Introduction
References
Avise JC (1994) Molecular markers, natural history and evolution. Chapman and Hall Publishing, New York
Bauchan GR, Campbell TA, Hossain MA (2003) Comparative chromosome banding studies of nondormant alfalfa germplasm. Crop Science 43:2037–2042
Barnes DK, Bingham ET, Murphy RP, Hunt OJ, Beard DF, Skrdla WH, Teuber LR (1977) Alfalfa germplasm in the United States: Genetic vulnerability, use, improvement, and maintenance. USDA Tech Bull 1571
Barnes DK, Goplen BP, Baylor JE (1988) Highlights in the USA and Canada. In: Hanson AA, Barnes DK, Hill RR (eds) Alfalfa and Alfalfa Improvement, American Society of Agronomy Press, Madison, pp. 1–24
Bingham ET (1993) Registration of WISFAL alfalfa (Medicago sativa subsp. falcata) tetraploid germplasm derived from diploids. Crop Science 33:218
Busbice TH, Hill RR, Carnahan HL (1972) Genetics and Breeding procedures. In: Hanson CH (ed.) Alfalfa Science and Technology, American Society of Agronomy, Madison pp. 283–318
Busbice TH, Wilsie CP (1966) Inbreeding depression and heterosis in autotetraploids with application to Medicago sativa L. Euphytica 15:52–67
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Graber LF (1956) Registration of vernal alfalfa. Agronomy J 48:587
Karp A, Edwards KJ (1998) DNA markers: A global overview. In: Caetano-Anollés G, Gresshoff PM (eds.) DNA markers: Protocols, applications, and overviews, Wiley-VCH, New York, pp. 1–13
Kidwell KK, Austin DF, Osborn TC (1994) RFLP evaluation of nine Medicago accessions representing the original germplasm sources for Northern American alfalfa cultivars. Crop Science 34:230–236
Lehman WF, Nielson MW, Marble VL, Stanford EH (1983) Registration of CUF 101 alfalfa. Crop Science 23:398
Li G, Quiros CF (2001) Sequence-related amplified polymorphism (SRAP), a new marker system based on a simple PCR reaction: its application to mapping and gene tagging in Brassica. Theor Appl Genet 103:455–461
Livak KJS, Flood JA, Marmaro J, Giusti W, Deetz K (1995) Oligonucleotides with fluorescent dyes at opposite ends provide a quenched probe system useful for detecting PCR products and nucleic acid hybridization. PCR Methods Appl 4:357–362
Melton B, Currier C, Miller D, Kimmell J (1989a) Registration of Malone alfalfa. Crop Science 29:485
Melton B, Wilson M, Currier C (1989b) Registration of Wilson alfalfa. Crop Science 29:485–486
Melton B, Currier C, Kimmell J (1990) Registration of alfalfa germplasm representing eight diversity groups and a very fall dormant population. Crop Science 30:1990
Murphy RP, Lowe CC (1968) Registration of Iroquois alfalfa. Crop Science 8:396
Murphy RP, Lowe CC (1989) Registration of Oneida alfalfa. Crop Science 29:487
Nei M, Li WH (1997) Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, USA 76:5269–5273
Peaden RN, Evans DW, Elgin JH, Rinker CM (1983) Registration of Vernema alfalfa. Crop Science 23: 1009
Quiros CF, Bauchan GR (1988) The Genus Medicago and the origin of the Medicago sativa complex. In: Hanson AA, Barnes DK, Hill RR (eds.) Alfalfa and Alfalfa Improvement, American Society of Agronomy Press, Madison, pp. 93–124
Quiros CF, Grellet F, Sadowski J, Suzuki T, Li G, Wroblewski T (2001) Arabidopsis and Brassica comparative sequence, structure and gene content in the ABI1-Rps2-Ck1 chromosomal segment and related regions. Genetics 157:1321–1330
SAS Institute (1999) SAS/STAT User's guide. Version 8.2 edition. SAS Institute, Inc., Cary, NC
Vos P, Hogers R, Bleeker M, Reijans M, van de Lee T, Hornes M, Frijters A, Pot J, Peleman J, Kuiper M, Zabeau M (1995) AFLP: A new technique for DNA fingerprinting. Nucl Acids Res 23:4407–4414
Williams JGK, Kubelik AR, Livak KJ, Rafalski JA, Tingey SV (1990) DNA polymorphisms amplified by arbitrary primers are useful as genetic markers. Nucl Acids Res 6531–6535
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vandemark, G.J., Ariss, J.J., Bauchan, G.A. et al. Estimating genetic relationships among historical sources of alfalfa germplasm and selected cultivars with sequence related amplified polymorphisms. Euphytica 152, 9–16 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9167-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-006-9167-7